Abstract
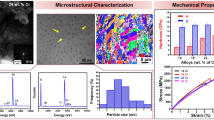
An investigation of lanthanum oxide (La2O3) addition to tungsten heavy alloy (WHA) with a ternary composition of W–7Ni–3Fe was reported in this study. The mixed powders were sintered using spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique. La2O3 was added in increments of 0.25 wt%, 0.50 wt%, 0.75 wt% and 1.00 wt% to WHA, respectively. The sintered samples were characterized for microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. The influences of La2O3 addition on density, grain size, hardness, ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and ductility on W–7Ni–3Fe system were discussed in this study. The highest relative sintered density of 87.95% was obtained for 0.25 wt% La2O3 addition to W–7Ni–3Fe. The lowest grain size of 7.89 μm was observed for 1.00 wt% La2O3 addition. Similarly, the highest hardness and UTS of HV 533 and 1110 MPa, respectively, were also obtained for the same composition. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) of the samples revealed homogenous distribution of La2O3 in the alloy matrix. Fractography of the sintered alloy samples revealed W–W intergranular fracture.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose A, German RM. Matrix composition effects on the tensile properties of tungsten-molybdenum heavy alloys. Metall Trans A. 1990;21A(5):1325.
Khalid FA, Bhatti MR. Microstructure and properties of sintered tungsten heavy alloys. J Mater Eng Perform. 1999;8(1):46.
Ding L, Xiang DP, Li YY, Zhao YW, Li JB. Phase, microstructure and properties evolution of fine-grained W–Mo–Ni–Fe alloy during spark plasma sintering. Mater Des. 2012;37:8.
Kim Y, Lee KH, Kim EP, Cheong DI, Hong SH. Fabrication of high temperature oxides dispersion strengthened tungsten composites by spark plasma sintering process. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2009;27(5):842.
Islam SH, Akhtar F, Askari SJ, Jokhio MT, Qu X. Enhancement of physical and mechanical properties of oxide dispersion-strengthened tungsten heavy alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2016;47:2387.
Upadhyaya A, Tiwari SK, Mishra P. Microwave sintering of W–Ni–Fe alloy. Scr Mater. 2007;56(1):5.
Caliskan NK, Durlu N, Bor S. Swaging of liquid phase sintered 90W–7Ni–3Fe tungsten heavy alloy. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2013;36:260.
Lee KH, Cha SI, Ryu HJ, Hong SH. Effect of oxide dispersoids addition on mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying process. Mater Sci Eng A. 2007;452–453:55.
Kumari A, Sankaranarayana M, Nandy TK. On structure property correlation in high strength tungsten heavy alloys. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2017;67:18.
Sahin Y, Recent progress in processing of tungsten heavy alloys. J Powder Technol. 2014, Article ID 764306. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/764306.
Belhadjhamid A, German RM. The effects of powder pretreatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloys. Adv Powder Metall. 1991;175:353.
Kiran UR, Panchal A, Kumar MP, Sankaranarayana M. Refractory metal alloying: a new method for improving mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2017;709:609.
Ding L, Xiang DP, Pan YL, Li YY. Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of Mo–Co-co-strengthened W–Ni–Fe alloys by spark plasma sintering. J Alloy Compd. 2017;712:593.
Ryu HJ, Hong SH. Fabrication and properties of mechanically alloyed oxide-dispersed tungsten heavy alloys. Mater Sci Eng. 2003;A363:179.
Kim Y, Hong MH, Lee SH, Kim EP, Lee S, Noh JW. The effect of yttrium oxide on the sintering behavior and hardness of tungsten. Met Mater Int. 2006;12(3):245.
Fan JL, Liu T, Cheng HC, Wang DL. Preparation of fine grain tungsten heavy alloy with high properties by mechanical alloying and yttrium oxide addition. J Mater Process Technol. 2008;208(1–3):463.
Aguirre MV, Martín A, Pastor JY, LLorca J, Monge MA, Pareja R. Mechanical properties of tungsten alloys with Y2O3 and titanium addition. J Nucl Mater. 2011;417(1–3):516.
Wang JF, Zuoa DW, Zhu L, Li WW, Tu ZB, Sheng D. Effects and influence of Y2O3 addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of binder less tungsten carbide fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Int J Refract Metal Hard Mater. 2018;71:167.
Zhao MY, Zhou ZJ, Zhong M, Tan J, Lian YY, Liu X. Thermal shock behavior of fine grained W–Y2O3 materials fabricated via two different manufacturing technologies. J Nucl Mater. 2016;470:236.
Daoush WM, Elsayed AH, El Kady OA, Sayed MA, Dawood OM. Enhancement of physical and mechanical properties of oxide dispersion-strengthened tungsten heavy alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2016;47(5):2387.
Patra A, Saxena R, Karak SK. Combined effect of Ni and nano-Y2O3 addition on microstructure, mechanical and high temperature behavior of mechanically alloyed W–Mo. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2016;60:131.
Chen HY, Luo LM, Zan X, Xu Q, Zhu XY, Liu JQ, Cheng JG, Wu YC. Microstructure and helium irradiation performance of W–ZrC/Sc2O3 composites prepared spark plasma sintering. Int J Refract Metal Hard Mater. 2018;72:373.
Itoh Y, Ishiwata Y. Strength properties of yttrium-oxide-dispersed tungsten alloy. JSME Int J. 1996;39(3):429.
Liu R, Zhou Y, Hao T, Zhang T, Wang XP, Liu CS, Fang QF. Microwave synthesis and properties of fine-grained oxides dispersion strengthened tungsten. J Nucl Mater. 2012;424:171.
Ghezzi F, Zani M, Magni S, Vanacore GM, Tagliaferri A. Surface and bulk modification of W–La2O3 armor mock-up. J Nucl Mater. 2009;393:522–6.
Wei C, Ren QQ, Fan JL, Gong HR. Cohesion properties of W/La2O3 interfaces from first principles calculation. J Nucl Mater. 2015;466:234.
Mabuchi M, Okamoto K, Saito N, Asahina T, Igarashi T. Deformation behavior and strengthening mechanisms at intermediate temperatures in W–La2O3. Mater Sci Eng A. 1997;237:241.
Chen ZC, Zhou ML, Zuo TY. Morphological evolution of second-phase particles during thermomechanical processing of W–La2O3 alloy. Scr Mater. 2000;43(4):291.
Muñoz A, Monge MA, Savoini B, Rabanal ME, Garces G, Pareja R. La2O3-reinforced W and W–V alloys produced by hot isostatic pressing. J Nucl Mater. 2011;417(1–3):508.
Yar MA, Wahlberg S, Bergqvist H, Salem HG, Johnsson M, Muhammed M. Chemically produced nanostructured ODS–lanthanum oxide–tungsten composites sintered by spark plasma. J Nucl Mater. 2011;408(2):129.
Zhang XX, Yan QZ, Yang CT, Wang TN, Ge CC. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bonding characteristic of deformed tungsten. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2014;43(26):302.
Schmitz J, Litnovsky AM, Klein F, Tan X, Breuer U, Rasinski M, Ertmer S, Kreter A, Gonzalez-Julian J, Bram M, Coenen JW. Argon-seeded plasma exposure and oxidation performance of tungsten-chromium-yttrium smart alloys. Tungsten. 2019;1(2):159.
Wu YC. Manufacturing of tungsten and tungsten composites for fusion application via different routes. Tungsten. 2019;1(1):80.
Hu K, Li X, Qu S, Li Y. Spark-plasma sintering of W–5.6Ni–1.4Fe heavy alloys: densification and grain growth. Metall Mater Trans A. 2013;44(2):923.
Mondal A, Upadhyaya A, Agrawal D. Microwave and conventional sintering of 90W–7Ni–3Cu alloys with premixed and pre-alloyed binder phase. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527:6870.
Ding L, Xiang DP, Li YY, Li C, Li JB. Effects of sintering temperature on fine-grained tungsten heavy alloy produced by high-energy ball milling assisted spark plasma sintering. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 2012;33:65.
Das J, Rao GA, Pabi SK. Microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527(29–30):7841.
Faleschini M, Kreuzer H, Kiener D, Pippan R. Fracture toughness investigations of tungsten alloys and SPD tungsten alloys. J Nucl Mater. 2007;367–370:800.
Mabuchi M, Okamoto K, Saito N, Nakanishi M, Yamada Y, Asahina T. Tensile properties at elevated temperature of W–1%La2O3. Mater Sci Eng. 1996;A214(1–2):174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AyyappaRaj, M., Yadav, D., Agrawal, D.K. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma-sintered La2O3 dispersion-strengthened W–Ni–Fe alloy. Rare Met. 40, 2230–2236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01390-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01390-9