Abstract
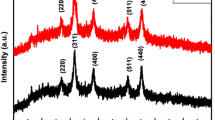
Zn2SnO4 plates, particles and spheres are successfully prepared via a facile synthesis way by carefully adjusting the solvothermal conditions, which are further applied as photoanodes in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) to explore the relationships between the photoanode nanostructure and the photovoltaic performances. As a result, the DSSCs based on Zn2SnO4 spheres photoanode showcased the best power conversion efficiency (PCE, 4.85%), compared to Zn2SnO4 plates (3.80%) and particles (4.13%). It is found that Zn2SnO4 spheres exhibit the highest light-scattering abilities, as evidenced by ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) diffuse reflectance spectra. Additionally, investigations on dynamic electron transport and recombination properties via intensity-modulated photovoltage/photocurrent spectroscopy (IMVS/IMPS), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements demonstrate that the Zn2SnO4 spheres-based DSSCs possess the fastest electron transport rate, the longest electron lifetime, the highest electron collection efficiency (ηcc), and the largest charge recombination resistance, compared with the Zn2SnO4 plates and particles, all of which are highly beneficial for the powder conversion efficiency enhancements.
Graphical abstract

摘要
采用简单的溶剂热方法合成Zn2SnO4材料, 通过调节实验条件, 成功制备出Zn2SnO4盘、颗粒和分等级球纳米材料, 进一步将其作为光阳极材料应用到染料敏化太阳能电池中, 研究光阳极材料结构与电池性能之间的关系。其中, 基于Zn2SnO4球作为光阳极材料时, 电池获得最高的光电转换效率(4.85%), 高于Zn2SnO4盘(3.80%)和Zn2SnO4颗粒(4.13%), 研究发现, 主要归因于Zn2SnO4球光阳极材料具有最好的光散射能力。进一步 用强度调制光电流、强度调制光电压技术和电化学阻抗技术来研究不同Zn2SnO4材料影响光电转换效率的机理。Zn2SnO4球与Zn2SnO4盘、颗粒材料相比, 具有最快的电子传输速率、最长的电子传输寿命、最高的电子收集效率和最大的复合阻抗, 这些对于提高其光电转换效率都是有益的。







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coutts YJ, Young DL, Li X, Mulligan WP, Wu X. Search for improved transparent conducting oxides: a fundamental investigation of CdO, Cd2SnO4, and Zn2SnO4. J Vac Sci Tech A. 2000;18(6):2646.
Tan B, Toman E, Li YG, Wu YY. Zinc Stannate (Zn2SnO4) dye-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129(14):4162.
Al-Attafi K, Jawdat FH, Qutaish H, Hayes P, Al-Keisy A, Shim K, Yamauchi Y, Dou SX, Nattestad A, Kim JH. Cubic aggregates of Zn2SnO4 nanoparticles and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nnao Energy. 2019;57:202.
Wang YF, Li KN, Xu YF, Su CY, Kuang DB. Hierarchical Zn2SnO4 nanosheets consisting of nanoparticles for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Energy. 2013;2(6):1287.
Wu WQ, Chen DH, Li F, Cheng YB, Caruso RA. Solution-processed Zn2SnO4 electron transporting layer for efficient planar perovskite solar cells. Today Energy. 2018;7:260.
Ng HT, Li J, Smith MK, Nguyen P, Cassell A, Han J, Meyyappan M. Growth of epitaxial nanowires at the junctions of nanowalls. Science. 2003;300(5623):1249.
Chuang HY, Wu XL, Amal R, Ng YH. Balancing the crystallinity and specific surface area of bismuth tungstate for photocatalytic water oxidation. Mol Catal. 2020;487:110887.
Tangcharoen T, T-Thienprasert J, Kongmark C. Effect of calcination temperature on structural and optical properties of MAl2O4 (M = Ni, Cu, Zn) aluminate spinel nanoparticles. J Adv Ceram. 2019;8(3):352.
Wang LL, Zhou TT, Zhang R, Lou Z, Deng JN, Zhang T. Comparison of toluene sensing performances of zinc stannate with different morphology-based gas sensors. Sens Actuators B: Chem. 2016;227:448.
Liu L, Mei XM, Zhang B, Meng SX, Feng YQ. Synthesis of nano-TiO2 assisted by diethylene glycol for use in high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Chin Chem Lett. 2017;28(4):765.
Wang YF, Lei BX, Hou YF, Zhao WX, Liang CL, Su CY, Kuang DB. Facile fabrication of hierarchical SnO2 microspheres film on transparent FTO glass. Inorg Chem. 2010;49(4):1679.
Zhang M, Cui X, Wang YF, Wang B, Ye MD, Wang WL, Ma CY, Lin ZQ. Simple route to interconnected, hierarchically structured, porous Zn2SnO4 nanospheres as electron transport layer for efficient perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy. 2020;71:104620.
Chen XY, Wang XZ, Liu FJ, Zhang GS, Song XJ, Tian J, Cui HZ. Fabrication of porous Zn2TiO4–ZnO microtubes and analysis of their acetone gas sensing properties. Rare Met. 2021;6(40):1528.
Xu WZ, Zheng LY, Zhu T, Liu L, Gong X. Bulk heterojunction perovskite solar cells incorporated with Zn2SnO4 nanoparticles as the electron acceptors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(37):34020.
Liu FJ, Chen XY, Wang XZ, Han Y, Song XJ, Tian J, He XM, Cui HZ. Fabrication of 1D Zn2SnO4 nanowire and 2D ZnO nanosheet hybrid hierarchical structures for use in triethylamine gas sensors. Sens Actuators B: Chem. 2019;291:155.
Yang XL, Gao HY, Zhao LP, Wang TS, Sun P, Liu FM, Lu GY. Enhanced gas sensing properties of monodisperse Zn2SnO4 octahedron functionalized by PdO nanoparticals. Sens Actuators B: Chem. 2018;266:302.
Mali SS, Shim CS, Hong CK. Highly porous zinc stannate (Zn2SnO4) nanofibers scaffold photoelectrodes for efficient methyl ammonium halide perovskite solar cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):11424.
Xin X, Zhang JN, ChenCJ Li G, Qin J, Yang ZB, Lu HB, Gao JZ, Wang CL, He Z. UV-activated porous Zn2SnO4 nanofibers for selective ethanol sensing at low temperatures. J Alloys Compd. 2019;780:228.
Wang YF, Li KN, Xu YF, Rao HS, Su CY, Kuang DB. Hydrothermal fabrication of hierarchically macroporous Zn2SnO4 for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale. 2013;5(13):5940.
Fan DW, Bao CZ, Khan MS, Wang CL, Zhang Y, Liu QZ, Zhang X, Wei Q. A novel label-free photoelectrochemical Zn2SnO4 sensor based on N, S-GQDs and CdS co-sensitized hierarchical cube for detection of cardiac troponin I. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;106:14.
Zhu HL, Yang DR, Yu GX, Zhang H, Jin DL, Yao KH. Hydrothermalsynthesis of Zn2SnO4 nanorods in the diameter regime of sub-5 nm and theirproperties. J Phy Chem B. 2006;110(15):7631.
Wang X, Wang YF, Luo QP, Ren JH, Li DJ, Li XF. Highly uniform hierarchical Zn2SnO4 microspheres for the construction of high performance dyesensitized solar cells. Rsc Adv. 2017;7(69):43403.
Xiong YJ, Cai HG, Wiley BJ, Wang JG, Kim MJ, Xia YN. Synthsis and mechanistic study of palladium nanobars and nanorods. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129(12):3665.
Kuang DB, Ito S, Werger B, Klein C, Moser JE, Moser JE, Humphry-Baker R, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M. High molar extinction coefficient heteroleptic ruthenium complexes for thin film dye-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128(12):4146.
Zhu K, Neale NR, Miedaner A, Frank AJ. Enhanced charge-collection efficiencies and light scattering in dye-sensitized solar cells using oriented TiO2 nanotubes arrays. Nano Lett. 2007;7(1):69.
Wu JJ, Chen YR, Liao WP, Wu CT, Chen CY. Construction of nanocrystalline film on nanowire array via swelling electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone-hosted nanofibers for use in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano. 2010;4(10):5679.
Wu CT, Liao WP, Wu JJ. Three-dimensional ZnO nanodendrite/nanoparticle composite solar cells. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(9):2871.
Ramasamy E, Lee J. Ordered mesoporous SnO2-Based photoanodes for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114(50):22032.
Oekermann T, Zhang D, Yoshida T, Minoura H. Electron transport and back reaction in nanocrystalline TiO2 films prepared by hydrothermal crystallization. J Phys Chem B. 2004;108(7):2227.
Choi SH, Hwang D, Kim DY, Kervella Y, Maldivi P, Jang SY, Demadrille R, Kim ID. Amorphous zinc stannate (Zn2SnO4) nanofibers networks as photoelectrodes for organic dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23(25):3146.
van de Lagemaat J, Park NG, Frank AJ. Influence of electrical potential distribution, charge transport, and recombination on the photopotential and photocurrent conversion efficiency of dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells: a study by electrical impedance and optical modulation techniques. J Phys Chem B. 2000;104(9):2044.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Application Development Foundation of Guangzhou Lu Chao Science and Technology Company (No. 53H19044), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U20A20238), the Talents Project of Beijing Municipal Committee Organization Department (No. 2018000021223ZK21) and the Key Research & Development and Transformation Projects in Qinghai Province (No. 2021-HZ-808).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YF., Feng, H., Deng, YR. et al. Solvothermal growth of Zn2SnO4 for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Rare Met. 41, 942–950 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01820-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01820-2