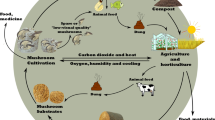
Abstract
Purpose
This study evaluated the treatment of naked oat straw with four species of white rot fungi (Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Pleurotus ostreatus, Irpex lacteus, and Phlebia acerina) for solid-state fermentation in terms of the changes in chemical composition, lignocellulosic structure, and in vitro ruminal digestion.
Methods
All the fungi were inoculated in naked oat straw for 28 days to evaluate the changes of above indexes weekly.
Results
The results showed that all of the fungus species could alter the multi-scale structure of the straw to different extents when compared to the control. P. acerina caused the greatest degradation of acid detergent lignin (46.51%), followed by P. chrysosporium (44.20%), while P. ostreatus and I. lacteus were slightly weaker in terms of acid detergent lignin degradation than the other two species. The dry matter loss for all treatments was below 20% except for P. chrysosporium, and all of the fungus species caused holocellulose degradation during treatment, with P. chrysosporium in particular exhibiting non-selectivity. Compared with the other fungi, I. lacteus treatment resulted in moderate losses of hemicellulose and cellulose (31.92% and 15.44%, respectively). In addition to P. chrysosporium, the in vitro dry matter digestion was improved with treatment by the other three fungi. Treatment with I. lacteus, led to improvement in dry matter, neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber degradability of 16.22%, 37.12%, and 40.05%, respectively.
Conclusion
Irpex lacteus outperformed the other three fungi in terms of decomposing three-dimensional structures and improving the nutritional value of naked oat straw.
Graphic Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, W., Wu, S., Cai, L., Liu, X., Wu, H., Xin, F., Zhang, M., Jiang, M.: Improved treatment and utilization of rice straw by Coprinopsis cinerea. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 184(2), 616–629 (2018)
Yu, Q., Liu, R., Li, K., Ma, R.: A review of crop straw pretreatment methods for biogas production by anaerobic digestion in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 107, 51–58 (2019)
Li, L., Qu, M., Liu, C., Xu, L., Pan, K., OuYang, K., Song, X., Li, Y., Liang, H., Chen, Z.: Effects of recombinant swollenin on the enzymatic hydrolysis, rumen fermentation, and rumen microbiota during in vitro incubation of agricultural straws. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 122, 348–358 (2019)
Nie, H., Wang, Z., You, J., Zhu, G., Wang, H., Wang, F.: Comparison of in vitro digestibility and chemical composition among four crop straws treated by Pleurotus ostreatus. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 33, 24–34 (2018)
Kim, K.H., Dutta, T., Sun, J., Simmons, B., Singh, S.: Biomass pretreatment using deep eutectic solvents from lignin derived phenols. Green Chem. 20(4), 809–815 (2018)
Sindhu, R., Binod, P., Pandey, A.: Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass–an overview. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 76–82 (2016)
Earnshaw, S.R., McDade, C.L., Chu, Y., Fleige, L.E., Sievenpiper, J.L.: Cost-effectiveness of maintaining daily intake of oat β-glucan for coronary heart disease primary prevention. Clin. Ther. 39(4), 804–818 (2017)
Jönsson, L.J., Martín, C.: Pretreatment of lignocellulose: formation of inhibitory by-products and strategies for minimizing their effects. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 103–112 (2016)
Rouches, E., Herpoël-Gimbert, I., Steyer, J., Carrere, H.: Improvement of anaerobic degradation by white-rot fungi pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 59, 179–198 (2016)
Voběrková, S., Vaverková, M.D., Burešová, A., Adamcová, D., Vršanská, M., Kynický, J., Brtnický, M., Adam, V.: Effect of inoculation with white-rot fungi and fungal consortium on the composting efficiency of municipal solid waste. Waste Manage. 61, 157–164 (2017)
van Kuijk, S.J., Sonnenberg, A.S., Baars, J.J., Hendriks, W.H., Cone, J.W.: Fungal treatment of lignocellulosic biomass: importance of fungal species, colonization and time on chemical composition and in vitro rumen degradability. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 209, 40–50 (2015)
He, Y., Dijkstra, J., Sonnenberg, A.S., Mouthier, T.M., Kabel, M.A., Hendriks, W.H., Cone, J.W.: The nutritional value of the lower maize stem cannot be improved by ensiling nor by a fungal treatment. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 247, 92–102 (2019)
Nayan, N., Sonnenberg, A.S., Hendriks, W.H., Cone, J.W.: Differences between two strains of Ceriporiopsis subvermispora on improving the nutritive value of wheat straw for ruminants. J. Appl. Microbiol. 123(2), 352–361 (2017)
Niu, D., Zuo, S., Jiang, D., Tian, P., Zheng, M., Xu, C.: Treatment using white rot fungi changed the chemical composition of wheat straw and enhanced digestion by rumen microbiota in vitro. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 237, 46–54 (2018)
Zuo, S., Niu, D., Jiang, D., Tian, P., Li, R., Wu, W., Xu, C.: Effect of white-rot fungal treatments on the in Vitro rumen degradability of two kinds of corn stover. BioResources 14(1), 895–907 (2018)
Van Soest, P.V., Robertson, J., Lewis, B.: Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 74(10), 3583–3597 (1991)
Menke, K.H.: Estimation of the energetic feed value obtained from chemical analysis and in vitro gas production using rumen fluid. Anim. Res. Dev. 28, 7–55 (1988)
Tirado-González, D.N., Jáuregui-Rincón, J., Tirado-Estrada, G.G., Martínez-Hernández, P.A., Guevara-Lara, F., Miranda-Romero, L.A.: Production of cellulases and xylanases by white-rot fungi cultured in corn stover media for ruminant feed applications. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 221, 147–156 (2016)
van Kuijk, S.J., José, C., Rencoret, J., Gutiérrez, A., Sonnenberg, A.S., Baars, J.J., Hendriks, W.H., Cone, J.W.: Selective ligninolysis of wheat straw and wood chips by the white-rot fungus Lentinula edodes and its influence on in vitro rumen degradability. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 7(1), 55 (2016)
Zuo, S., Niu, D., Zheng, M., Jiang, D., Tian, P., Li, R., Xu, C.: Effect of Irpex lacteus, Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus cystidiosus pretreatment of corn stover on its improvement of the in vitro rumen fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 98(11), 4287–4295 (2018)
Mertens, D.: Predicting intake and digestibility using mathematical models of ruminal function. J. Anim. Sci. 64(5), 1548–1558 (1987)
Nayan, N., Sonnenberg, A.S., Hendriks, W.H., Cone, J.W.: Variation in the solubilization of crude protein in wheat straw by different white-rot fungi. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 242, 135–143 (2018)
Meehnian, H., Jana, A.K., Jana, M.M.: Effect of particle size, moisture content, and supplements on selective pretreatment of cotton stalks by Daedalea flavida and enzymatic saccharification. 3 Biotech 6(2), 235 (2016)
Yu, Z., Zhang, B., Yu, F., Xu, G., Song, A.: A real explosion: the requirement of steam explosion pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 121, 335–341 (2012)
You, T., Li, X., Wang, R., Zhang, X., Xu, F.: Effects of synergistic fungal pretreatment on structure and thermal properties of lignin from corncob. Bioresour. Technol. 272, 123–129 (2019)
Tuyen, V.D., Cone, J.W., Baars, J.J.P., Sonnenberg, A.S.M., Hendriks, W.H.: Fungal strain and incubation period affect chemical composition and nutrient availability of wheat straw for rumen fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 111(5), 336–342 (2012)
Zhang, N., Liu, Y., Lu, J.H., Wang, J., Yang, S., Zhang, N., Meng, Q., Teng, L.: Isolation, purification and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Irpex lacteus. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 28(2), 249–254 (2012)
Xu, C., Ma, F., Zhang, X., Chen, S.: Biological pretreatment of corn stover by Irpex lacteus for enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(20), 10893–10898 (2010)
Salvachúa, D., Prieto, A., Vaquero, M.E., Martínez, Á.T., Martínez, M.J.: Sugar recoveries from wheat straw following treatments with the fungus Irpex lacteus. Bioresour. Technol. 131, 218–225 (2013)
Sharma, R., Arora, D.: Changes in biochemical constituents of paddy straw during degradation by white rot fungi and its impact on in vitro digestibility. J. Appl. Microbial. 109(2), 679–686 (2010)
Zhao, X., Gong, J., Zhou, S., OuYang, K., Song, X., Fu, C., Xu, L., Qu, M.: Effect of fungal treatments of rape straw on chemical composition and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics. BioResources 10(1), 622–637 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System of the People's Republic of China (Grant No. CARS-07-E-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, M., Zuo, S., Niu, D. et al. Effect of Four Species of White Rot Fungi on the Chemical Composition and In Vitro Rumen Degradability of Naked Oat Straw. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 435–443 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00991-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00991-w