Abstract
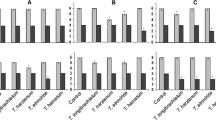
Damage by the shoot-tip borer Hypsipyla robusta (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) has limited the commercial cultivation of Chukrasia tabularis (Meliaceae) in many parts of the world. Recently, a number of C. tabularis families in Vietnam have shown field resistance to H. robusta. This study explores whether endophytic bacteria in C. tabularis can inhibit the development of H. robusta. Endophytic bacteria from resistant trees had strong repellent (73–97%) and antifeedant (74–84%) activity with H. robusta in laboratory trials. The most biologically active isolates were identified as Bacillus bombysepticus (4 isolates) and Bacillus velezensis (2 isolates) based on phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA, gyrB, pycA and rpoB. Fifteen days after releasing H. robusta larvae in a nursery trial, spray inoculation with bacterial solutions from resistant trees reduced shoot tip damage by over 60% compared with the control. Spray treatments with bacterial endophytes from susceptible trees were less effective. These findings have application to the future development of biological control of H. robusta, and the selection of resistant trees for breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, W. S. (1925). A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. Journal of Economic Entomology, 18(2), 265–267.
Adelskov J., Patel B. K. C. (2014). Draft genome sequence of Bacillus subtilis strain D7XPN1, isolated from commercial bioreactor-degrading food Waste. Genome Announcements, 2(5), e00989–00914. https://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/genomeA.00989-14
Bacon C. W., Palencia E. R., Hinton D. M. (2015). Abiotic and biotic plant stress-tolerant and beneficial secondary metabolites produced by endophytic Bacillus species. In Arora NK (ed) Plant Microbes Symbiosis: Applied Facets (pp. 163–177). Springer India. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2068-8_8
Balderas-Ruíz, K. A., Gómez-Guerrero, C. I., Trujillo-Roldán, M. A., Valdez-Cruz, N. A., Aranda-Ocampo, S., Juárez, A. M., Leyva, E., Galindo, E., & Serrano-Carreón, L. (2021). Bacillus velezensis 83 increases productivity and quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.): Pre and postharvest assessment. Current Research in Microbial Sciences, 2, 100076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100076
Borriss, R., Chen, X.-H., Rueckert, C., Blom, J., Becker, A., Baumgarth, B., Fan, B., Pukall, R., Schumann, P., Sproer, C., Junge, H., Vater, J., Puhler, A., & Klenk, H. P. (2011). New taxa-firmicutes and related organisms. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 61, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.023267-0
Cheng, T., Lin, P., Jin, S., Wu, Y., Fu, B., Long, R., Liu, D., Guo, Y., Peng, L., & Xia, Q. (2014). Complete genome sequence of Bacillus bombysepticus, a pathogen leading to Bombyx mori black chest septicemia. Genome Announcements, 2(3), e00312-00314. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00312-14
Chi, N. M., Tuan, D. X., & Thanh, L. B. (2019). Assessing the impacts of ecological factors on the potential infection of shoot borers of Chukrasia tabularis in the Northwest and North Central, Vietnam. Science and Technology Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development, 20, 67–73.
Chi, N. M., Quang, D. N., Hien, B. D., Dzung, P. N., Nhung, N. P., Nam, N. V., Thuy, P. T. T., Tuong, D. V., & Dell, B. (2021). Management of Hypsipyla robusta Moore (Pyralidae) damage in Chukrasia tabularis A. Juss (Meliaceae). International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 41(4), 2341–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00405-3
Chi, N. M., Anh, D. T. K., Hung, T. X., Nhung, N. P., Bao, H. Q., Toan, D., Nga, N. T. T., Thuy, P. T. T., Vo, D. N., Dell, B. (2021b). Soft rot disease caused by Dickeya fangzhongdai in epiphytic orchids in Vietnam. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661.2021.1998226
Chi, N. M. (2020). Investigation of screening and planting methods for high value and shoot tip borer tolerance of Chukrasia tabularis in Vietnam. Vietnamese Academy of Forest Sciences, 86p.
Couilloud, R., & Guiol, F. (1980). Elevage en laboratoire d’Hypsipyla robusta Moore (Lep. Pyralidae). Revue Bios Forest Des Tropiques, 194, 35–42.
Cunningham, S. A., Floyd, R. B., Griffiths, M. W., & Wylie, F. R. (2005). Patterns of host use by the shoot-borer Hypsipyla robusta (Pyralidae: Lepidoptera) comparing five Meliaceae tree species in Asia and Australia. Forest Ecology and Management, 205(1–3), 351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.10.042
da Costa, F. S. S., Praça, L. B., Gomes, A. C. M. M., dos Santos, R. C., Soares, C. M. S., & Monnerat, R. G. (2020). Bacillus thuringiensis effect on the vegetative development of cotton plants and the biocontrol of Spodoptera frugiperda. Agronomy, 10(12), 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121889
da Costa, F. S. S., de Castro, M. T., & Monnerat, R. (2021). The endophytism of Bacillus thuringiensis in cotton plants at acquisition and oviposition by Bemisia tabaci. Agricultural Research & Technology, 26(3), 556340. https://doi.org/10.19080/ARTOAJ.2021.26.556340
Daligault, H. E., Davenport, K. W., Minogue, T. D., Bishop-Lilly, K. A., Broomall, S. M., Bruce, D. C., Chain, P. S., Coyne, S. R., Frey, K. G., Gibbons, H. S., Jaissle, J., Koroleva, G. I., Ladner, J. T., Lo, C. C., Munk, C., Palacios, G. F., Redden, C. L., Rosenzweig, C. N., Scholz, M. B., & Johnson, S. L. (2014). Twenty whole-genome Bacillus sp. assemblies. Genome Announcements, 2(5), e00958-00914. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00958-14
de Castro, M. T., Montalvão, S. C. L., & Monnerat, R. G. (2019). Control of mahogany shoot borer, Hypsipyla grandella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), with Bacillus thuringiensis in a systemic way. Nativa: Pesquisas Agrárias e Ambientais, 7(4), 426–430. https://doi.org/10.31413/nativa.v7i4.6567
Domínguez-Arrizabalaga, M., Villanueva, M., Escriche, B., Ancín-Azpilicueta, C., & Caballero, P. (2020). Insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis proteins against coleopteran pests. Toxins, 12(7), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070430
Dunlap, C. A., Kim, S. J., Kwon, S. W., & Rooney, A. P. (2016). Bacillus velezensis is not a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Bacillus methylotrophicus, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum and ‘Bacillus oryzicola’ are later heterotypic synonyms of Bacillus velezensis based on phylogenomics. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66(3), 1212–1217. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000858
Eid, A. M., Fouda, A., Abdel-Rahman, M. A., Salem, S. S., Elsaied, A., Oelmüller, R., Hijri, M., Bhowmik, A., Elkelish, A., & Hassan, S.E.-D. (2021). Harnessing bacterial endophytes for promotion of plant growth and biotechnological applications: An overview. Plants, 10(5), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050935
Espinosa, Zaragoza S., Sánchez-Cruz, R., Sanzón-Gómez, D., Escobar-Sandoval, M. C., Yañez-Ocampo, G., Morales-Constantino, M. A., & Wong-Villarreal, A. (2021). Identification of endophytic bacteria of seeds from Cedrela odorata L. (Meliaceae) with biotechnological characteristics. Acta Biológica Colombiana, 26(2), 196–206. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v26n2.85325
Etminani, F., & Harighi, B. (2018). Isolation and identification of endophytic bacteria with plant growth promoting activity and biocontrol potential from wild pistachio trees. Plant Pathology Journal, 34(3), 208–217. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.OA.07.2017.0158
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: A justification. Evolution, 39, 783–791.
Ferreira, M. C., Vieira, Md. L. A., Zani, C. L., Alves, TMd. A., Junior, P. A. S., Murta, S. M. F., Romanha, A. J., Gil, L. H. V. G., Carvalho, AGd. O., Zilli, J. E., Vital, M. J. S., Rosa, C. A., & Rosa, L. H. (2015). Molecular phylogeny, diversity, symbiosis and discover of bioactive compounds of endophytic fungi associated with the medicinal Amazonian plant Carapa guianensis Aublet (Meliaceae). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 59, 36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.12.017
Gunn, B. V., Aken, K., & Pinyopusarerk, K. (2006). Provenance performance of Chukrasia in a five-year-old field trial in the Northern Territory, Australia. Australian Forestry, 69(2), 122–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/00049158.2006.10676238
Hartman, E. (1931). A flacherie disease of silkworms caused by Bacillus bombysepticus. Lignan Science Journal, 10, 279–289.
Harun-Or-Rashid, M., Khan, A., Hossain, M. T., & Chung, Y. R. (2017). Induction of systemic resistance against aphids by endophytic Bacillus velezensis YC7010 via expressing PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT4 in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 211. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00211
Harun-Or-Rashid, M., Kim, H. J., Yeom, S. I., Yu, H. A., Manir, M. M., Moon, S. S., Kang, Y. J., & Chung, Y. R. (2018). Bacillus velezensis YC7010 enhances plant defenses against brown planthopper through transcriptomic and metabolic changes in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01904
Huang, L., Cheng, T., Xu, P., Cheng, D., Fang, T., & Xia, Q. (2009). A genome-wide survey for host response of silkworm, Bombyx mori during pathogen Bacillus bombyseptieus infection. PLoS ONE, 4(12), e8098. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008098
Ivanova, N., Sorokin, A., Anderson, I., Galleron, N., Candelon, B., Kapatral, V., Bhattacharyya, A., Reznik, G., Mikhailova, N., Lapidus, A., Chu, L., Mazur, M., Goltsman, E., Larsen, N., D’Souza, M., Walunas, T., Grechkin, Y., Pusch, G., Haselkorn, R., … Kyrpides, N. (2003). Genome sequence of Bacillus cereus and comparative analysis with Bacillus anthracis. Nature, 423(6935), 87–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01582
Jeong, H., Jeong, D. E., Kim, S. H., Song, G. C., Park, S. Y., Ryu, C. M., Park, S. H., & Choia, S. K. (2012). Draft genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus siamensis KCTC 13613T. Journal of Bacteriology, 194(15), 4148. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00805-12
Jiménez, G., Urdiain, M., Cifuentes, A., López-López, A., Blanch, A. R., Tamames, J., Kämpfer, P., Kolstø, A. B., Ramón, D., Martínez, J. F., Codoñer, F. M., & Rosselló-Móra, R. (2013). Description of Bacillus toyonensis sp. nov., a novel species of the Bacillus cereus group, and pairwise genome comparisons of the species of the group by means of ANI calculations. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 36(6), 383–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2013.04.008
Johnson, S. L., Daligault, H. E., Davenport, K. W., Jaissle, J., Frey, K. G., Ladner, J. T., Broomall, S. M., Bishop-Lilly, K. A., Bruce, D. C., Gibbons, H. S., Coyne, S. R., Lo, C. C., Meincke, L., Munk, A. C., Koroleva, G. I., Rosenzweig, C. N., Palacios, G. F., Redden, C. L., Minogue, T. D., & Chain, P. S. (2015). Complete genome sequences for 35 biothreat assay-relevant Bacillus species. Genome Announcements, 3(2), e00151-e115. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00151-15
Kalinganire, A., & Pinyopusarerk, K. (2000). Chukrasia: Biology, cultivation and utilisation (Vol. 49). ACIAR publications Canberra.
Kharwar, R. N., Sharma, V. K., Mishra, A., Kumar, J., Singh, D. K., Verma, S. K., Gond, S. K., Kumar, A., Kaushik, N., Revuru, B., & Kusari, S. (2020). Harnessing the phytotherapeutic treasure troves of the ancient medicinal plant Azadirachta indica (Neem) and associated endophytic microorganisms. Planta Medica, 86(13/14), 906–940. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1107-9370
Ko, K. S., Kim, J. W., Man, K. J., Kim, W., Chung, S. I., Kim, I. J., & Kook, Y. H. (2004). Population structure of the Bacillus cereus group as determined by sequence analysis of six housekeeping genes and the plcR gene. Infection and Immunity, 72(9), 5253–5261. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.72.9.5253-5261.2004
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7), 1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Küster, E., & Williams, S. T. (1964). Selection of media for isolation of Streptomycetes. Nature, 202(4935), 928–929. https://doi.org/10.1038/202928a0
Li, H., Soares, M. A., Torres, M. S., Bergen, M., & White, J. F. (2015). Endophytic bacterium, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, enhances ornamental hosta resistance to diseases and insect pests. Journal of Plant Interactions, 10(1), 224–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2015.1056261
Liang, L., Fu, Y., Deng, S., Wu, Y., & Gao, M. (2022). Genomic, antimicrobial, and aphicidal traits of Bacillus velezensis ATR2, and its biocontrol potential against ginger rhizome rot disease caused by Bacillus pumilus. Microorganisms, 10(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010063
Liu, Y., Lai, Q., Dong, C., Sun, F., Wang, L., Li, G., & Shao, Z. (2013). Phylogenetic diversity of the Bacillus pumilus group and the marine ecotype revealed by multilocus sequence analysis. PLoS ONE, 8(11), e80097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080097
Liu, Y., Du, J., Lai, Q., Zeng, R., Ye, D., Xu, J., & Shao, Z. (2017). Proposal of nine novel species of the Bacillus cereus group. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 67(8), 2499–2508. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001821
Liu, X., Wang, L., Han, M., Xue, Q. H., Zhang, G. S., Gao, J., & Sun, X. (2020). Bacillus fungorum sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from spent mushroom substrate. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 70(3), 1457–1462. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003673
Myo, E. M., Liu, B., Ma, J., Shi, L., Jiang, M., Zhang, K., & Ge, B. (2019). Evaluation of Bacillus velezensis NKG-2 for bio-control activities against fungal diseases and potential plant growth promotion. Biological Control, 134, 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.03.017
Ngo, V. A., Wang, S. L., Nguyen, V. B., Doan, C. T., Tran, T. N., Tran, D. M., Tran, T. D., & Nguyen, A. D. (2020). Phytophthora antagonism of endophytic bacteria isolated from roots of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.). Agronomy, 10(2), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10020286
Pinyopusarerk, K., Kalinganire, A. (2003). Domestication of Chukrasia. ACIAR Monograph 98, Aciar Publishing: 45p.
Podolich, O., Ardanov, P., Zaets, I., Pirttilä, A. M., & Kozyrovska, N. (2015). Reviving of the endophytic bacterial community as a putative mechanism of plant resistance. Plant and Soil, 388(1), 367–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2235-1
Rabbee, M. F., Ali, M. S., Choi, J., Hwang, B. S., Jeong, S. C., & Baek, K. H. (2019). Bacillus velezensis: A valuable member of bioactive molecules within plant microbiomes. Molecules, 24(6), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061046
Ruiz de Escudero, I., Banyuls, N., Bel, Y., Maeztu, M., Escriche, B., Muñoz, D., Caballero, P., & Ferré, J. (2014). A screening of five Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3A proteins for their activity against lepidopteran pests. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 117, 51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2014.01.006
Ruiz-García, C., Béjar, V., Martínez-Checa, F., Llamas, I., & Quesada, E. (2005). Bacillus velezensis sp. nov., a surfactant-producing bacterium isolated from the river Vélez in Málaga, southern Spain. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 55(1), 191–195. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63310-0
Saikkonen, K., Gundel, P. E., & Helander, M. (2013). Chemical ecology mediated by fungal endophytes in grasses. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 39(7), 962–968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-013-0310-3
Savi, D. C., Aluizio, R., Galli-Terasawa, L., Kava, V., & Glienke, C. (2016). 16S-gyrB-rpoB multilocus sequence analysis for species identification in the genus Microbispora. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 109(6), 801–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0680-y
Schardl, C. L., Young, C. A., Faulkner, J. R., Florea, S., & Pan, J. (2012). Chemotypic diversity of epichloae, fungal symbionts of grasses. Fungal Ecology, 5(3), 331–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2014.01.006
Shifa, H., Gopalakrishnan, C., & Velazhahan, R. (2018). Management of late leaf spot (Phaeoisariopsis personata) and root rot (Macrophomina phaseolina) diseases of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, systemic acquired resistance inducers and plant extracts. Phytoparasitica, 46(1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-018-0644-z
Srivatsan, A., Han, Y., Peng, J., Tehranchi, A. K., Gibbs, R., Wang, J. D., & Chen, R. (2008). High-precision, whole-genome sequencing of laboratory strains facilitates genetic studies. PLoS Genetics, 4(8), e1000139. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000139
Sullivan, T. J., Rodstrom, J., Vandop, J., Librizzi, J., Graham, C., Schardl, C. L., & Bultman, T. L. (2007). Symbiont-mediated changes in Lolium arundinaceum inducible defenses: Evidence from changes in gene expression and leaf composition. New Phytologist, 176(3), 673–679. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02201.x
Talukder, F. A., & Howse, P. E. (1994). Laboratory evaluation of toxic and repellent properties of the pithraj tree, Aphanamixis polystachya Wall & Parker, against Sitophilus oryzae (L.). International Journal of Pest Management, 40(3), 274–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670879409371897
Thanh, V. N., Duc, Hien D., Yaguchi, T., Sampaio, J. P., & Lachance, M.-A. (2018). Moniliella sojae sp. nov., a species of black yeasts isolated from Vietnamese soy paste (tuong), and reassignment of Moniliella suaveolens strains to Moniliella pyrgileucina sp. nov., Moniliella casei sp. nov. and Moniliella macrospora emend. comb. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 68(5), 1806–1814. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002690
Thu, P. Q., Quang, D. N., Chi, N. M., Hung, T. X., Binh, L. V., & Dell, B. (2021). New and emerging insect pest and disease threats to forest plantations in Vietnam. Forests, 12(10), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12101301
Thyagaraja, N. E., Rani, A. T. (2019). Techniques for determining the repellent and antifeedant activity to phytophagous insects. In: Experimental techniques in host-plant resistance (pp. 183–186). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2652-3_20
Tran, D. M., Huynh, T. U., Nguyen, T. H., Do, O. T., Vinh, N. Q., & Nguyen, D. A. (2022). Molecular analysis of genes involved in chitin degradation from the chitinolytic bacterium Bacillus velezensis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 115(2), 215–231. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-998405/v1
Untergasser, A., Cutcutache, I., Koressaar, T., Ye, J., Faircloth, B. C., Remm, M., & Rozen, S. G. (2012). Primer3-new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(15), e115–e115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596
Wang, L. T., Lee, F. L., Tai, C. J., & Kuo, H. P. (2008). Bacillus velezensis is a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58(3), 671–675. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65191-0
Wu, W., Chen, W., Liu, S., Wu, J., Zhu, Y., Qin, L., & Zhu, B. (2021). Beneficial relationships between endophytic bacteria and medicinal plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 758. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.646146
Yi, H., Chun, J., & Cha, C. J. (2014). Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the three subspecies of Bacillus subtilis. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 37(2), 95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2013.09.006
Zwick, M. E., Joseph, S. J., Didelot, X., Chen, P. E., Bishop-Lilly, K. A., Stewart, A. C., Willner, K., Nolan, N., Lentz, S., & Thomason, M. K. (2012). Genomic characterization of the Bacillus cereus sensu lato species: Backdrop to the evolution of Bacillus anthracis. Genome Research, 22(8), 1512–1524. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.134437.111
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Agricultural and Rural Development of Vietnam under decree number 3710/QD-BNN-KHCN dated 15/9/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of the authors, there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tra, T.T.L., Chi, N.M., Anh, D.T.K. et al. Bacterial endophytes from Chukrasia tabularis can antagonize Hypsipyla robusta larvae. Phytoparasitica 50, 655–668 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-022-01001-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-022-01001-6