Abstract
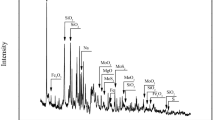
The preparation process of sodium molybdate has the disadvantages of high energy consumption, low thermal efficiency, and high raw material requirement of molybdenum trioxide, in order to realize the green and efficient development of molybdenum concentrate resources, this paper proposes a new process for efficient recovery of molybdenum from molybdenum concentrate and preparation of sodium molybdate by microwave-enhanced roasting and alkali leaching. Thermodynamic analysis indicated the feasibility of oxidation roasting of molybdenum concentrate. The effects of roasting temperature, holding time, and power-to-mass ratio on the oxidation product and leaching product sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4·2H2O) were investigated. Under the optimal process conditions: roasting temperature of 700°C, holding time of 110 min, and power-to-mass ratio of 110 W/g, the molybdenum state of existence was converted from MoS2 to MoO3. The process of preparing sodium molybdate by alkali leaching of molybdenum calcine was investigated, the optimal leaching conditions include a solution concentration of 2.5 mol/L, a liquid-to-solid ratio of 2 mL/g, a leaching temperature of 60°C, and leaching solution termination at pH 8. The optimum conditions result in a leaching rate of sodium molybdate of 96.24%. Meanwhile, the content of sodium molybdate reaches 94.08wt% after leaching and removing impurities. Iron and aluminum impurities can be effectively separated by adjusting the pH of the leaching solution with sodium carbonate solution. This research avoids the shortcomings of the traditional process and utilizes the advantages of microwave metallurgy to prepare high-quality sodium molybdate, which provides a new idea for the high-value utilization of molybdenum concentrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.S. Zhou, W.T. Yun, J.T. Xi, et al., Molybdenite–limestone oxidizing roasting followed by calcine leaching with ammonium carbonate solution, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 27(2017), No. 7, p. 1618.
W. Yang, B.J. Deng, L.Q. Hou, et al., Sulfur-fixation strategy toward controllable synthesis of molybdenum-based/carbon nanosheets derived from petroleum asphalt, Chem. Eng. J., 380(2020), art. No. 122552.
O.P. Parenago, G.N. Kuz’mina, and T.A. Zaimovskaya, Sulfurcontaining molybdenum compounds as high-performance lubricant additives (Review), Pet. Chem., 57(2017), No. 8, p. 631.
S. Kapri and S. Bhattacharyya, Molybdenum sulfide-reduced graphene oxide p–n heterojunction nanosheets with anchored oxygen generating manganese dioxide nanoparticles for enhanced photodynamic therapy, Chem. Sci., 9(2018), No. 48, p. 8982.
R.R. Mendel and F. Bittner, Cell biology of molybdenum, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1763(2006), No. 7, p. 621.
B.N. Kaiser, K.L. Gridley, J. Ngaire Brady, T. Phillips, and S.D. Tyerman, The role of molybdenum in agricultural plant production, Ann. Bot., 96(2005), No. 5, p. 745.
S.C. Wang and L.Z. Wang, Recent progress of tungsten- and molybdenum-based semiconductor materials for solar-hydrogen production, Tungsten, 1(2019), No. 1, p. 19.
W.W. Zhang, C.Y. Li, W.J. Wang, et al., Laminarin and sodium molybdate as efficient sustainable inhibitor for Q235 steel in sodium chloride solution, Colloids Surf., A, 637(2022), art. No. 128199.
D.Q. Wang, M. Wu, J. Ming, and J.J. Shi, Inhibitive effect of sodium molybdate on corrosion behaviour of AA6061 aluminium alloy in simulated concrete pore solutions, Constr. Build. Mater., 270(2021), art. No. 121463.
Y. Zhou, Y. Zuo, and B. Lin, The compounded inhibition of sodium molybdate and benzotriazole on pitting corrosion of Q235 steel in NaCl+NaHCO3 solution, Mater. Chem. Phys., 192(2017), p. 86.
O. Lopez-Garrity and G.S. Frankel, Corrosion inhibition of aluminum alloy 2024-T3 by sodium molybdate, J. Electrochem. Soc., 161(2013), No. 3, p. C95.
M.M. Heravi and M. Zakeri, Use of sodium molybdate dihydrate as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of benzopyranopyrimidine derivatives, Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Org. Nano Met. Chem., 43(2013), No. 2, p. 211.
F. Torun, B. Hostins, P. De Schryver, N. Boon, and J. De Vrieze, Molybdate effectively controls sulphide production in a shrimp pond model, Environ. Res., 203(2022), art. No. 111797.
J. Bolitschek, S. Luidold, and M. O’Sullivan, A study of the impact of reduction conditions on molybdenum morphology, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 71(2018), p. 325.
L. Wang, G.H. Zhang, J.S. Wang, and K.C. Chou, Influences of different components on agglomeration behavior of MoS2 during oxidation roasting process in air, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 47(2016), No. 4, p. 2421.
J.D. Lessard, D.G. Gribbin, and L.N. Shekhter, Recovery of rhenium from molybdenum and copper concentrates during the Looping Sulfide Oxidation process, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 44(2014), p. 1.
R. Jakhar, J.E. Yap, and R. Joshi, Microwave reduction of graphene oxide, Carbon, 170(2020), p. 277.
J.P. Wang, T. Jiang, Y.J. Liu, and X.X. Xue, Influence of microwave treatment on grinding and dissociation characteristics of vanadium titano-magnetite, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 2, p. 160.
Y. He, J. Liu, J.H. Liu, C.L. Chen, and C.L. Zhuang, Carbothermal reduction characteristics of oxidized Mn ore through conventional heating and microwave heating, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 28(2021), No. 2, p. 221.
S. Das, A.K. Mukhopadhyay, S. Datta, and D. Basu, Prospects of microwave processing: An overview, Bull. Mater. Sci., 31(2008), No. 7, p. 943.
R.M. Anklekar, D.K. Agrawal, and R. Roy, Microwave sintering and mechanical properties of PM copper steel, Powder Metall., 44(2001), No. 4, p. 355.
J. Liu, C.H. Liu, Y. Hong, and L.B. Zhang, Basic study on microwave carbon-thermal reduction senarmontite (Sb2O3) to produce antimony: High-temperature dielectric properties and a microwave reduction mechanism, Powder Technol., 389(2021), p. 482.
V.Kvapilová, Evaluation of microwave drying effects on historical brickwork and modern building materials, IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 867(2020), No. 1, art. No. 012026.
M. Oghbaei and O. Mirzaee, Microwave versus conventional sintering: A review of fundamentals, advantages and applications, J. Alloys Compd., 494(2010), No. 1–2, p. 175.
G.Y. Zhu, Z.W. Peng, L. Yang, H.M. Tang, X.L. Fang, and M.J. Rao, Facile preparation of thermal insulation materials by microwave sintering of ferronickel slag and fly ash cenosphere, Ceram. Int., 49(2023), No. 8, p. 11978.
P. Parhi and P. Misra, Hydrometallurgical investigation routed through microwave (MW) assisted leaching and solvent extraction using ionic liquids for extraction and recovery of molybdenum from spent desulphurization catalyst, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 149(2023), p. 110394.
P.K. Parhi and P.K. Misra, Environmental friendly approach for selective extraction and recovery of molybdenum (Mo) from a sulphate mediated spent Ni-Mo/Al2O3 catalyst baked leach liquor, J. Environ. Manage., 306(2022), art. No. 114474.
S. Kan, K. Benzeşik, Ö.C. Odabaş, and O. Yücel, Investigation of molybdenite concentrate roasting in chamber and rotary furnaces, Min. Metall. Explor., 38(2021), No. 3, p. 1597.
Y.L. Jiang, B.G. Liu, P. Liu, J.H. Peng, L.B. Zhang, Dielectric characterization and microwave roasting of molybdenite concentrates at 915 MHz frequency, J. Harbin Inst. Technol. (New Series), 26(2019), No. 3, p. 58.
M. Pervaiz, A. Munawar, S. Hussain, et al., A green approach for extraction of ammonium molybdate from molybdenite using indigenous resources, Pol. J. Environ. Stud., 30(2021), No. 2, p. 1771.
M.P. Zhang, C.H. Liu, X.J. Zhu, et al., Preparation of ammonium molybdate by oxidation roasting of molybdenum concentrate: A comparison of microwave roasting and conventional roasting, Chem. Eng. Process.: Process. Intensif., 167(2021), art. No. 108550.
M.D. Lane, J.L. Bishop, M.D. Dyar, et al., Mid-infrared emission spectroscopy and visible/near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy of Fe-sulfate minerals, Am. Mineral., 100(2015), No. 1, p. 66.
L. Wang, G.H. Zhang, J. Dang, and K.C. Chou, Oxidation roasting of molybdenite concentrate, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 25(2015), No. 12, p. 4167.
H. Sun, G.H. Li, Q.Z. Bu, et al., Features and mechanisms of self-sintering of molybdenite during oxidative roasting, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 32(2022), No. 1, p. 307.
C. Kansomket, P. Laokhen, T. Yingnakorn, T. Patcharawit, and S. Khumkoa, Extraction of molybdenum from a spent HDS catalyst using alkali leaching reagent, J. Met. Mater. Miner., 32(2022), No. 2, p. 88.
C. Wang, Y.F. Guo, S. Wang, et al., Characteristics of the reduction behavior of zinc ferrite and ammonia leaching after roasting, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 27(2020), No. 1, p. 26.
Y.I. Nam, S.Y. Seo, Y.C. Kang, M.J. Kim, G. Senanayake, and T. Tran, Purification of molybdenum trioxide calcine by selective leaching of copper with HCl-NH4Cl, Hydrometallurgy, 109(2011), No. 1–2, p. 9.
H. Sun, J.J. Yu, G.H. Li, et al., Co-volatilizing-water leaching process for efficient utilization of rhenium-bearing molybdenite concentrate, Hydrometallurgy, 192(2020), art. No. 105284.
J.H. Chen, D. Tang, S.P. Zhong, W. Zhong, and B.Z. Li, The influence of micro-cracks on copper extraction by bioleaching, Hydrometallurgy, 191(2020), art. No. 105243.
L.P. Jia, Z.W. Zhao, X.H. Liu, and L.H. He, Recovery of valuable metals from molybdenum-removal sludge by reverse sulfurization leaching, Hydrometallurgy, 193(2020), art. No. 105323.
Y.B. Li, Q.H. Xiao, Z.M. Li, and Gerson A, Enhanced leaching of Mo by mechanically co-grinding and activating MoS2 with NaClO3 as an oxidizing additive, Hydrometallurgy, 203(2021), art. No. 105625.
S. Ali, Y. Iqbal, I. Khan, et al., Hydrometallurgical leaching and kinetic modeling of low-grade manganese ore with banana peel in sulfuric acid, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 28(2021), No. 2, p. 193.
J. Liu, Z.F. Qiu, J. Yang, L.M. Cao, and W. Zhang, Recovery of Mo and Ni from spent acrylonitrile catalysts using an oxidation leaching-chemical precipitation technique, Hydrometallurgy, 164(2016), p. 64.
Z.X. Liu, L. Sun, J. Hu, et al., Selective extraction of molybdenum from copper concentrate by air oxidation in alkaline solution, Hydrometallurgy, 169(2017), p. 9.
P. Wang, Y.J. Pan, X. Sun, and Y.Q. Zhang, Leaching molybdenum from a low-grade roasted molybdenite concentrate, SN Appl. Sci., 1(2019), No. 4, art. No. 311.
M. Vosough, G.R. Khayati, and S. Sharafi, Ammonia leaching of MoO3 concentrate: Finding the reaction mechanism and kinetics analysis, Chem. Pap., 76(2022), No. 5, p. 3227.
Z.P. Zhao, M. Guo, and M. Zhang, Extraction of molybdenum and vanadium from the spent diesel exhaust catalyst by ammonia leaching method, J. Hazard. Mater., 286(2015), p. 402.
Y. Liu, Y.F. Zhang, F.F. Chen, and Y. Zhang, The alkaline leaching of molybdenite flotation tailings associated with galena, Hydrometallurgy, 129–130(2012), p. 30.
Y. Guo, H.Y. Li, Y.H. Yuan, et al., Microemulsion leaching of vanadium from sodium-roasted vanadium slag by fusion of leaching and extraction processes, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 28(2021), No. 6, p. 974.
G.J. Olson and T.R. Clark, Bioleaching of molybdenite, Hydrometallurgy, 93(2008), No. 1–2, p. 10.
Y.F. Fu, Q.G. Xiao, Y.Y. Gao, P.G. Ning, H.B. Xu, and Y. Zhang, Pressure aqueous oxidation of molybdenite concentrate with oxygen, Hydrometallurgy, 174(2017), p. 131.
J.P. Wang, Y.M. Zhang, J. Huang, and T. Liu, Synergistic effect of microwave irradiation and CaF2 on vanadium leaching, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 24(2017), No. 2, p. 156.
S.A. Kapole, B.A. Bhanvase, D.V. Pinjari, et al., Investigation of corrosion inhibition performance of ultrasonically prepared sodium zinc molybdate nanopigment in two-pack epoxy-polyamide coating, Compos. Interfaces, 21(2014), No. 9, p. 833.
S. Nakagaki, A. Bail, V.C. dos Santos, et al., Use of anhydrous sodium molybdate as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for soybean oil methanolysis, Appl. Catal. A, 351(2008), No. 2, p. 267.
Y. Mochizuki, J. Bud, J.Q. Liu, M. Takahashi, and N. Tsubouchi, Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous using iron hydroxides prepared by various methods, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 9(2021), No. 1, art. No. 104645.
S.Q. Wang, J. Xie, J.D. Hu, H.Y. Qin, and Y.L. Cao, Fe-doped α-MoO3 nanoarrays: Facile solid-state synthesis and excellent xylene-sensing performance, Appl. Surf. Sci., 512(2020), art. No. 145722.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51964046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Liu, C., Chandrasekar, S. et al. Preparation of sodium molybdate from molybdenum concentrate by microwave roasting and alkali leaching. Int J Miner Metall Mater 31, 91–105 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-023-2727-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-023-2727-1