Abstract
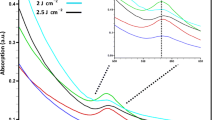
In this study, Cu nanoparticles were synthesized for the first time using an electric field-assisted pulsed laser ablation in liquid media (EPLAL) process and the influence of electric field on the properties of the synthesized nanoparticles was investigated. As-synthesized nanoparticles were successfully characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), electron dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR), Raman spectra, Dynamic light scattering analysis (DLS) and ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy. The XRD analysis demonstrated face centered cubic (FCC) structure of pure Cu nanoparticles. The FE-SEM and TEM analyses revealed that increasing the strength of electric field leads to fabricating nanoparticles with narrower range of size distribution. Also, the copper nanoparticles formation were confirmed by the characteristic surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak in UV–Vis spectra. On the other hand, the UV–Vis spectra displayed the blue-shifts from 588 to 582 nm of SPR peak by increasing the strength of applied electric field, which indicated the size of Cu nanoparticles were reduced. Furthermore, the DLS analysis confirmed that the size of Cu nanoparticles reduced from 115.8 to 91.7 nm by increasing the strength of applied electric field.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Haddad, R., Hamid, M., Jumaa, T.: Electric field effect on the synthesis of nanogold particles by PLAL. Int. J. Chem. Nat. Sci. 3, 269–274 (2015)
Bahador, A., Otaqsara, S.T., Baizaee, S.: A fast, room temperature excimer laser route for the synthesis of Ag/MWCNT nanocomposite without using reducing agent and investigating its photoresponse behavior to visible illumination. Appl. Surf. Sci. 457, 1087–1095 (2018)
Barcikowski, S., Compagnini, G.: Advanced nanoparticle generation and excitation by lasers in liquids. PCCP 15(9), 3022–3026 (2013)
Baruah, P.K., Singh, A., Rangan, L., Sharma, A.K., Khare, A.: Optimization of copper nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in distilled water as a viable SERS substrate for karanjin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 220, 111–117 (2018)
DellʼAglio, M., Gaudiuso, R., De Pascale, O., De Giacomo, A.: Mechanisms and processes of pulsed laser ablation in liquids during nanoparticle production. Appl. Surf. Sci. 348, 4–9 (2015)
Desarkar, H., Kumbhakar, P., Mitra, A.: Effect of ablation time and laser fluence on the optical properties of copper nano colloids prepared by laser ablation technique. Appl. Nanosci 2(3), 285–291 (2012)
Fernández-Arias, M., Boutinguiza, M., Del Val, J., Covarrubias, C., Bastias, F., Gómez, L., Maureira, M., Arias-González, F., Riveiro, A., Pou, J.: Copper nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation in liquids as bactericidal agent for dental applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 507, 145032 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.145032
Gahlawat, G., Choudhury, A.R.: A review on the biosynthesis of metal and metal salt nanoparticles by microbes. RSC Adv. 9(23), 12944–12967 (2019)
Herbani, Y., Nasution, R., Mujtahid, F., Masse S Pulse laser ablation of Au, Ag, and Cu metal targets in liquid for nanoparticle production. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol 1. IOP Publishing, pp. 012005 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/985/1/012005
Ismail, R.A., Fadhil, F.A.: Effect of electric field on the properties of bismuth oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in water. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(3), 1435–1440 (2014)
Jillani, S., Jelani, M., Hassan, N.U., Ahmad, S., Hafeez, M.: Synthesis, characterization and biological studies of copper oxide nanostructures. Mater. Res. Express 5(4), 045006 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aab864
Jiménez, J.A.: Thermal effects on the surface plasmon resonance of Cu nanoparticles in phosphate glass: impact on Cu+ luminescence. Nanoscale Adv. 1(5), 1826–1832 (2019)
Khalil, A.: Development of double-pulse lasers ablation system for generating gold ion source under applying an electric field. Opt. Laser Technol. 75, 105–114 (2015)
Kreibig, U., Vollmer, M.: Optical properties of metal clusters, vol. 25. Springer Science & Business Media (2013)
Kumar, B., Thareja, R.K.: Laser ablated copper plasmas in liquid and gas ambient. J. Plasma Phys. 20(5), 053503 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4807041
Li, Y., Musaev, O., Wrobel, J., Kruger, M.: Laser ablation in liquids of germanium in externally applied electric fields. J. Laser Appl. 28(2), 022004 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4940793
Lin, X., Liu, P., Yu, J., Yang, G.: Synthesis of CuO nanocrystals and sequential assembly of nanostructures with shape-dependent optical absorption upon laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(40), 17543–17547 (2009)
Liu, P., Wang, C., Chen, X., Yang, G.: Controllable fabrication and cathodoluminescence performance of high-index facets GeO2 micro-and nanocubes and spindles upon electrical-field-assisted laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Chem. C 112(35), 13450–13456 (2008)
Liu, P., Wang, H., Li, X., Rui, M., Zeng, H.: Localized surface plasmon resonance of Cu nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid media. RSC Adv. 5(97), 79738–79745 (2015)
Mahdieh, M.H., Mozaffari, H.: Characteristics of colloidal aluminum nanoparticles prepared by nanosecond pulsed laser ablation in deionized water in presence of parallel external electric field. Phys. Lett. A 381(38), 3314–3323 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106083
Marzun, G., Bönnemann, H., Lehmann, C., Spliethoff, B., Weidenthaler, C., Barcikowski, S.: Role of dissolved and molecular oxygen on Cu and PtCu alloy particle structure during laser ablation synthesis in liquids. Chem. Phys. Chem. 18(9), 1175–1184 (2017)
Moniri, S., Hantehzadeh, M.R., Ghoranneviss, M., Asadabad, M.A.: Study of the optical and structural properties of Pt nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation as a function of the applied electric field. Appl. Phys. A 123(11), 1–11 (2017a)
Moniri, S., Ghoranneviss, M., Hantehzadeh, M.R., Asadabad, M.A.: Synthesis and optical characterization of copper nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation. Bull. Mater. Sci. 40(1), 37–43 (2017b)
Mozaffari, H., Mahdieh, M.H.: Synthesis of colloidal aluminum nanoparticles by nanosecond pulsed laser and the effect of external electric field and laser fluence on ablation rate. Opt. Laser Technol. 126, 106083 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106083
Muniz-Miranda, M., Gellini, C., Giorgetti, E.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from copper nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(12), 5021–5027 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1086027
Oguchi, H., Sakka, T., Ogata, Y.H.: Effects of pulse duration upon the plume formation by the laser ablation of Cu in water. J. Appl. Phys. 102(2), 023306 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2759182
Peng-Fei, Y., Rong, Z., Qian, L., Jian-Chang, H., Yin-Bing, L., Ning, L.: Preparation of micropowder by a combination of jet-milling and electrostatic dispersion. Chin. Phys. Lett. 30(9), 098104 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/30/9/098104
Sapkota, D., Li, Y., Musaev, O.R., Wrobel, J.M., Kruger, M.B.: Effect of electric fields on tin nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in water. J. Laser Appl. 29(1), 012002 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4963270
Serkov, A., Barmina, E., Shafeev, G., Voronov, V.: Laser ablation of titanium in liquid in external electric field. Appl. Surf. Sci. 348, 16–21 (2015)
Shahzadi, I., Suleman, S., Saleem, S., Nadeem, S.: Utilization of Cu-nanoparticles as medication agent to reduce atherosclerotic lesions of a bifurcated artery having compliant walls. Comput. Meth. Prog. Bio. 184, 105123 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105123
Suresh, A.K.: Metallic nanocrystallites and their interaction with microbial systems. Springer Science & Business Media (2012)
Suresh, S., Karthikeyan, S., Jayamoorthy, K.: FTIR and multivariate analysis to study the effect of bulk and nano copper oxide on peanut plant leaves. J. Sci.-Adv. Mater. Dev. 1(3), 343–350 (2016)
Sylvestre, J.-P., Poulin, S., Kabashin, A.V., Sacher, E., Meunier, M., Luong, J.H.: Surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles produced by laser ablation in aqueous media. J. Phys. Chem. B 108(43), 16864–16869 (2004)
Tan, M.I.S.M.H., Omar, A.F., Rashid, M., Hashim, U.: VIS-NIR spectral and particles distribution of Au, Ag, Cu, Al and Ni nanoparticles synthesized in distilled water using laser ablation. Results Phys. 14, 102497 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102497
Tilaki, R., Mahdavi, S.: Size, composition and optical properties of copper nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in liquids. Appl. Phys. A 88(2), 415–419 (2007)
Uchinokura, K., Sekine, T., Matsuura, E.: Raman scattering by silicon. Solid State Commun. 11(1), 47–49 (1972)
Yan, Z., Chrisey, D.B.: Pulsed laser ablation in liquid for micro-/nanostructure generation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 13(3), 204–223 (2012)
Yang, G.: Laser ablation in liquids: applications in the synthesis of nanocrystals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 52(4), 648–698 (2007)
Yeshchenko, O.A., Dmitruk, I.M., Dmytruk, A.M., Alexeenko, A.A.: Influence of annealing conditions on size and optical properties of copper nanoparticles embedded in silica matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 137(1–3), 247–254 (2007)
Zeng, H., Du, X.W., Singh, S.C., Kulinich, S.A., Yang, S., He, J., Cai, W.: Nanomaterials via laser ablation/irradiation in liquid: a review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22(7), 1333–1353 (2012)
Zhao, H., Liu, X., Stephen, D.T.: Control of nanoparticle size and agglomeration through electric-field-enhanced flame synthesis. J. Nanoparticle Res. 10(6), 907–923 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razaghianpour, M., Hantehzadeh, M.R., Sari, A.H. et al. Electric field assisted-laser ablation of cu nanoparticles in ethanol and investigation of their properties. Opt Quant Electron 54, 23 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03286-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03286-z