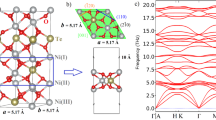
Abstract
Materials featuring topological energy bands and nontrivial surface states hold significant promise in unlocking unprecedented opportunities for innovating electrocatalytic mechanism. However, it remains a challenge to realize superior topological catalysts which can carry both high catalytic activity and excellent catalytic stability. Here, we propose that a family of Ni-based binary materials hosting fantasying topological conjunct-nodal-point state and a large nontrivial energy window (NEWD) represents an ideal choice for such superior topological catalysts in hydrogen evolution reaction. The presence of conjunct-nodal-points ensures long Fermi arcs on the surface, thereby enabling an extremely high catalytic activity. The NEWD plays a crucial role in stabilizing the high catalytic activity against external perturbations, such as strain and electron/hole injection. The roles for conjunct-nodal-points and NEWD are substantiated by the observable weakening of catalytic performance during topological phase transitions, which result in the removal of the conjunct-nodal-points, NEWD and their corresponding long Fermi arcs. Our work unveils a hidden mechanism and opens a feasible route for developing superior quantum catalysts from novel topology point of view.
Graphical abstract

摘要
具有拓扑能带和非平庸表面态的材料,在创新电催化机制方面具有重要潜力。然而,当前实现既具有高催化活性又具有优异催化稳定性的超级拓扑催化剂仍是一个挑战。本文基于一族镍基二元材料体系,提出一类具有奇异共轭拓扑结点和大非平庸能量窗口的拓扑半金属,可作为析氢反应中这种超级拓扑催化剂的理想选择。共轭节点的存在确保材料表面上存在着长费米弧,从而实现了极高的催化活性。非平庸能量窗口在稳定高催化活性方面发挥关键作用,可以抵抗来自外部扰动(如应变和电子/空穴注入)的影响。共轭节点和非平庸能量窗口的作用通过观察在拓扑相变期间催化性能的明显减弱得以证实(拓扑相变导致共轭节点、非平庸能量窗口及其相应的长费米弧被移除)。本工作揭示了一种隐藏的催化机制,并从新的拓扑视角打开了开发优越量子催化剂的可行途径。.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun JY, Tian F, Yu F, Yang Z, Yu B, Chen S, Ren ZF, Zhou HQ. Robust hydrogen-evolving electrocatalyst from heterogeneous molybdenum disulfide-based catalyst. ACS Catal. 2020;10(2):1511. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03030.
Van Geem K, Galvita V, Marin G. Making chemicals with electricity. Science. 2019;364(6442):734. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax5179.
Wang XX, Swihart MT, Wu G. Achievements, challenges and perspectives on cathode catalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells for transportation. Nat Catal. 2019;2(7):578. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0304-9.
Abbasi R, Setzler B, Lin SS, Wang JH, Zhao Y, Xu H, Pivovar B, Tian BY, Chen X, Wu G, Yan YS. A roadmap to low-cost hydrogen with hydroxide exchange membrane electrolyzers. Adv Mater. 2019;31(31):1805876. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201805876.
Shi YS, Zhang B. Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45(6):1529. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CS00434A.
Zhu J, Hu LS, Zhao PX, Lee LYS, Wong KY. Recent advances in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using nanoparticles. Chem Rev. 2020;120(2):851. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00248.
Hao R, Feng QL, Wang XJ, Zhang YC, Li KS. Morphology-controlled growth of large-area PtSe2 films for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Rare Met. 2022;41(4):1314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01877-z.
Zhao X, Zheng XR, Lu Q, Li Y, Xiao FP, Tang B, Wang SX, Yu DYW, Rogach AL. Electrocatalytic enhancement mechanism of cobalt single atoms anchored on different MXene substrates. EcoMat. 2023;5(2):e12293. https://doi.org/10.1002/eom2.12293.
Yuan FH, Mohammadi MR, Ma LL, Cui ZD, Zhu SL, Li ZY, Wu SL, Jiang H, Liang YQ. Electrodeposition of self-supported NiMo amorphous coating as an efficient and stable catalyst for hydrogen evolution reactio. Rare Met. 2022;41(8):2624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-01967-6.
Sajjad S, Wang C, Deng CW, Ji F, Ali T, Shezad B, Ji HQ, Yan CL. Unravelling critical role of metal cation engineering in boosting hydrogen evolution reaction activity of molybdenum diselenide. Rare Met. 2022;41(6):1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01948-1.
Feng YG, Zhao ZL, Li F, Bu LZ, Shao Q, Li LG, Wu JB, Zhu X, Lu G, Huang XQ. Highly surface-distorted Pt superstructures for multifunctional electrocatalysis. Nano Lett. 2021;21(12):5075. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00902.
Ping XF, Liang D, Wu YY, Yan XX, Zhou SX, Hu DK, Pan XQ, Lu PF, Jiao LY. Activating a two-dimensional PtSe2 basal plane for the hydrogen evolution reaction through the simultaneous generation of atomic vacancies and Pt clusters. Nano Lett. 2021;21(9):3857. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00380.
Kibsgaard J, Chorkendorff I. Considerations for the scaling-up of water splitting catalysts. Nat Energy. 2019;4(6):430. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0407-1.
Wang J, Xu F, Jin HY, Chen YQ, Wang Y. Non-noble metal- based carbon composites in hydrogen evolution reaction: fundamentals to applications. Adv Mater. 2017;29(14):1605838. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201605838.
Fan HS, Yu H, Zhang YF, Zheng Y, Luo YB, Dai ZF, Li B, Zong Y, Yan QY. Fe-doped Ni3C nanodots in N-doped carbon nanosheets for efficient hydrogen-evolution and oxygen-evolution electrocatalysis. AngewChem Int Ed. 2017;56(41):12566. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201706610.
Chhetria M, Sultana S, Raoa CNR. Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reactionactivity comparable to platinum exhibited by the Ni/Ni(OH)2/graphite electrode. PNAS. 2017;114(34):8986. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1710443114.
Escalera-Lopez D, Niu YB, Yin JL, Cooke K, Rees NV, Palmer RE. Enhancement of the hydrogen evolution reaction from Ni-MoS2 hybrid nanoclusters. ACS Catal. 2016;6(9):6008. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b01274.
Adán C, Pérez-Alonso FJ, Rojas S, Peña MA, Fierro JLG. Enhancement of electrocatalytic activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction by boron-modified nickel nanoparticles. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2012;37(20):14984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.07.094.
Qiao BT, Wang AQ, Yang XF, Allard LF, Jiang Z, Cui YT, Liu JY, Li J, Zhang T. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nat Chem. 2011;3(8):634. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1095.
Zhu CZ, Fu SF, Shi QR, Du D, Lin YH. Single-atom electrocatalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2017;56(45):13944. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201703864.
Guo JJ, Huo JJ, Liu Y, Wu WJ, Wang Y, Wu MH, Liu H, Wang GX. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon supported nonprecious metal single-atom electrocatalysts: from synthesis to application. Small Methods. 2019;3(9):1900159. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.201900159.
Peng Y, Lu BZ, Chen SW. Carbon-supported single atom catalysts for electrochemical energy conversion and storage. Adv Mater. 2018;30(48):1801995. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201801995.
Sun YG, Alimohammadi F, Zhang DT, Guo GS. Enabling colloidal synthesis of edge-oriented MoS2 with expanded interlayer spacing for enhanced HER catalysis. Nano Lett. 2017;17(3):1963. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05346.
Zhang B, Liu J, Wang JS, Ruan YJ, Ji X, Xu K, Chen C, Wan HZ, Miao L, Jiang JJ. Interface engineering: the Ni(OH)2/MoS2 Heterostructure for highly efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy. 2017;37:74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.05.011.
Fang ZW, Peng LL, Qian YM, Zhang X, Xie YJ, Cha JJ, Yu GH. Dual tuning of Ni−Co−A (A = P, Se, O) nanosheets by anion substitution and holey engineering for efficient hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(15):5241. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b01548.
Li G, Felser C. Heterogeneous catalysis at the surface of topological materials. Appl Phys Lett. 2020;116(7):070501. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5143800.
Kong DH, Cui Y. Opportunities in chemistry and materials science for topological insulators and their nanostructures. Nat Chem. 2011;3(11):845. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1171.
Xiao JP, Kou LZ, Yam CY, Frauenheim T, Yan BH. Toward Rational design of catalysts supported on a topological insulator substrate. ACS Catal. 2015;5(12):7063. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b01966.
Chen H, Zhu WG, Xiao D, Zhang ZY. CO oxidation facilitated by robust surface states on Au-covered topological insulators. Phys Rev Lett. 2011;107(5):056804. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.056804.
Meinzer N. Catalysis: topology does the water splits. Nat Rev Mater. 2017;2(4):17021. https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2017.21.
Xie RK, Zhang T, Weng HM, Chai GL. Progress, advantages, and challenges of topological material catalysts. Small Sci. 2022;2(4):2100106. https://doi.org/10.1002/smsc.202100106.
Li JX, Ma H, Xie Q, Feng SB, Ullah S, Li RH, Dong JH, Li DZ, Li YY, Chen XQ. Topological quantum catalyst: dirac nodal line states and a potential electrocatalyst of hydrogen evolution in the TiSi family. Science China Materials. 2018;23:61. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1704.07043.
Wang LR, Zhang XM, Meng WZ, Liu Y, Dai XF, Liu GD. A topological quantum catalyst: the case of two-dimensional traversing nodal line states associated with high catalytic performance for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9(39):22453. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA06553J.
Rajamathi CR, Gupta U, Kumar N, Yang H, Sun Y, Süß V, Shekhar C, Schmidt M, Blumtritt H, Werner P, Yan BH, Parkin S, Felser C, Rao CNR. Weyl semimetals as hydrogen evolution catalysts. Adv Mater. 2017;29(19):1606202. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201606202.
Lu DL, Ren XH, Ren L, Xue WM, Liu SQ, Liu YD, Chen Q, Qi X, Zhong JX. Direct vapor deposition growth of 1T’ MoTe2 on Carbon cloth for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2020;3(4):3212. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b01589.
Lei B, Zhang YY, Du SX. Prediction of structured void-containing 1T-PtTe2 monolayer with potential catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chin Phys B. 2020;29(5):058104. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab8203.
Kong XP, Jiang T, Gao JJ, Shi XB, Shao J, Yuan YH, Qiu HJ, Zhao WW. Development of a Ni-doped VAl3 topological semimetal with a significantly enhanced HER catalytic performance. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021;12(15):3740. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c00238.
Liu W, Zhang XM, Meng WZ, Liu Y, Dai XF, Liu GD. Theoretical realization of hybrid Weyl state and associated high catalytic performance for hydrogen evolution in NiSi. iScience. 2022;25(1):103543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103543.
Yang Q, Li GW, Manna K, Fan FR, Felser C, Sun Y. Topological engineering of Pt-group-metal-based chiral crystals toward high-efficiency hydrogen evolution catalysts. Adv Mater. 2020;32(14):1908518. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201908518.
Li GW, Fu CG, Shi WJ, Jiao L, Wu JQ, Yang Q, Saha R, Kamminga ME, Srivastava AK, Liu E, Yazdani AN, Zhang J, Blake GR, Liu XJ, Fahlman M, Wirth S, Auffermann G, Gooth J, Parkin S, Madhavan V, Feng XL, Sun Y, Felser C. Dirac nodal arc semimetal PtSn4: an ideal platform for understanding surface properties and catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;131(37):13241. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201906109.
Jiang MC, Guo GY, Hirayama M, Yu TH, Nomoto T, Arita R. Efficient hydrogen evolution reaction due to topological polarization. Phys Rev B. 2022;106(16):165120. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.106.165120.
Meng WZ, Zhang XM, Liu Y, Dai X, Liu GD, Gu YT, Kenny EP, Kou LZ. Multifold fermions and fermi arcs boosted catalysis in nanoporous electride 12CaO·7Al2O3. Adv Sci. 2023;10(6):2205940. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202205940.
Zhang XM, Meng WZ, Liu Y, Dai XF, Liu GD, Kou LZ. Magnetic electrides: high-throughput material screening, intriguing properties, and applications. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145(9):5523. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c00284.
Zhang XM, Wang LR, Li MH, Meng WZ, Liu Y, Dai XF, Liu GD, Gu YT, Liu JX, Kou LZ. Topological surface state: universal catalytic descriptor in topological catalysis. Mater Today. 2023;67:23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2023.05.002.
Tomoo S, Yoshinao M, Seiji M. Evaluation of the data for the plastic behaviour of Ni3(A1, X) single crystals. MSEA. 1991;146(1–2):245260. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(91)90281-Q.
Wei LF, Zhao ZL, Gao JJ, Cui K, Chen S, Guo JY, Liu L. Lamellar Ni3Si microchannels and Ni3Si micropore arrays in Ni–Ni3Si hypereutectic alloys. J Electrochem Soc. 2018;165(2):E45. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0941802jes.
Zhou GF, Bakker H. Atomic disorder and phase transformation in L12-structure Ni3Si by ball milling. Acta Metall Mater. 1994;42(9):903972. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(94)90397-2.
Weng HM, Fang C, Fang Z, Dai X. Topological semimetals with triply degenerate nodal points in θ-phase tantalum nitride. Phys Rev B. 2016;93(24):241202. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.93.241202.
Zhu ZM, Winkler G, Wu QS, Li J, Soluyanov AA. Triple point topologicametals. Phy Rev X. 2016;6(3):031003. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.6.031003.
Zhang XM, Yu ZM, Sheng XL, Yang HY, Yang SY. Coexistence of four-band nodal rings and triply degenerate nodal points in centrosymmetric metal diborides. Phys Rev B. 2017;95(23):235116. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.95.235116.
Hinnemann B, Moses PG, Bonde J, Jørgensen KP, Nielsen JH, Horch S, Chorkendorff I, Nørskov JK. Biomimetic hydrogen evolution: MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst for hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(15):5308. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0504690.
Skúlason E, Karlberg GS, Rossmeisl J, Bligaard T, Greeley J, Jónsson H, Nørskov JK. Density functional theory calculations for the hydrogen evolution reaction in an electrochemical double layer on the Pt (111) electrode. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2007;9(25):3241. https://doi.org/10.1039/B700099E.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12274112). The work is also funded by the Overseas Scientists Sponsorship Program of Hebei Province (No. C20210330), the State Key Laboratory of Reliability and Intelligence of Electrical Equipment of Hebei University of Technology (No. EERI_PI2020009), and S&T Program of Hebei (No. 225676163GH)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Wang, LR., Liu, W. et al. Rational design of superior catalysts from topological semimetals with nontrivial energy window. Rare Met. 43, 1956–1964 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02574-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02574-9