Abstract
Background
Sarcopenia is defined as the loss of skeletal muscle mass and function associated with aging. Muscle mass can be reliably and accurately quantified using clinical CT scans but reference measurements are lacking, particularly in healthy US populations.
Methods
Two-phase CT scans from healthy kidney donors (age 18-40) at the University of Michigan between 1999-2010 were utilized. Muscle mass was quantified using two thoracic and two lumbar muscle cross-sectional area (CSA) measures. Indexed measurements were computed as area divided by height-squared. Paired analyses of non-contrast and contrast phases and different Hounsfield Unit (HU) ranges for muscle were conducted to determine their effect on CSA muscle measures. We report the means, standard deviations, and 2SD sarcopenia cutoffs from this population.
Results
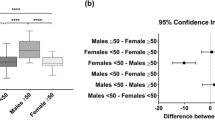
Healthy population CSA (cm2) cutoffs for N=604 males/females respectively were: 34.7/20.9 (T12 Dorsal Muscle), 91.5/55.9 (T12 Skeletal Muscle), 141.7/91.2 (L3 Skeletal Muscle), 23.5/14.3 (L4 Total Psoas Area), and 23.4/14.3 (L4 Psoas Muscle Area). Height-indexed CSA (cm2/m2) cutoffs for males/females respectively were: 10.9/7.8 (T12 Dorsal Muscle), 28.7/20.6 (T12 Skeletal Muscle), 44.6/34.0 (L3 Skeletal Muscle), 7.5/5.2 (L4 Total Psoas Area), and 7.4/5.2 (L4 Psoas Muscle Area). We confirmed that a mask of -29 to 150 HU is optimal and shows no significant difference between contrast-enhanced and non-contrast CT scan CSA measurements.
Conclusions
We quantified reference values for lumbar and thoracic muscle CSA measures in a healthy US population. We defined the effect of IV contrast and different HU ranges for muscle. Combined, these results facilitate the extraction of clinically valuable data from the large numbers of existing scans performed for medical indications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. A. Studenski, K. W. Peters, D. E. Alley, P. M. Cawthon, R. R. McLean, T. B. Harris, L. Ferrucci, J. M. Guralnik, M. S. Fragala, A. M. Kenny, D. P. Kiel, S. B. Kritchevsky, M. D. Shardell, T. T. Dam, M. T. Vassileva, The fnih sarcopenia project: rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2014;69: 547–58.
A. J. Cruz-Jentoft, J. P. Baeyens, J. M. Bauer, Y. Boirie, T. Cederholm, F. Landi, F. C. Martin, J. P. Michel, Y. Rolland, S. M. Schneider, E. Topinkova, M. Vandewoude, M. Zamboni, Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the european working group on sarcopenia in older people, Age Ageing, 2010;39:412–23.
L. K. Chen, L. K. Liu, J. Woo, P. Assantachai, T. W. Auyeung, K. S. Bahyah, M. Y. Chou, L. Y. Chen, P. S. Hsu, O. Krairit, J. S. Lee, W. J. Lee, Y. Lee, C. K. Liang, P. Limpawattana, C. S. Lin, L. N. Peng, S. Satake, T. Suzuki, C. W. Won, C. H. Wu, S. N. Wu, T. Zhang, P. Zeng, M. Akishita, H. Arai, Sarcopenia in asia: consensus report of the asian working group for sarcopenia, J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2014;15:95–101.
I. H. Rosenberg, Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance, J Nutr, 1997;127:990S–991S.
S. B. Heymsfield, M. Adamek, M. C. Gonzalez, G. Jia, D. M. Thomas, Assessing skeletal muscle mass: historical overview and state of the art, J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2014;5:9–18.
M. Mourtzakis, C. M. Prado, J. R. Lieffers, T. Reiman, L. J. McCargar, V. E. Baracos, A practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care, Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2008;33:997–1006.
S. L. Gomez-Perez, J. M. Haus, P. Sheean, B. Patel, W. Mar, V. Chaudhry, L. McKeever, C. Braunschweig, Measuring abdominal circumference and skeletal muscle from a single cross-sectional computed tomography image: A step-by-step guide for clinicians using national institutes of health imagej, JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2016;40 (2016) 308–18.
N. Mitsiopoulos, R. N. Baumgartner, S. B. Heymsfield, W. Lyons, D. Gallagher, R. Ross, Cadaver validation of skeletal muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography, J Appl Physiol 1998;(1985) 85:115–22.
R. A. Fielding, B. Vellas, W. J. Evans, S. Bhasin, J. E. Morley, A. B. Newman, G. Abellan van Kan, S. Andrieu, J. Bauer, D. Breuille, T. Cederholm, J. Chandler, C. De Meynard, L. Donini, T. Harris, A. Kannt, F. Keime Guibert, G. Onder, D. Papanicolaou, Y. Rolland, D. Rooks, C. Sieber, E. Souhami, S. Verlaan, M. Zamboni, Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. international working group on sarcopenia, J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2011;12:249–56.
C. M. Prado, J. R. Lieffers, L. J. McCargar, T. Reiman, M. B. Sawyer, L. Martin, V. E. Baracos, Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study, Lancet Oncol, 2008;9:629–35.
C. M. Prado, V. E. Baracos, L. J. McCargar, T. Reiman, M. Mourtzakis, K. Tonkin, J. R. Mackey, S. Koski, E. Pituskin, M. B. Sawyer, Sarcopenia as a determinant of chemotherapy toxicity and time to tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving capecitabine treatment, Clin Cancer Res, 2009;15:2920–6.
C. M. Prado, S. B. Heymsfield, Lean tissue imaging: a new era for nutritional assessment and intervention, JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2014;38:940–53.
L. Martin, L. Birdsell, N. Macdonald, T. Reiman, M. T. Clandinin, L. J. McCargar, R. Murphy, S. Ghosh, M. B. Sawyer, V. E. Baracos, Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index, J Clin Oncol, 2013;31:1539–47.
M. J. Englesbe, S. P. Patel, K. He, R. J. Lynch, D. E. Schaubel, C. Harbaugh, S. A. Holcombe, S. C. Wang, D. L. Segev, C. J. Sonnenday, Sarcopenia and mortality after liver transplantation, J Am Coll Surg, 2010;211:271–8.
M. J. Englesbe, J. S. Lee, K. He, L. Fan, D. E. Schaubel, K. H. Sheetz, C. M. Harbaugh, S. A. Holcombe, J. Campbell, D. A., C. J. Sonnenday, S. C. Wang, Analytic morphomics, core muscle size, and surgical outcomes, Ann Surg, 2012;256:255–61.
L. D. Canvasser, A. A. Mazurek, D. C. Cron, M. N. Terjimanian, E. T. Chang, C. S. Lee, M. B. Alameddine, J. Claflin, E. D. Davis, T. M. Schumacher, S. C. Wang, M. J. Englesbe, Paraspinous muscle as a predictor of surgical outcome, J Surg Res, 2014;192:76–81.
C. S. Lee, D. C. Cron, M. N. Terjimanian, L. D. Canvasser, A. A. Mazurek, E. Vonfoerster, L. M. Tishberg, P. W. Underwood, E. T. Chang, S. C. Wang, C. J. Sonnenday, M. J. Englesbe, Dorsal muscle group area and surgical outcomes in liver transplantation, Clin Transplant, 2014;28:1092–8.
A. Hiraoka, T. Aibiki, T. Okudaira, A. Toshimori, T. Kawamura, H. Nakahara, Y. Suga, N. Azemoto, H. Miyata, Y. Miyamoto, et al., Muscle atrophy as pre-sarcopenia in japanese patients with chronic liver disease: computed tomography is useful for evaluation, Journal of gastroenterology, 2015;50:1206–1213.
Y. Hamaguchi, T. Kaido, S. Okumura, A. Kobayashi, A. Hammad, Y. Tamai, N. Inagaki, S. Uemoto, Proposal for new diagnostic criteria for low skeletal muscle mass based on computed tomography imaging in asian adults, Nutrition, 2016;32:1200–1205.
J. Aubrey, N. Esfandiari, V. Baracos, F. Buteau, J. Frenette, C. Putman, V. Mazurak, Measurement of skeletal muscle radiation attenuation and basis of its biological variation, Acta physiologica, 2014;210:489–497.
B. H. Goodpaster, D. E. Kelley, R. R. Wing, A. Meier, F. L. Thaete, Effects of weight loss on regional fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in obesity, Diabetes, 1999;48:839–47.
R. D. Boutin, J. M. Kaptuch, C. P. Bateni, J. S. Chalfant, L. Yao, Influence of iv contrast administration on ct measures of muscle and bone attenuation: Implications for sarcopenia and osteoporosis evaluation, American Journal of Roentgenology, 2016;207:1046–1054.
A. Werf, I. M. Dekker, M. R. Meijerink, N. J. Wierdsma, M. A. Schueren, J. A. Langius, Skeletal muscle analyses: agreement between noncontrast and contrast ct scan measurements of skeletal muscle area and mean muscle attenuation, Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging, 2017.
D. A. Hanauer, Q. Mei, J. Law, R. Khanna, K. Zheng, Supporting information retrieval from electronic health records: A report of university of michigan’s nineyear experience in developing and using the electronic medical record search engine (emerse), J Biomed Inform, 2015;55:290–300.
I. Janssen, S. B. Heymsfield, R. Ross, Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability, Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 2002;50:889–896.
R. W. Hingson, T. Heeren, E. M. Edwards, R. Saitz, Young adults at risk for excess alcohol consumption are often not asked or counseled about drinking alcohol, Journal of General Internal Medicine, 2012;27:179–184.
J. Stamler, R. Stamler, J. D. Neaton, D. Wentworth, M. L. Daviglus, D. Garside, A. R. Dyer, K. Liu, P. Greenland, Low risk-factor profile and long-term cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality and life expectancy: findings for 5 large cohorts of young adult and middle-aged men and women, JAMA, 1999;282:2012–2018.
C. L. Ogden, M. D. Carroll, L. R. Curtin, M. A. McDowell, C. J. Tabak, K. M. Flegal, Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the united states, 1999-2004, JAMA, 2006;295:1549–1555.
A. M. Geiger, S. M. Castellino, Delineating the age ranges used to define adolescents and young adults, Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2011;29:e492–e493.
V. Krishnamurthy, P. Zhang, S. Ethiraj, B. Enchakalody, A. K. Waljee, L. Wang, S. C. Wang, G. L. Su, Use of analytic morphomics of liver, spleen, and body composition to identify patients at risk for cirrhosis, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015;13:360–368 e5.
L. A. J. Quetelet, A treatise on man and the development of his faculties, W. and R. Chambers, Edinburgh, 1842.
A. Keys, F. Fidanza, M. J. Karvonen, N. Kimura, H. L. Taylor, Indices of relative weight and obesity, J Chronic Dis, 1972;25:329–43.
R. F. Burton, Why is the body mass index calculated as mass/height2, not as mass/height3?, Ann Hum Biol 34:656–63.
S. B. Heymsfield, M. Heo, D. Thomas, A. Pietrobelli, Scaling of body composition to height: relevance to height-normalized indexes, Am J Clin Nutr, 2011;93:736–40.
R Core Team, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria,, 2016.
S. A. Holcombe, S. C. Wang, Subcutaneous Fat Distribution in the Human Torso, in: IRCOBI Conference, volume, 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derstine, B.A., Holcombe, S.A., Goulson, R.L. et al. Quantifying Sarcopenia Reference Values Using Lumbar and Thoracic Muscle Areas in a Healthy Population. J Nutr Health Aging 22, 180–185 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-017-0983-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-017-0983-3