Abstract
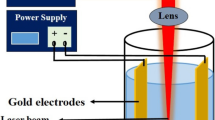
Cu nanoparticles have been prepared in different liquids i.e. aqueous solution of sodium dodecyl sulfate, acetone and ethanol with the help of laser ablation from a bulk copper target using 1,064 nm from Nd:YAG laser. Transmission electron microscopy and UV–vis spectrometry have been employed for the analysis of size and optical properties of the nanoparticles, respectively. X-ray diffraction patterns confirm the formation of Cu nanoparticles. The nanoparticles exhibit hexagonal nature with average particle size of 15–25 and 20–30 nm in case of sodium dodecyl sulfate and acetone respectively, whereas they posses spherical symmetry with bigger particle size of 30–40 nm in ethanol. The surface plasmon resonance peak shifts from 587 to 613 nm in different solvents, which is partly related to the change in shape and size of the particles. Further, Cu nanoparticles in different solvents have been added to polymer with terbium (Tb3+) ions to seek into the optical properties of the samples. The photoluminescence of Tb3+ ions varies with Cu nanoparticles in different solvents in polyvinyl alcohol and the result has been further verified by lifetime analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Moreno, R Hernandez and D Lopez Eur. Polym. J. 46 2099 (2010)
E Purushotham and N G Krishna Indian J. Phys. 84 887 (2010)
D P Chattopadhyay and B H Patel Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol. 9 1 (2012)
X Ren, D Chen and F Tang J. Phys. Chem. B 109 15803 (2005)
H S Wu and D H Chen J. Colloid Interface Sci. 273 165 (2004)
Y Gotoh et al. J. Mater. Chem. 10 2548 (2000)
T N Rostovshchikov et al. Appl. Catal. A Gen 296 70 (2005)
A Quaranta et al. J. Non Cryst Solids 345 671 (2004)
Z L Wang, ZW Quan and P Y Jia Chem. Mat. 18 2030 (2006)
W E Wallace, A Elattear, H Imamura, R S Craig and A G Moldvan The Science and Technology of Rare Earth Materials (New York: Academic Press) (eds.) W E Wallace and E C Subbarao p 329 (1980)
W E Wallace Rare Earth Intermetallics (New York: Academic Press Inc) (ed.) A M Alper et al. (1973)
R R Tang, G L Gu and Q Zhao Spectrochim. Acta A 71 371 (2008)
G Kaur, Y Dwivedi and S B Rai Mat. Chem. Phys. 130 1351 (2011)
G Kaur and S B Rai J. Appl. Phys. D 44 425 (2011)
T Tsuji, KenzoIryo, Y Nishimura and M Tsuji J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 145 201 (2001)
P V Kazakevich, V V Voronov, A V Simakin and G A Shafeev Quantum Electronics 34 951 (2004)
J Lee, D K Kim and WK Bull Korean Chem. Soc. 27 1869 (2006)
H S Desarkar, P Kumbhakar and A K Mitra Appl. Nanosci. 2 285 (2012)
V Amendola and Moreno Meneghetti Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11 3805 (2009)
M R Tilaki, A Irajizad and S M Mahdavi Appl. Phys. A 88 415 (2007)
B G Ganga, P N Santosh J. Alloys Compd. 612 456 (2014)
P Maneeratanasarn, T V Khai, S Y Kim, B G Choi and K B Shim Phys Status Solidi A 3 563 (2013)
P B Khoza, M J Moloto and L M Sikhwivhilu J. Nanotech. 2012 195106 (2011)
T M D Dang, T T T Le, E F Blanc and M C Dang Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2 015009 (2011)
C Noguez J. Phys. Chem. C 111 3806 (2007)
R K Verma, K Kumar and S B Rai J. Colloid Interface Sci. 390 11 (2013)
B Kumar, G Kaur, P Singh and S B Rai Appl. Phys. B 110 345 (2013)
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Germany, for providing pulsed Nd:YAG laser. Authors would like to acknowledge Prof. O N Srivastava, B. H. U. Varanasi, for TEM measurements. Authors would also like to acknowledge Prof. R. N. Rai, BHU Varanasi, for absorption measurements. One of the authors B Kumar would like to acknowledge UGC for Meritorious fellowship in Science. G Kaur would like to acknowledge DST for the project grant in the form of WOS-A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, B., Kaur, G. & Rai, S.B. Study of laser ablated copper nanoparticles in different liquids and their effect on optical properties of Tb3+ in PVA. Indian J Phys 89, 629–634 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-014-0617-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-014-0617-0