Abstract
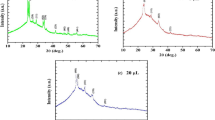
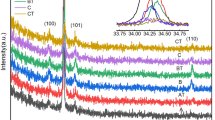
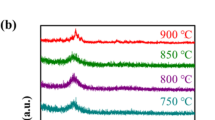
Indium sulfide thin films were prepared by chemical bath deposition method on glass substrates for about 40 min as deposition time and 60 °C as deposition temperature. The films were post-annealed at different temperatures such as 100 °C, 200 °C, 300 °C and 400 °C, for about 1 h. Structural and optical properties of In2S3 thin films after post-annealing process have been investigated. The crystallinity and nanostructures of the films were studied by using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy analysis. Optical reflectance and transmittance of layers were measured in the wavelength of 300–1100 nm by spectrophotometer instrument. Kramers–Kronig relations were used to calculate the optical constants. The X-ray diffraction measurements showed transformation of an amorphous nature to a crystalline structure by increasing the annealing temperature. The atomic force microscopy images showed by increasing the annealing temperature, the roughness of the thin films increased. The scanning electron microscopy images revealed that growth rate increased consistently with the increase in annealing temperature and well-dispersed quasi-spherical nanoparticles with high agglomeration rate are formed at 400 °C. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy results show reduction in the S/In ratio from 1.61 to 1.49 when annealing temperature increased. Optical results showed the highest optical band gap of 3.65 eV was achieved at the highest annealing temperature (400 °C).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J George, K S Joseph, B Pradeep, T I Palson Phys. Stat. Sol. A 106 123 (1988)
E B Yousfi, T Asikainen, V Pietu, P Cowache, M Powlla, D Lincot Thin Solid Films 361 183 (2000)
N Barreau, J C Bernede, S MarsilIac J. Cryst. Growth 241 51 (2002)
M I Hossain Chalcogenide Lett. 9 185 (2012)
M Ichimura, A Nakamura, K Takenchi, E Arai Thin Solid Films 384 157 (2001)
R Kumareasan, M Ichimura, N Stato, P Ramasamy Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 96 37 (2002)
N Kamoun, R Bennaceur, M Amlouk, S Belgacem, N Mliki, J M Frigerio, M C Theye Phys. Status Solidi A Appl. Res. 169 97 (1998)
N Bouguila, H Bouzouita, E Lacaze, A BelHadj Amara, H Bouchriha, A Dhouib J. Physique III 7 1647 (1997)
N Naghavi, R Henriquez, V Laptev, D Lincot Appl. Surf. Sci. 222 65 (2004)
T Asikainen, M Ritila, M Leskela Appl. Surf. Sci. 82/83 122 (1994)
J.George, K S Joseph, B Prodeep, T I Palson Phys. Status Solidi A Appl. Res. 106 123 (1988)
A A Elshazly, D Abdelkady, H S Metoually, M A M. Segman J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 10 5943 (1998)
C Guille´an, T Garico, J Herrero, M T Gutie´rrez, F Briones Thin Solid Films 112 451 (2004)
J H Kim, D Shin, B T Ahn Curr. Appl. Phys. 16 1040 (2016)
H Kangarlou, M Motallebi Agh Gonbad, A Abdollahi Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 1 1 (2015)
S Rasool, K Saritha, K T Ramakrishna Reddy, M S Tivanov, A V Trofimova, S E Tikoto, L Bychto, A Patryn, M Maliński, V F Gremenok Curr. Appl. Phys. 11 16 (2018)
O A Castelo-Gonaz´ lez, H C Santacruz-Ortega, M A Quevedo-Lo´pez M Sotelo-Lerma J. Electr. Mater. 41 695 (2012)
E Jalili, H Kangarlou, P Esmaili Optik 127 11235 (2016)
D Diehl, R Nitsche J. Crystal Growth 20 38 (1973)
K S J B M Kambas Phys. Status Solidi (b) 105 291 (1981)
M T Bhatti, A M Rana, A F Khan Mater. Chem. Phys. 84 126 (2004)
E Li ta, J E Sanchez J. Appl. Phys. 85 876 (1999)
G B Arfken, H J Weber Mathematical methods for physics (Port Harcourt: Harcourt Science and Technology Company) (2001)
E D Palik Handbook of optical constants of solids (Cambridge: Courtesy Academic Press Inc) (1985)
LWard The optical constants of bulk materials and films (Philadelphia: Institute of Physics) (1988)
C C Ting, S Y Chen J. Appl. Phys. 88 4628 (2000)
G Zhang, K Lu, X Zhang, W Yuan, M Shi, H Ning, R Tao, X Liu, R Yao, J. Peng Micromachines 9 377 (2018)
S. Asgary, M. Hantehzadeh, M. Ghoranneviss, A. Boochani Rare Metals 40 1 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasiri Sarvi, M., Esmaili, P. & Asgary, S. Effect of annealing on structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin layers produced by chemical bath deposition method. Indian J Phys 94, 1545–1552 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01601-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01601-9