Abstract
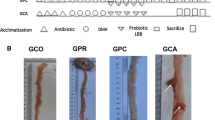
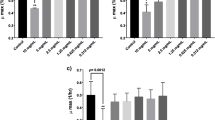
Gastrointestinal mucositis associated with the use of chemotherapeutic drugs can seriously affect the quality of life of patients. In this study, a probiotic mixture, BIO-THREE, was used to alleviate intestinal damage caused by oxaliplatin in mice and human patients. Kunming mice were injected with 15 mg/kg of oxaliplatin twice, and BIO-THREE tablets were administered to mice for 12 days. Patients with gastric cancer undergoing oxaliplatin treatment took BIO-THREE tablets for 2 weeks. The changes in the composition of fecal microbiota both in patients and mice were analyzed using 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing. In mice, oxaliplatin caused a drop in body weight and produced lesions in the liver and small intestines. Probiotic therapy successfully mitigated the damage caused by oxaliplatin to the intestinal tract, but it was not very effective for the liver damage and weight loss caused by oxaliplatin. The sequencing of the gut microflora indicated that oxaliplatin treatment increased the abundance of Bacteroidetes and decreased the abundance of Prevotella in mice. After taking probiotics, the feces of mice and human patients both had a higher abundance of Plovitella and a lower abundance of Bacteroides. The increase in Bacteroidetes and decrease in Prevotella in the gut community might be associated with oxaliplatin-induced intestinal damage. Probiotics appeared to be beneficial, decreasing intestinal damage by restoring the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Prevotella.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) Database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA659425/).
References
Newsroom (2018) Cancer. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer#tab=tab_1
Ruiz-González R, Milán P, Bresolí-Obach R, Stockert JC, Villanueva A, Cañete M, Nonell S (2017) Photodynamic synergistic effect of pheophorbide a and doxorubicin in combined treatment against tumoral cells. Cancers (Basel) 9:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9020018
Feather CE, Lees JG, Makker PGS, Goldstein D, Kwok JB, Moalem-Taylor G, Polly P (2018) Oxaliplatin induces muscle loss and muscle-specific molecular changes in mice. Muscle Nerve 57:650–658. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25966
Wang J, Feng W, Zhang S, Chen L, Tang F, Sheng Y, Ao H, Peng C (2019) Gut microbial modulation in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced diarrhea with Shenzhu Capsule. BMC Complement Altern Med 19:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2548-y
Stein A, Voigt W, Jordan K (2010) Chemotherapy-induced diarrhea: pathophysiology, frequency and guideline-based management. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758834009355164
Abu-Sbeih H, Mallepally N, Goldstein R, Chen E, Tang T, Dike UK, Al-Asadi M, Westin S, Halperin D, Wang Y (2020) Gastrointestinal toxic effects in patients with cancer receiving platinum-based therapy. J Cancer 11:3144–3150. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.37777
Shen S, Lim G, You Z, Ding W, Huang P, Ran C, Doheny J, Caravan P, Tate S, Hu K, Kim H, McCabe M, Huang B, Xie Z, Kwon D, Chen L, Mao J (2017) Gut microbiota is critical for the induction of chemotherapy-induced pain. Nat Neurosci 20:1213–1216. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4606
Touchefeu Y, Montassier E, Nieman K, Gastinne T, Potel G, Bruley des Varannes S, Le Vacon F, de La Cochetiere MF, (2014) Systematic review: the role of the gut microbiota in chemotherapy- or radiation-induced gastrointestinal mucositis - current evidence and potential clinical applications. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 40:409–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.12878
Wilkins T, Sequoia J (2017) Probiotics for gastrointestinal conditions: a summary of the evidence. Am Fam Physician 96:170–178
Seminario-Amez M, Lopez-Lopez J, Estrugo-Devesa A, Ayuso-Montero R, Jane-Salas E (2017) Probiotics and oral health: a systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 22(3):e282–e288. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.21494
Wan C-F, Zheng L-L, Liu Y, Yu X (2016) Houttuynia cordata Thunb reverses oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain in rat by regulating Th17/Treg balance. Am J Transl Res 8:1609–1614
Marmol I, Quero J, Rodriguez-Yoldi MJ, Cerrada E (2019) Gold as a possible alternative to platinum-based chemotherapy for colon cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel) 11(6):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060780
Chamaillard M, Stojanovska V, McQuade RM, Fraser S, Prakash M, Gondalia S, Stavely R, Palombo E, Apostolopoulos V, Sakkal S, Nurgali K (2018) Oxaliplatin-induced changes in microbiota, TLR4+ cells and enhanced HMGB1 expression in the murine colon. PLoS ONE 13(6):e0198359. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198359
Tsuda Y, Yoshimatsu Y, Aoki H, Nakamura K, Irie M, Fukuda K, Hosoe N, Takada N, Shirai K, Suzuki Y (2007) Clinical effectiveness of probiotics therapy (BIO-THREE) in patients with ulcerative colitis refractory to conventional therapy. Scand J Gastroenterol 42:1306–1311. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520701396091
Yoshimatsu Y, Yamada A, Furukawa R, Sono K, Osamura A, Nakamura K, Aoki H, Tsuda Y, Hosoe N, Takada N, Suzuki Y (2015) Effectiveness of probiotic therapy for the prevention of relapse in patients with inactive ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 21:5985–5994. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i19.5985
Feng P, Ye Z, Han H, Ling Z, Zhou T, Zhao S, Virk AK, Kakade A, Abomohra AE, El-Dalatony MM, Salama ES, Liu P, Li X (2020) Tibet plateau probiotic mitigates chromate toxicity in mice by alleviating oxidative stress in gut microbiota. Commun Biol 3:242. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-0968-3
Huber VC, Abdo Z, LeCureux J, LaVoy A, Eklund B, Ryan EP, Dean GA (2019) Impact of oral probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus vaccine strains on the immune response and gut microbiome of mice. PLoS ONE 14(12):e0225842. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225842
Liu M, Lu X, Khan A, Ling Z, Wang P, Tang Y, Liu P, Li X (2019) Reducing methylmercury accumulation in fish using Escherichia coli with surface-displayed methylmercury-binding peptides. J Hazard Mater 367:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.058
Schultz KK, Strait EL, Erickson BZ, Levy N (2012) Optimization of an antibiotic sensitivity assay for Mycoplasma hyosynoviae and susceptibility profiles of field isolates from 1997 to 2011. Vet Microbiol 158:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.02.002
Yu X, Shi J, Khan A, Yun H, Zhang P, Zhang P, Kakade A, Tian Y, Pei Y, Jiang Y, Huang H, Wu K, Li X (2020) Immobilized-microbial bioaugmentation protects aerobic denitrification from heavy metal shock in an activated-sludge reactor. Bioresour Technol 307:123185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123185
Yao Y, Lu Z, Zhu F, Min H, Bian C (2013) Successful bioaugmentation of an activated sludge reactor with Rhodococcus sp. YYL for efficient tetrahydrofuran degradation. J Hazard Mater 261:550–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.007
Sookoian S, Pirola CJ (2015) Liver enzymes, metabolomics and genome-wide association studies: from systems biology to the personalized medicine. World J Gastroenterol 21:711–725. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.711
Sorensen JC, Petersen AC, Timpani CA, Campelj DG, Cook J, Trewin AJ, Stojanovska V, Stewart M, Hayes A, Rybalka E (2017) BGP-15 protects against oxaliplatin-induced skeletal myopathy and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in mice. Front Pharmacol 8:137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00137
Stringer AM, Al-Dasooqi N, Bowen JM, Tan TH, Radzuan M, Logan RM, Mayo B, Keefe DM, Gibson RJ (2013) Biomarkers of chemotherapy-induced diarrhoea: a clinical study of intestinal microbiome alterations, inflammation and circulating matrix metalloproteinases. Support Care Cancer 21:1843–1852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-013-1741-7
Graham MA, Lockwood GF, Greenslade D, Brienza S, Bayssas M, Gamelin E (2000) Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin: a critical review. Clin Cancer Res 6:1205–1218
Mi H, Dong Y, Zhang B, Wang H, Peter CCK, Gao P, Fu H, Gao Y (2017) Bifidobacterium infantis ameliorates chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis via regulating T cell immunity in colorectal cancer rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 42:2330–2341. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480005
Zwielehner J, Lassl C, Hippe B, Pointner A, Switzeny OJ, Remely M, Kitzweger E, Ruckser R, Haslberger AG (2011) Changes in human fecal microbiota due to chemotherapy analyzed by TaqMan-PCR, 454 sequencing and PCR-DGGE fingerprinting. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28654. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028654
Alexander JL, Wilson ID, Teare J, Marchesi JR, Nicholson JK, Kinross JM (2017) Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:356–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.20
Fijlstra M, Ferdous M, Koning AM, Rings EH, Harmsen HJ, Tissing WJ (2015) Substantial decreases in the number and diversity of microbiota during chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucositis in a rat model. Support Care Cancer 23:1513–1522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-014-2487-6
Wexler HM (2007) Bacteroides: the good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin Microbiol Rev 20:593–621. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00008-07
Saint-Cyr MJ, Perrin-Guyomard A, Houee P, Rolland JG, Laurentie M (2013) Evaluation of an oral subchronic exposure of deoxynivalenol on the composition of human gut microbiota in a model of human microbiota-associated rats. PLoS ONE 8(11):e80578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080578
Precup G, Vodnar DC (2019) Gut Prevotella as a possible biomarker of diet and its eubiotic versus dysbiotic roles: a comprehensive literature review. Br J Nutr 122:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114519000680
Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson A, Akrami R, Lee YS, De Vadder F, Arora T, Hallen A, Martens E, Bjorck I, Backhed F (2015) Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella. Cell Metab 22:971–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.001
Koren O, Knights D, Gonzalez A, Waldron L, Segata N, Knight R, Huttenhower C, Ley RE (2013) A guide to enterotypes across the human body: meta-analysis of microbial community structures in human microbiome datasets. PLOS Comput Biol 9:e1002863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002863
Veloo ACM, Baas WH, Haan FJ, Coco J, Rossen JW (2019) Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Bacteroides spp. and Prevotella spp. Dutch clinical isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect 25:1156 e1159–1156 e1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2019.02.017
Forsgard RA, Marrachelli VG, Korpela K, Frias R, Collado MC, Korpela R, Monleon D, Spillmann T, Osterlund P (2017) Chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal toxicity is associated with changes in serum and urine metabolome and fecal microbiota in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80:317–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3364-z
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the central laboratory of School of Life Science, Lanzhou University, for providing various instruments and equipment.
Funding
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities grant (grant numbers: lzujbky-2017-br01), National Natural Science Foundation grant (grant numbers: 31870082), and Lanzhou science and technology plan project (grant numbers: 2019-4-40).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Wenzhen Yuan and Xingpeng Xiao; Methodology, Xingpeng Xiao; Software, Fuquan Xie, Jingyuan Wu; Investigation, Xingpeng Xiao, Xuan Yu, Pengya Feng, and Ze Ye; Resources, Peng Zhang, Wenzhen Yuan, and Xiangkai Li; Writing—original draft preparation, Xuan Yu; Writing—review and editing, Kamran Malik; Project administration, Xiangkai Li. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All the animal experiments were performed in accordance with the approval of the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of School of Life Sciences of Lanzhou University, China (201912021).
Consent to Participate
In the research that involves human subjects, all subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., Xiao, X., Yu, X. et al. Probiotic Therapy (BIO-THREE) Mitigates Intestinal Microbial Imbalance and Intestinal Damage Caused by Oxaliplatin. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 14, 60–71 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09795-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09795-3