Abstract
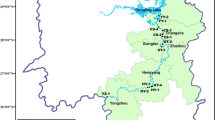
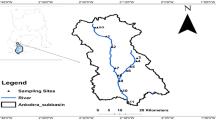
Sediment quality criteria (SQC) of heavy metals (copper, lead, zinc and cadmium) for surface sediment have been developed to evaluate sediment contamination in the Xiang-jiang River of China using the equilibrium partitioning approach. USEPAs fresh water quality criteria [criterion continuous concentration (CCC), criterion maximum concentration (CMC)] were referenced to derive sediment quality criteria (SQC-low and SQC-high) of the Xiang-jiang River. The toxicological implications of SQC-low and SQC-high were similar with CCC and CMC, which were used to protect benthic organisms from short-term- and long-term exposure to pollutants. Sediment Pollution Index method was established based on the SQC-low and SQC-high values to evaluate sediment quality qualitatively and quantitatively. The evaluation method was applied to the Xiang-jiang River, and the result indicated that the cadmium contamination in the sediments was of concern; especially, in the Zhu-zhou, Yue-yang, and the middle and downstream reaches of Heng-yang section.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen HE, Fu GM, Deng BL (1993) Analysis of acid volatile sulfide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEM) for estimation of potential toxicity in aquatic sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1441–1453
Boothman WS, Helmstetter A (1992) Vertical and seasonal variability of acid volatile sulfides in marine sediments. EPA 600/X-93/036. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Narragansett
Burton GA (2002) Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology 3:65–75
Burton GA Jr (1993) Sediment sampling and analysis plan-west branch G rand C alumet River 1993 sediment toxicity test data summaries. USEPA
Chapman PM, Wang FY, Adams WJ, Green A (1993) Appropriate applications of sediment quality values for metals and metalloids. Environ Sci Technol 33:3937–3941
Chapman PM, Wang FY, Janssen C, Persoone G (1998) Ecotoxicology of metals in aquatic sediments binding and release, bioavailability, risk assessment, and remediation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:2221–2243
Chen JS (1987) The environmental chemistry of water. Beijing Education Press, Beijing, pp 186–187
Chen JS, Dong L, Deng BS, Wan LB, Wang M, Xiong ZL (1987) Modeling study on copper partitioning in sediments, a case study of Poyang Lake. Acta Sci Circumst 7:140–149 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen YZ, Yang H, Zhang ZK, Qin MZ (2005) The difference and cause analyses of freshwater sediment quality criteria. J Lake Sci 17:193–201 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cornwell JC, Morse JW (1987) The characterization of iron sulfide minerals in recent anoxic marine sediments. Mar Chem 22:193–206
Davidson CM, Thomas TP, McVey SE, Perala R, Littlejohn D, Ure AM (1994) Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of heavy metals in sediments. Anal Chim Acta 291:277–286
Deng BL, Zhu LY, Liu M, Liu NN, Yang LP, Du Y (2011) Sediment quality criteria and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in Taihu Lake and Liao River. Res Environ Sci 24:33–42 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Di Toro DM, Mahony JD, Hansen DJ, Scott KJ, Hicks MB, Mayr SM, Redmond MS (1990) Toxicity of cadmium in sediments: the role of acid volatile sulfide. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1487–1502
Di Toro DM, Zarba CS, Hansen DJ, Berry WJ, Swartz RC, Cowan CE, Pavlou SP, Allen HE, Thomas NA, Paquin PR (1991) Technical basis for establishing sediments quality criteria for nonionic organic chemicals by using equilibrium partitioning. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:1541–1583
Fang T, Xu XQ (2007) Establishment of sediment quality criteria for metals in water of the Yangze River using equilibrium partitioning approach. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 16:525–531 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gambrell RP, Reddy CN, Khalid RA (1983) Characterization of trace and toxic materials in sediments of a lake being restored. Water Pollut Control Fed 55:1201–1210
Guo FY (2007) The safety evaluation on water resources of Hunan Province. Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha (in Chinese)
Guo RC, He XY (2013) Spatial variations and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments on the upper reaches of Hun River, Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 70(3):1083–1090
Hakanson L (1980) An Ecological Risk Index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hou J, Wang C, Wang PF, Qian J (2012) Sediment quality guidelines and potential ecological risk assessment for heavy metals based on equilibrium partitioning approach in Taihu Lake. Acta Sci Circumst 32:2951–2959 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huo WY, Chen JS (1997) Water particulate distribution coefficient of heavy metal and application in sediment quality criteria in China River. Chin J Environ Sci 18:10–14 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huo WY, Huang FR, Chen JS, Jia ZB (1997) Comparative study of assessment method for river particulate heavy metal pollution. Sci Gelgraphica 17:81–86 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang BF, Sang LX, Sun WL, Hao W, Li L, Deng BS (2013) Derivation and application of sediment quality criteria of Cd and Hg for the Xiangjiang River. Environ Sci 34:98–107 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang ZL, Liu BL, Liu H, Yang J (2014) Trace metals in Daihai Lake sediments, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(1):255–266
Lei M, Qin PF, Tie BQ (2010) The status and analysis of heavy metal pollution in Xiangjiang Basin of Hunan. Agro-Environ Dev 4:62–65 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li X, Wang Y, Li BH, Feng CH, Chen YX, Shen ZY (2013) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yangtze estuary and coastal areas. Environ Earth Sci 69(5):1537–1547
Lin CY, He MC, Liu XT, Guo W, Liu SQ (2013) Distribution and contamination assessment of toxic trace elements in sediment of the Daliao River System, China. Environ Earth Sci 70(7):3163–3173
Liu WX, Tang HT (1998) Developing sediment quality criteria for heavy metal pollution in the Le An River with equilibrium partitioning approach. J Environ Sci 10:399–404 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Long ER, Morgan LG (1990) The potential for biological effects of sediment sorbed contaminations tested in the national status and trends program. In: National oceanic and atmospheric administration technical memorandum, NOS OMA 52
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Mao LJ, Mo DW, Guo YY, Fu Q, Yang JH, Jia YF (2013) Multivariate analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments from lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River, southern China. Environ Earth Sci 69(3):765–771
Marchand C, Allenbach M, Lallier-Verges E (2011) Relationships between heavy metals distribution and organic matter cycling in mangrove sediments (Conception Bay, New Caledonia). Geoderma 160:444–456
McCauley DJ, DeGraeve GM, Linton TK (2000) Sediment quality guidelines and assessment: overview and research needs. Environ Sci Policy 3:S133–S144
Meng W, Zhang Y, Zheng BH (2006) The quality criteria, standards of water environment and the water pollutant control strategy on watershed. Res Environ Sci 19:1–6 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
NOAA (1995) The utility of AVS/EqP in hazardous waste site evaluations. NOS ORCA 87, Seattle
Presaud D, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Water Resources Branch, Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Toronto
Quevauviller Ph, Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Rubio R, Ure A, Muntau H (1997) Certification of trace metal extractable contents in a sediment reference material (CRM 601) following a three-step sequential extraction procedure. Sci Total Environ 205:223–234
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller Ph (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Sany SBT, Salleh A, Sulaiman AH, Sasekumar A, Rezayi M, Tehrani GM (2013) Heavy metal contamination in water and sediment of the Port Klang coastal area, Selangor, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 69(6):2013–2025
Sheng YQ, Sun QY, Bottrell SH, Mortimer RJG, Shi WJ (2013) Anthropogenic impacts on reduced inorganic sulfur and heavy metals in coastal surface sediments, North Yellow Sea. Environ Earth Sci 68(5):1367–1374
Smith SL (1996) The development and implementation of Canadian sediment quality guidelines. Development and progress in sediment quality assessment: rational, challenge, techniques and strategies. SPB Academic Publishing, Amsterdam, pp 233–249
State Environmental Protection (2002) The editorial board of analysis methods of water and waste water monitoring. Analysis methods of water and waste water monitoring, 4th edn. China Environment Science Press, Beijing, pp 211–213
Tian XS, Zhu C, Sun ZB, Shui T (2013) An evaluation of heavy metal pollution within historic cultural strata at a specialized salt production site at Zhongba in the Three Gorges Reservoir region of the Yangtze River,China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2129–2138
Umoren IU, Udoh AP, Udousoro II (2007) Concentration and chemical speciation for the determination of Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb and Cd from refuse dump soils using the optimized BCR sequential extraction procedure. Environmentalist 27:241–252
USEPA (1989) Briefing report to the EPA Science Advisory Board on the equilibrium partitioning approach to generating sediment quality criteria. EPA2440252892002, Washington DC
USEPA (1999) National recommended water quality criteria correction. USEPA, Washington DC
USEPA (2000) Office of Water of Science and Technology, Draft implementation framework for the use of equilibrium partitioning sediment quality guideline. Washington DC: 4217
USEPA (2002a). An overview of sediment quality in the United States. EPA 905/9-88-002. Office of Water Regulations and Standards, Washington, DC, and EPA Region 5, Chicago
USEPA (2002b) National recommended water quality criteria. EPA 822-R-02-047
Wang L, Wang YP, Zhang WZ, Xu CX, An ZY (2014) Multivariate statistical techniques for evaluating and identifying the environmental significance of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Yangtze River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(3):1183–1193
Webster J, Ridgway I (1994) The application of the equilibrium partitioning approach for establishing sediment quality criteria at two UK Sea disposal and outfall sites. Mar Pollut Bull 28:653–661
Xia Q, Chen YQ, Liu XB (2004) Water quality criteria and water quality standards. China Standard Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhao JT, Hu BQ, Li J, Yang J, Bai FL, Dou YG, Yin XB (2014) One hundred-year sedimentary record of heavy metal accumulation in the southeastern Liaodong Bay of China. Environ Earth Sci 71(3):1073–1082
Zonta R, Zaggia L, Argese E (1994) Heavy metal and grain-size distributions in estuarine shallow water sediments of the Cona Marsh (Venice Lagoon, Italy). Sci Total Environ 151:19–28
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely appreciate the financial support by the major program of the national water pollution control and management in China (No. 2012ZX07503-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, C., Qin, Y., Zheng, B. et al. Sediment quality assessment for heavy metal pollution in the Xiang-jiang River (China) with the equilibrium partitioning approach. Environ Earth Sci 72, 5007–5018 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3368-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3368-5