Abstract
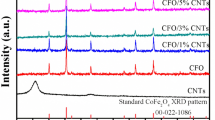
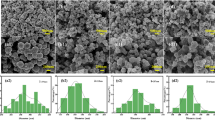
Developing high-performance electromagnetic absorbing materials remains a challenge. In this work, Gd-Co ferrite@carbon core–shell structure composites were synthesized by a two-step hydrothermal method. The effects of rare earth Gd doping amount on the microstructure and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of cobalt ferrite@carbon composites were mainly studied. The results show that an appropriate amount of Gd doping can refine the crystal grain size of cobalt ferrite@carbon composites. However, when the doping amount of Gd exceeds the solid solubility threshold, the secondary phase GdFeO3 will be generated and the grain size will increase. When the doping amount of Gd is x = 0.04, the reflection loss (RL) of the CoFe1.96Gd0.04O4@C composites reaches the minimum value of − 9.26 dB at the absorption layer thickness of 2.0 mm and a frequency of 13.67 GHz, and the effective absorption band (EAB) is 5.01 GHz (10.95–15.96 GHz). Compared with the CoFe2O4@C composites, the RL of the CoFe1.96Gd0.04O4@C composites is increased by 79.35%, and the EAB is broadened by 3.51%. Gd ions enhance the dielectric loss through the grain size effect, and the increase of magnetocrystalline anisotropy enhances the magnetic loss. The CoFe1.96Gd0.04O4@C composites have excellent impedance matching, which relies on the strong magnetic loss of ferrite, the interface polarization, and dipole polarization formed by the carbon shell to attenuate electromagnetic waves.
Graphical abstract

摘要
开发高性能电磁波吸收材料仍然是一项挑战。在本工作中,通过两步水热法合成了Gd-Co铁氧体@碳核壳结构复合材料。重点研究了稀土离子Gd掺杂量对Gd-Co铁氧体@碳复合材料微观结构和电磁波吸收性能的影响。结果表明,适量的Gd离子掺杂可以细化Gd-Co铁氧体@碳复合材料的晶粒尺寸。但是,当Gd离子掺杂量超过固溶度阈值时,会产生二次相GdFeO3,并增大晶粒尺寸。当Gd离子的掺杂量x=0.04时,CoFe1.96Gd0.04O4@C复合材料的反射损耗值在吸收层厚度为2.0 mm,频率为13.67 GHz处达到最小值为‒39.26 dB,有效吸收频带为5.01 GHz(10.95‒15.96 GHz)。相比于CoFe2O4@C复合材料,CoFe1.96Gd0.04O4@C复合材料的反射损耗提升了79.35%,有效吸收频带拓宽了3.51%。Gd离子通过晶粒尺寸效应强化了介电损耗,磁晶各向异性的增大强化了磁损耗。CoFe1.96Gd0.04O4@C复合材料具有优异的阻抗匹配,依靠铁氧体强烈的磁损耗和碳壳形成的界面极化和偶极极化衰减电磁波。







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong Y, Zhang TL, Wang H, Liu X, Jiang CB. Chemical synthesis and characterization of SmCo5/Co magnetic nanocomposite particles. Rare Met. 2021;40(5):1224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01640-w.
Li HJ, Wu Q, Yue M, Li YQ, Zhu RC, Liang JM, Zhang JX. Structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline dysprosium powders. Rare Met. 2020;39(1):28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-01201-2.
Chen HW, Weng XY, Ma ZJ, Guan ZH. Microwave absorption properties of Mn-Zn ferrite with different Pr3+ doping content. Chin J Rare Met. 2020;44(12):1339.
Wang F, Gu WH, Chen JB, Wu Y, Zhou M, Tang SL, Cao XZ, Zhang P, Ji GB. The point defect and electronic structure of K doped LaCo0.9Fe0.1O3 perovskite with enhanced microwave absorbing ability. Nano Res. 2022;15(4):3720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3955-1.
Wang F, Gu WH, Chen JB, Huang QQ, Han MY, Wang GH, Ji GB. Improved electromagnetic dissipation of Fe doping LaCoO3 toward broadband microwave absorption. J Mater Sci Technol. 2022;105:92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.058.
Gu BX. Magnetic properties and magneto-optical effect of Co0.5Fe2.5O4 nanostructured films. Appl Phys Lett. 2003;82(21):3707. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1573357.
Khanna L, Verma NK, Tripathi SK. Burgeoning tool of biomedical applications-superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd. 2018;752:332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.093.
Giri AK, Kirkpatrick EM, Moongkhamklang P, Majetich SA. Photomagnetism and structure in cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett. 2002;80(13):2341. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1464661.
Lu MM, Cao MS, Chen YH, Cao WQ, Liu J, Shi HL, Zhang DQ, Wang WZ, Yuan J. Multiscale assembly of grape-like ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: a smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2015;7(34):19408. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b05595.
Qiang R, Du YC, Zhao HT, Wang Y, Tian CH, Li ZG, Han XJ, Xu P. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3(25):13426. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA01457C.
Wang GZ, Gao Z, Tang SW, Chen CQ, Duan FF, Zhao SC, Lin SW, Feng YH, Zhou L, Qin Y. Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. J Acs Nano. 2012;6(12):11009. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn304630h.
Li YJ, Yuan MW, Liu HH, Sun GB. In situ synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanocrystals decorated in mesoporous carbon nanofibers with enhanced electromagnetic performance. J Alloy Compd. 2020;826:154147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154147.
Rostami M, Ara MHM. The dielectric, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Cu-substituted Mg-Ni spinel ferrite-MWCNT nanocomposites. Ceram Int. 2019;45(6):7606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.056.
Duan HZ, Zhou FL, Cheng X, Chen GH, Li QL. Preparation of hollow microspheres of Ce3+ doped NiCo ferrite with high microwave absorbing performance. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;427:467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.069.
Eltabey MM, Agami WR, Mohse HT. Improvement of the magnetic properties for Mn-Ni-Zn ferrites by rare earth Nd3+ ion substitution. J Adv Res. 2014;5(5):601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.08.005.
Lee JH, Huh YM, Jun YW, Seo JW, Jang JT, Song HT, Kim SJ, Cho EJ, Yoon HG, Suh JS, Cheon JW. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat Med. 2007;13:95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1467.
Kogan MJ, Bastus NG, Amigo R, Bosch DG, Araya E, Turiel A, Labarta A, Giralt E, Puntes VF. Nanoparticle-mediated local and remote manipulation of protein aggregation. Nano Lett. 2006;6(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0516862.
Gadkari AB, Shinde TJ, Vasambekar PN. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties of La3+ added Mg-Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. J Alloy Compd. 2011;509:966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.08.155.
Yuan HL, Wang YQ, Zhou SM, Liu LS, Chen XL, Lou SY, Yuan RJ, Hao YM, Li N. Low-temperature preparation of superparamagnetic CoFe2O4 microspheres with high saturation magnetization. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2010;5:1817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9718-7.
Bennet J, Tholkappiyan R, Vishista K, Jaya NV, Hamed F. Attestation in self-propagating combustion approach of spinel AFe2O4 (A=Co, Mg and Mn) complexes bearing mixed oxidation states: magnetostructural properties. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;383:113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.04.177.
Li MY, Mao YC, Yang H, Li W, Wang CS, Liu P, Tong YX. Controllable electrochemical synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanostructures on FTO substrate and their magnetic properties. New J Chem. 2013;37(10):3116. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nj00479a.
Shu RW, Li WJ, Zhou X, Tian DD, Zhang GY, Gan Y, Shi JJ, He J. Facile preparation and microwave absorption properties of RGO/MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 hybrid nanocomposites. J Alloy Compd. 2018;743:163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.016.
Yin PF, Deng Y, Zhang LM, Wu WJ, Wang J, Feng X, Sun XY. One-step hydrothermal synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4/graphene composites in low frequency band. Ceram Int. 2018;44(17):20896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.08.096.
Peng JH, Peng ZW, Zhu ZP, Augustine R, Mahmoud MM, Tang HM, Rao MJ, Zhang YB, Li GH, Jiang T. Achieving ultra-high electromagnetic wave absorption by anchoring Co0.33Ni0.33Mn0.33Fe2O4 nanoparticles on graphene sheets using microwave-assisted polyol method. Ceram Int. 2018;44:21015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.08.137.
Jaiswal R, Agarwal K, Pratap V, Soni A, Kumar S, Mukhopadhyay K, Prasad NE. Microwave–assisted preparation of magnetic ternary core–shell nanofiller (CoFe2O4/rGO/SiO2) and their epoxy nanocomposite for microwave absorption properties. Mat Sci Eng B-Adv. 2020;262:114711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114711.
Cui J, Zhou ZH, Jia MY, Chen X, Shi C, Zhao N, Guo XX. Solid polymer electrolytes with flexible framework of SiO2 nanofibers for highly safe solid lithium batteries. Polymers. 2020;12(6):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061324.
Park TJ, Papaefthymiou GC, Viescas AJ, Moodenbaugh AR, Wong SS. Size-dependent magnetic properties of single-crystalline multiferroic BiFeO3 nano particles. Nano Lett. 2007;7(3):766. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl063039w.
Lorgu AI, Maxim F, Matei C, Ferreira LP, Ferreira P, Cruz MM, Berger D. Fast synthesis of rare-earth (Pr3+, Sm3+, Eu3+ and Gd3+) doped bismuth ferrite powders with enhanced magnetic Properties. J Alloy Compd. 2015;629:62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.12.108.
Miles PA, Westphal WB, Hippel AV. Dielectric spectroscopy of ferromagnetic semiconductors. Rev Mod Phys. 1957;29:279. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.29.279.
Murugesan C, Chandrasekaran G. Impact of Gd3+ substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015;5(90):73714. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra14351a.
Min F, Jiao QZ, Zhao Y, Li HS. Vapor diffusion synthesis of CoFe2O4 hollow sphere/graphene composites as absorbing materials. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(3):735. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14050D.
Liu XF, Hao CC, Jiang H, Zeng M, Yu RH. Hierarchical NiCo2O4/Co3O4/NiO porous composite: a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber with tunable absorbing performance. J Mater Chem C. 2017;5(15):3770. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC05167G.
Micheli D, Apollo C, Pastore R, Marchetti M. X-band microwave characterization of carbon-based nanocomposite material, absorption capability comparison and RAS design simulation. Compos Sci Technol. 2010;70:400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.11.015.
Cao MS, Song WL, Hou ZL, Wen B, Yuan J. The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon. 2010;48:788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.10.028.
Deng LW, Ding L, Zhou KS, Huang SX, Hu ZW, Yang BC. Electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of W-type hexagonal ferrites doped with La3+. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323:1895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.02.034.
Du YC, Liu WW, Qiang R, Wang Y, Han XJ, Ma J, Xu P. Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2014;6:12997. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502910d.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51372108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Ma, ZJ., Liu, FL. et al. Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Gd-Co ferrite@carbon core–shell structure composites. Rare Met. 42, 254–262 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02123-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02123-w