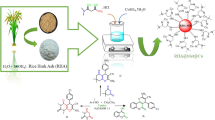
Abstract
Herein, low-cost, highly acidic γ-Al2O3 and silica were recovered from aluminum cans and silica beads wastes, respectively, using simple precipitation method. The prepared catalysts underwent thorough characterization using various techniques, including Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurements. Quantitative and qualitative measurements of total surface acidity, including Brönsted and Lewis acidity types, were determined through temperature-programmed desorption of pyridine (PY-TPD) and dimethyl pyridine (DMPY-TPD) as probe molecules. The prepared catalysts were tested in the dehydration of ethanol to ethylene and diethyl ether at a temperature range of 300–400 °C. The results revealed that the γ-Al2O3 catalyst outperformed silica at all reaction temperatures. Various kinetic parameters were investigated for the γ-Al2O3 catalyst within a temperature range of 200–400 °C, including the impact of weight hourly space velocity. Additionally, the catalyst exhibited impressive stability throughout four consecutive catalytic cycles, highlighting its durability over time.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdelkader, A., Osman, A.I., Halawy, S.A., Mohamed, M.A.: Preparation and characterization of mesoporous γ-Al2O3 recovered from aluminum cans waste and its use in the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. 20, 1428–1436 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0702-0
Grande, L., Vicente, M.Á., Korili, S.A., Gil, A.: Synthesis strategies of alumina from aluminum saline slags. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 172, 1010–1028 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2023.03.006
El-Katatny, E.A., Halawy, S.A., Mohamed, M.A., Zaki, M.I.: Surface composition, charge and texture of active alumina powders recovered from aluminum dross tailings chemical waste. Powder Technol. 132, 137–144 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-5910(03)00047-0
Fernandes, E.P., Silva, T.S., Carvalho, C.M., Selvasembian, R., Chaukura, N., Oliveira, L.M.: Meili, L: Efficient adsorption of dyes by γ-alumina synthesized from aluminum wastes: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics and toxicity assessment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 106198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106198
Sabarinathan, P., Annamalai, V.E.: Removal of aluminosilicate bond and process optimization on recovery of sol gel alumina abrasive grain from abrasive industry waste. SILICON 13, 495–505 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00466-6
Kumar, P., Chakraborty, S.: Rice husk-derived silica nanoparticles using optimized titrant concentration for the one-step nanofluid preparation. In Sustainable Chemical, Mineral and Material Processing: Select proceedings of 74th Annual Session of Indian Institute of Chemical Engineers. 303–318 (2022). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7264-5
Abdullah, N., Ainirazali, N., Chong, C.C., Razak, H.A., Setiabudi, H.D., Chin, S.Y., Jalil, A.A.: Effect of Ni loading on SBA-15 synthesized from palm oil fuel ash waste for hydrogen production via CH4 dry reforming. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45, 18411–18425 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.093
Razak, H., Abdullah, N., Setiabudi, H.D., Yee, C.S., Ainirazali, N.: Refluxed synthesis of SBA-15 using sodium silicate extracted from oil palm ash for dry reforming of methane. Mater Today Proc. 19, 1363–1372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.11.150
Li, G., Wang, B., Sun, Q., Xu, W.Q., Han, Y.: Adsorption of lead ion on amino-functionalized fly-ash-based SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieves prepared via two-step hydrothermal method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 252, 105–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.06.004
Mi, H.S.N., Panatarani, C., Faizal, F., Mulyana, C., Joni, I.M.: Synthesis of mesoporous Silica SBA-15 from geothermal sludge. Mater. 27, 101637 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2022.1016377
Chiang, H., Bhan, A.: Catalytic consequences of hydroxyl group location on the rate and mechanism of parallel dehydration reactions of ethanol over acidic zeolites. J. Catal. 271, 251–261 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2010.01.021
Qi, D.H., Chen, H., Geng, L.M., Bian, Y.Z.: Effect of diethyl ether and ethanol additives on the combustion and emission characteristics of biodiesel-diesel blended fuel engine. Renew Energ. 36, 1252–1258 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2010.09.021
Rossetti, I., Compagnoni, M., Finocchio, E., Ramis, G., Di Michele, A., Millot, Y., Dzwigaj, S.: Ethylene production via catalytic dehydration of diluted bioethanol: A step towards an integrated biorefinery. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 210, 407–420 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.007
Galadima, A., Muraza, O.: Zeolite catalysts in upgrading of bioethanol to fuels range hydrocarbons: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 31, 1–14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.07.015
Jamil, F., Aslam, M., Ala’a, H., Bokhari, A., Rafiq, S., Khan, Z., Bakar, M.S.A.: Greener and sustainable production of bioethylene from bioethanol: Current status, opportunities and perspectives. Rev Chem Eng. 38:85-207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2019-0026
Yakovleva, I.S., Banzaraktsaeva, S.P., Ovchinnikova, E.V., Chumachenko, V.A., Isupova, L.A.: Catalytic dehydration of bioethanol to ethylene. Catal. Ind. 8, 152–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070050416020148
Venu, H., Madhavan, V.: Influence of diethyl ether (DEE) addition in ethanol-biodiesel-diesel (EBD) and methanol-biodiesel-diesel (MBD) blends in a diesel engine. Fuel 189, 377–390 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.101
Uslu, S., Celik, M.B.: Prediction of engine emissions and performance with artificial neural networks in a single cylinder diesel engine using diethyl ether. Eng Sci Technol. 21, 1194–1201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2018.08.017
Di Cosimo, J.I., Dıez, V.K., Xu, M., Iglesia, E., Apesteguıa, C.R.: Structure and surface and catalytic properties of Mg-Al basic oxides. J. Catal. 178, 499–510 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1998.2161
Ramesh, K., Hui, L.M., Han, Y.F., Borgna, A.: Structure and reactivity of phosphorous modified H-ZSM-5 catalysts for ethanol dehydration. Catal. Commun. 10, 567–571 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2008.10.034
Sembiring, S., Riyanto, A., Situmeang, R., Sembiring, Z.: Bituminous composite comprising amorphous silica from rice husks. Ceram Silik 63, (2019). https://doi.org/10.13168/cs.2019.0021
Gao, Y., Hu, Y., Yao, K.: Surface molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of (–)-epigallocatechin gallate from toothpaste. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 9, 467–478 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-015-1526-2
Abdelkader, A., Hussien, B.M., Fawzy, E.M., Ibrahim, A.A.: Boehmite nanopowder recovered from aluminum cans waste as a potential adsorbent for the treatment of oilfield produced water. Appl Petrochem Res. 11, 137–146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13203-021-00267-x
ElKatatny, E.A., Halawy, S.A., Mohamed, M.A., Zaki, M.I.: A novel synthesis of high area alumina via H2O2 precipitated boehmite from sodium aluminate solutions. J Chem Technol. 72, 320-328 (1998). 0268-2575/98/s17.5
Maddalena, R., Hall, C., Hamilton, A.: Effect of silica particle size on the formation of calcium silicate hydrat [CSH] using thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta 672, 142–149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.09.003
Santos, B.P., Arias, J.R., Jorge, F.E., Santos, R.P., Fernandes, B.S., Candido, L.S., Marques, M.F.V.: PVDF containing different oxide nanoparticles for application in oil and gaspipelines. Mater Today Commun. 26, 101743 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101743
Sifontes, Á.B., Gutierrez, B., Mónaco, A., Yanez, A., Díaz, Y., Méndez, F.J., Brito, J.L.: Preparation of functionalized porous nano-γ-Al2O3 powders employing colophony extract. Biotechnol Rep. 4, 21–29 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2014.07.001
Osman, A.I., Abu-Dahrieh, J.K., Rooney, D.W., Halawy, S.A., Mohamed, M.A., Abdelkader, A.: Effect of precursor on the performance of alumina for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 127, 307–315 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.08.033
Darmakkolla, S.R., Tran, H., Gupta, A., Rananavare, S.B.: A method to derivatize surface silanol groups to Si-alkyl groups in carbon-doped silicon oxides. RSC Adv. 6, 93219–93230 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA20355H
Mekhemer, G.H., Halawy, S.A., Mohamed, M.A., Zaki, M.I.: Ketonization of acetic acid vapour over polycrystalline magnesia: in situ Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and kinetic studies. J. Catal. 230, 109–122 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2004.09.030
Dabbagh, H.A., Taban, K., Zamani, M.: Effects of vacuum and calcination temperature on the structure, texture, reactivity, and selectivity of alumina: Experimental and DFT studies. J Mol Catal A Chem: Chemical. 326, 55–68 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.04.007
Wang, C., Guo, H., Leng, S., Yu, J., Feng, K., Cao, L., Huang, J.: Regulation of hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of aluminosilicate zeolites: a review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 46(4), 330–348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408436.2020.1819198
Ijaz, A., Yagci, M.B., Ow-Yang, C.W., Demirel, A.L., Miko, A.: Formation of mesoporous silica particles with hierarchical morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 303, 110240 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110240
Gomaa, A.A., Halawy, S., Abdelkader, A.: Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline NiO by the thermal decomposition of oxalate salts for the dehydrogenation of 2-butanol to methyl ethyl ketone. Aswan Univ J Environ Studs. 2, 178–189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21608/aujes.2021.77260.1025
Khalfaoui, M., Knani, S., Hachicha, M.A., Lamine, A.B.: New theoretical expressions for the five adsorption type isotherms classified by BET based on statistical physics treatment. J. Colloid Interface sci. 263(2), 350–356 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00139-5
Li, J., Xu, X., Hao, Z., Zhao, W.: Mesoporous silica supported cobalt oxide catalysts for catalytic removal of benzene. J. Porous Mater. 15, 163–169 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-007-9119-1
Muthuswamy, E.: Synthetic levers enabling control of phase, size, and morphology in transition metal phosphide nanoparticles (iron, nickel) (Doctoral dissertation, Wayne State University) (2010). http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_dissertations. Accessed Aug 2023
Ferreira, R.K.M., Miled, M.B., Nishihora, R.K., Christophe, N., Carles, P., Motz, G., Bernard, S.: Low temperature in situ immobilization of nanoscale fcc and hcp polymorphic nickel particles in polymer-derived Si–C–O–N (H) to promote electrocatalytic water oxidation in alkaline media. Nanoscale Adv. 5, 701–710 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NA00821A
Trawczyński, J. T. Effect of aluminum hydroxide precipitation conditions on the alumina surface acidity. Ind. Amp; Eng. Chem., 35(1), 241–244 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie940703n
López, T., Gómez, R.: Evidence for Lewis and Brønsted acid sites on MgO obtained by sol–gel. J Sol Gel Sci Technol. 13, 1043–1047 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008624718503
Zaki, T.: Catalytic dehydration of ethanol using transition metal oxide catalysts. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 284, 606–613 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.10.048
Takahara, I., Saito, M., Inaba, M., Murata, K.: Dehydration of ethanol into ethylene over solid acid catalysts. Catal. Lett. 105, 249–252 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-005-8698-1
Phung, T.K., Busca, G.: Ethanol dehydration on silica-aluminas: active sites and ethylene/diethyl ether selectivities. Catal. Commun. 68, 110–115 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2015.05.009
Xiang, H., Xin, R., Prasongthum, N., Natewong, P., Sooknoi, T., Wang, J., Fan, X.: Catalytic conversion of bioethanol to value-added chemicals and fuels: A review. RCM 1, 47–68 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.recm.2021.12.002
Wu, C.Y., Wu, H.S.: Ethylene formation from ethanol dehydration using ZSM-5 catalyst. ACS Omega 2(8), 4287–4296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00680
Chen, G., Li, S., Jiao, F., Yuan, Q.: Catalytic dehydration of bioethanol to ethylene over TiO2/γ-Al2O3 catalysts in microchannel reactors. Catal. Today 125, 111–119 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2007.01.071
Gomaa, A.A., Osman, A.I., Halawy, S.A., Mohamed, M.A., Abdelkader, A.: Synthesis of highly basic, low-cost iron oxides from tin can waste as valorization of municipal solid waste and study of their catalytic efficiency as potent catalysts for MEK production. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-023-01865-8
Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Tao, L., Dai, B., Yang, M., Chen, Z., Zhu, X.: Dehydration reaction of bio-ethanol to ethylene over modified SAPO catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 16, 717–722 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2010.07.013
Singh, B., Sharma, V., Gaikwad, R.P., Fornasiero, P., Zboril, R., Gawande, M.B.: Single-atom catalysts: a sustainable pathway for the advanced catalytic applications. Small 17, 2006473 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202006473
Krutpijit, C., Tochaeng, P., Jongsomjit, B.: Temperature and ethanol concentration effects on catalytic ethanol dehydration behaviors over alumina-spherical silica particle composite catalysts. Catal. Commun. 145, 106102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2020.106102
Deng, L., Han, S., Zhou, D., Li, Y., Shen, W.: Morphology dependent effect of γ-Al2O3 for ethanol dehydration: Nanorods and nanosheets. Cryst Eng Comm. 24, 796–804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CE01316E
Phung, T.K., Busca, G.: Diethyl ether cracking and ethanol dehydration: acid catalysis and reaction paths. J. Chem. Eng. 272, 92–101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gomaa, A.A., Abdelkader, A. & Khodari, M. Highly Acidic, γ-Al2O3 Nanorods and SiO2 Nanoparticles Recovered from Solid Wastes as Promising Catalysts for Production of Ethylene and Diethyl Ether Biofuels. Waste Biomass Valor (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02518-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02518-z