Abstract
Inflammation plays an important role in depression pathology, making it a promising target for ameliorating depression-like behaviors. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α) is a transcriptional coactivator being able to constrain inflammatory events through NF-κB signaling. However, the role of PGC-1α in depression is not yet clear. This study was designed to investigate the role of PGC-1α in depression and explore the underlying mechanisms. Mice modeled with chronic unpredictable mild stimulation (CUMS) were explored for the relationship between depression-like behaviors and PGC-1α. Baicalin was used to evaluate the effect regulating PGC-1α. Furthermore, the anti-neuroinflammatory effect of baicalin was investigated both in BV2-SH-SY5Y co-culture system and in mice by LPS challenge. The role of PGC-1α in neuroinflammation was explored in cell co-culture systems under gene silencing conditions targeting NF-κB signaling. We found that the expression of PGC-1α was inhibited in the hippocampus of mice exposed to CUMS or LPS, while baicalin could increase the expression of PGC-1α and alleviate the depression-like behaviors. Furthermore, baicalin attenuated neuroinflammation in the hippocampus of mice and BV2-SH-SY5Y co-culture system by LPS challenge via regulating NF-κB signaling; however, knockdown of the PGC-1α could reverse the effect of baicalin on neuroinflammation and NF-κB signaling. Our results revealed a vital role for PGC-1α in attenuating neuroinflammation in depression, indicating that PGC-1α might be a therapeutic target for depression.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CUMS:
-
Chronic unpredictable mild stimulation
- BA:
-
Baicalin
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- PGC-1α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha
- NF-κB:
-
Transcription factor nuclear factor kappa light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1 beta
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- SPT:
-
Sucrose preference test
- TST:
-
Tail suspension test
- FST:
-
Forced swimming test
- MOD:
-
Mean optical density
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- NC:
-
Negative control
References
Abdel-Wahab BA, Salama RH (2011) Venlafaxine protects against stress-induced oxidative DNA damage in hippocampus during antidepressant testing in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100(1):59–65
Adebesin A, Adeoluwa OA, Eduviere AT, Umukoro S (2017) Methyl jasmonate attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviour in mice. J Psychiatr Res 94:29–35
Allison DJ, Nederveen JP, Snijders T, Bell KE (2019) Exercise training impacts skeletal muscle gene expression related to the kynurenine pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 316(3):C444–C448
Bhattacharya A, Lord B, Grigoleit JS, He Y (2018) Neuropsychopharmacology of JNJ-55308942: evaluation of a clinical candidate targeting P2X7 ion channels in animal models of neuroinflammation and anhedonia. Neuropsychopharmacology 43(13):2586–2596
Bombassaro B, Ignacio-Souza LM, Nunez CE, Razolli DS (2018) A20 deubiquitinase controls PGC-1alpha expression in the adipose tissue. Lipids Health Dis 17(1):90
Brites D, Fernandes A (2015) Neuroinflammation and depression: microglia activation, extracellular microvesicles and microRNA Dysregulation. Front Cell Neurosci 9:476
Bu X, Wu X, Lu L, Yang XX (2017) Role of SIRT1/PGC-1alpha in mitochondrial oxidative stress in autistic spectrum disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 13:1633–1645
Chen HY, Geng M, Hu YZ, Wang JH (2011) Effects of baicalin against oxidative stress injury of SH-SY5Y cells by up-regulating SIRT1. Yao Xue Xue Bao 46(9):1039–1044
Deng X, Ji Z, Xu B, Guo L, Xu L (2019) Suppressing the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 1: a new sight to treat depression. Cell Death Dis 10(5):370
Fan C, Song Q, Wang P, Li Y, Yang M (2018) Neuroprotective effects of curcumin on IL-1beta-induced neuronal apoptosis and depression-like behaviors caused by chronic stress in rats. Front Cell Neurosci 12:516
Fang P, Sun Y, Gu X, Shi M, Bo P (2019) Baicalin ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance and gluconeogenic activity through inhibition of p38 MAPK/PGC-1alpha pathway. Phytomedicine 64:153074
Fong SYK, Li C, Ho YC, Li R (2017) Brain uptake of bioactive flavones in Scutellariae Radix and its relationship to anxiolytic effect in mice. 14(9): 2908–2916
Fu X, Qin T, Yu J, Jiao J, Ma Z (2019) "Formononetin ameliorates cognitive disorder via PGC-1alpha pathway in neuroinflammation conditions in high-fat diet-induced mice." CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets
Gallagher D, Siddiqui F, Fish J, Charlat M (2019) "Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate peripheral stress-induced innate immune activation indirectly limiting the emergence of neuroinflammation-driven depressive and anxiety-like behaviors." Biol Psychiatry
Gu M, Li Y, Tang H, Zhang C, Li W (2018) "Endogenous omega (n)-3 fatty acids in Fat-1 mice attenuated depression-like behavior, imbalance between microglial M1 and M2 phenotypes, and dysfunction of Neurotrophins induced by lipopolysaccharide administration." Nutrients 10(10)
Guo LT, Wang SQ, Su J, Xu LX (2019) "Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway." 16(1): 95
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J, Kaarniranta K (2013) Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-kappaB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell Signal 25(10):1939–1948
Kim YK, Won E (2017) The influence of stress on neuroinflammation and alterations in brain structure and function in major depressive disorder. Behav Brain Res 329:6–11
Li YC, Wang LL, Pei YY, Shen JD (2015) Baicalin decreases SGK1 expression in the hippocampus and reverses depressive-like behaviors induced by corticosterone. Neuroscience 311:130–137
Li S, Sun X, Xu L, Sun R, Ma Z (2017) Baicalin attenuates in vivo and in vitro hyperglycemia-exacerbated ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating mitochondrial function in a manner dependent on AMPK. Eur J Pharmacol 815:118–126
Liang R, Han RM, Fu LM, Ai XC (2009) Baicalin in radical scavenging and its synergistic effect with beta-carotene in antilipoxidation. J Agric Food Chem 57(15):7118–7124
Liang W, Huang X, Chen W (2017) The effects of baicalin and baicalein on cerebral ischemia: a review. Aging Dis 8(6):850–867
Liao Z, Zhang J, Wang J, Yan T, Xu F (2019) The anti-nephritic activity of a polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) via modulation of AMPK-Sirt1-PGC-1alpha signaling axis mediated anti-oxidative in type 2 diabetes model mice. Int J Biol Macromol 140:568–576
Lu Y, Sun G, Yang F, Guan Z (2019) Baicalin regulates depression behavior in mice exposed to chronic mild stress via the Rac/LIMK/cofilin pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 116:109054
Łukaszuk B, Kurek K, Mikłosz A, Żendzian-Piotrowska M (2015) The role of PGC-1α in the development of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle - revisited. Cell Physiol Biochem 37(6):2288–2296
Miller AH, Raison CL (2016) The role of inflammation in depression: from evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat Rev Immunol 16(1):22–34
O'Connor JC, Lawson MA, André C, Moreau M, Lestage J (2008) Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol Psychiatry 14(5):511–522
Oeckinghaus A, Ghosh S (2009) The NF- B family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(4):a000034–a000034
Oh DR, Yoo JS, Kim Y, Kang H (2018) Vaccinium bracteatum leaf extract reverses chronic restraint stress-induced depression-like behavior in mice: regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal Axis, serotonin turnover systems, and ERK/Akt phosphorylation. Front Pharmacol 9:604
Peng K, Yang L, Wang J, Ye F (2017) The interaction of mitochondrial biogenesis and fission/fusion mediated by PGC-1alpha regulates rotenone-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Mol Neurobiol 54(5):3783–3797
Pfau ML, Menard C, Russo SJ (2018) Inflammatory mediators in mood disorders: therapeutic opportunities. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 58:411–428
Qin T, Fang F, Song M, Li R, Ma Z (2017) Umbelliferone reverses depression-like behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced rats by attenuating neuronal apoptosis via regulating ROCK/Akt pathway. Behav Brain Res 317:147–156
Ribeiro BMM, Chaves Filho AJM, Costa D, de Menezes AT (2019) N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and clozapine abrogates poly I: C-induced immune alterations in primary hippocampal neurons. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 90:186–196
Ryan KM, Patterson I, McLoughlin DM (2019) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator-1 alpha in depression and the response to electroconvulsive therapy. Psychol Med 49(11):1859–1868
Shabab T, Khanabdali R, Moghadamtousi SZ, Kadir HA (2017) Neuroinflammation pathways: a general review. Int J Neurosci 127(7):624–633
Song Y, Sun R, Ji Z, Li X (2018) Perilla aldehyde attenuates CUMS-induced depressive-like behaviors via regulating TXNIP/TRX/NLRP3 pathway in rats. Life Sci 206:117–124
Su WJ, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Gong H (2017) NLRP3 gene knockout blocks NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathway in CUMS-induced depression mouse model. Behav Brain Res 322(Pt A):1–8
Szalardy L, Molnar MF, Zadori D, Cseh EK (2018) Non-motor behavioral alterations of PGC-1alpha-deficient mice - a peculiar phenotype with slight male preponderance and no apparent progression. Front Behav Neurosci 12:180
Tyrtyshnaia AA, Lysenko LV, Madamba F, Manzhulo IV (2016) Acute neuroinflammation provokes intracellular acidification in mouse hippocampus. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):283
Villena JA (2015) New insights into PGC-1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond. FEBS J 282(4):647–672
Walker FR, Nilsson M, Jones K (2013) Acute and chronic stress-induced disturbances of microglial plasticity, phenotype and function. Curr Drug Targets 14(11):1262–1276
Walker AK, Wing EE, Banks WA, Dantzer R (2019) Leucine competes with kynurenine for blood-to-brain transport and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Mol Psychiatry 24(10):1523–1532
Wang Y, Ruan W, Mi J, Xu J, Wang H (2018) Balasubramide derivative 3C modulates microglia activation via CaMKKbeta-dependent AMPK/PGC-1alpha pathway in neuroinflammatory conditions. Brain Behav Immun 67:101–117
Wu RM, Sun YY, Zhou TT, Zhu ZY (2014) Arctigenin enhances swimming endurance of sedentary rats partially by regulation of antioxidant pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35(10):1274–1284
Yang X, Xu S, Qian Y, Xiao Q (2017) Resveratrol regulates microglia M1/M2 polarization via PGC-1alpha in conditions of neuroinflammatory injury. Brain Behav Immun 64:162–172
Yu H, Zhang F, Guan X (2019) Baicalin reverse depressive-like behaviors through regulation SIRT1-NF-kB signaling pathway in olfactory bulbectomized rats. Phytother Res 33(5):1480–1489
Zhang K, Lu J, Mori T, Smith-Powell L, Synold TW (2011) Baicalin increases VEGF expression and angiogenesis by activating the ERR{alpha}/PGC-1{alpha} pathway. Cardiovasc Res 89(2):426–435
Zhang K, Pan X, Wang F, Ma J, Su G (2016) Baicalin promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via SGK1- and FKBP5-mediated glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in a neuroendocrine mouse model of anxiety/depression. Sci Rep 6:30951
Zhang Y, Chen C, Jiang Y, Wang S, Wu X (2017) PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) protects neuroblastoma cells against amyloid-beta (Abeta) induced cell death and neuroinflammation via NF-kappaB pathway. BMC Neurosci 18(1):69
Zhang CY, Zeng MJ, Zhou LP, Li YQ (2018) Baicalin exerts neuroprotective effects via inhibiting activation of GSK3beta/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 signal pathway in a rat model of depression. Int Immunopharmacol 64:175–182
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all those who contributed to the thesis. The authors acknowledge the help of a supervisor, Professor Shiping Ma, who has offered suggestions in academic studies. The authors also have a special debt of gratitude to all the teachers in Department of Chinese Medicine Pharmacology of China Pharmaceutical University.
Funding
This work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703735, No. 81573701) and the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
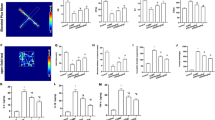
CUMS downregulated the expression of PGC-1α in hippocampus of mice.
Baicalin upregulated the expression of PGC-1α in SH-SY5Y cells.
The amelioration of baicalin for depression-like behaviors in LPS-induced mice is related to the attenuation of neuroinflammation.
PGC-1α/NF-κB signaling pathway involves in the anti-neuroinflammatory effect of baicalin.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(RAR 68857 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Jiao, J., Qin, T. et al. A New Perspective on Ameliorating Depression-Like Behaviors: Suppressing Neuroinflammation by Upregulating PGC-1α. Neurotox Res 39, 872–885 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00292-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00292-z