Abstract
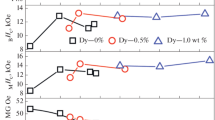
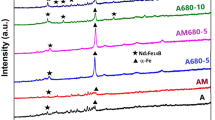
Relationship between atomic local structures and Curie temperature of NdFeB permanent magnets was investigated semi-quantitatively using synchrotron radiation technique. Fe K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) was employed to study the local structure of Fe atoms for samples before and after doping Dy, Tb or Gd. It is found that the bond lengths and coordination numbers are changed. Thus, the exchange interaction between Fe atoms increases with Dy, Tb or Gd doping, resulting in the improvement of Curie temperature of NdFeB permanent magnets. The doping effect is proven by experimental measurement of the magnetic properties. Microstructural characterization using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was also used to further analyze the effect of different rare earth elements doping on Curie temperature of NdFeB permanent magnets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goll D, Seeger M, Kronmüller H. Magnetic and microstructural properties of nanocrystalline exchange coupled PrFeB permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 1998;185(1):49.
Liu YH, Guo S, Liu XM, Lee D, Yan AR. Magnetic properties and microstructure of Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets with DyH x addition. J Appl Phys. 2012;111(7):07A705.
Başoğlu M, Yanmaz E. Improvement of coercivity and Curie temperature of sintered Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets by addition of Cu and Ni. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2014;27(10):2295.
Bolzoni F, Leccabue F, Moze O, Pareti L, Solzi M, Deriu A. 3d and 4f magnetism in Nd2Fe14–x Co x B and Y2Fe14–x Co x B compounds. J Appl Phys. 1987;61(12):5369.
Wang SY, Li TJ, Jin JZ. Effect of high-magnetic-field annealing on the magnetic properties and microstructure of sintered NdFeB magnets. Rare Metal Mat Eng. 2008;37(5):896.
Hussain M, Zhao LZ, Zhang C, Jiao DL, Zhong XC, Liu ZW. Composition-dependent magnetic properties of melt-spun La or/and Ce substituted nanocomposite NdFeB alloys. Phys B Condens Matter. 2016;483(4):69.
Ma BM, Liu WL, Liang YL, Scott DW, Bounds CO. Comparison of the improvement of thermal stability of NdFeB sintered magnets: intrinsic and/or microstructural. J Appl Phys. 1994;75(10):6628.
Zhou SY, Zhou L, Chen SK, Luo JJ. Effect of annealing on microstructure and magnetic properties of sintered NdFeB magnets. Rare Metal Mat Eng. 2006;35(6):1006.
Tokunaga M, Kogure H, Endoh M, Harada H. Improvement of thermal stability of Nd–Dy–Fe–Co–B sintered magnets by additions of Al, Nb and Ga. IEEE Trans Magn. 1987;23(5):2287.
Hussain M, Liu J, Zhao LZ, Zhong XC, Zhang GQ, Liu ZW. Composition related magnetic properties and coercivity mechanism for melt spun [(La0.5Ce0.5)1–x RE x ]10Fe84B6(RE = Nd or Dy) nanocomposite alloys. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;399(3):26.
Arinicheva OA, Lileev AS, Reissner M, Lukin AA, Starikova AS. Magnetic and microstructural properties of (Nd, Pr)–(Tb, Dy, Gd)–(Fe Co, Al, Cu)–B type magnets. Hyperfine Interact. 2013;219(1–3):89.
Yu LQ, Zhang J, Hu SQ, Han ZD, Yan M. Production for high thermal stability NdFeB magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2008;320(8):1427.
Mottram RS, Williams AJ, Harris IR. Blending additions of cobalt to Nd16Fe76B8 milled powder to produce sintered magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2000;217(1–3):27.
Ma BM, Narasimban KSVL. NdFeB magnets with higher Curie temperature. IEEE Trans Magn. 1986;22(5):916.
Pandian S, Chandrasekaran V, Markandeyulu G, Iyer KJL, Rao KVSR. Effect of Co, Dy and Ga on the magnetic properties and the microstructure of powder metallurgically processed Nd–Fe–B magnets. J Alloy Compd. 2004;364(1–2):295.
Truong NX, Vuong NV. Preparation and magnetic properties of MnBi alloy and its hybridization with NdFeB. J Magn. 2015;20(4):336.
Zhang DT, Wang PF, Yue M, Liu WQ, Zhang JX, Sundararajan JA, Qiang Y. High-temperature magnetic properties of anisotropic MnBi/NdFeB hybrid bonded magnets. Rare Met. 2016;35(6):471.
Yan WL, Yan SH, Yu DB, Li KS, Li HW, Luo Y, Yang HC. Influence of gadolinium on microstructure and magnetic properties of sintered NdGdFeB magnets. J Rare Earths. 2012;30(2):133.
Lukin AA, II’Yashenko EI, Skjeltorp AT, Helgesen G. Improvement of thermal stability of Nd–Tb–Fe–Co–B sintered magnets by additions of Pr, Ho, Al, and Cu. Phys Res Int. 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/416717
Hou XL, Shi YJ, Luo JJ, Li ZF, Zhang HL, Pang W. Effects of elements addition on properties sintered NdFeB permanent magnets. Rare Met Mat Eng. 2004;33(6):150.
Yan GH, Chen RJ, Ding Y, Guo S, Yan AR. The preparation of sintered NdFeB magnet with high-coercivity and high temperature-stability. J Phys Conf Ser. 2011;266(1):687.
Liu ZW, Ramanujan RV, Davies HA. Improved thermal stability of hard magnetic properties in rapidly solidified RE-TM-B alloys. J Mater Res. 2008;23(23):2733.
Ravel B, Newville M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J Synchrotron Radiat. 2005;12(4):537.
Diener A, Neumann T, Kramar U, Schild D. Structure of selenium incorporated in pyrite and mackinawite as determined by XAFS analyses. J Contam Hydrol. 2012;133(3):30.
Newville Matthew. IFEFFIT: interactive XAFS analysis and FEFF fitting. J Synchrotron Radiat. 2001;8(Pt 2):322.
Yan M, Peng XL. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 8th ed. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press; 2006. 148.
Slater JC. Cohesion in monovalent metals. Phys Rev. 1930;35(5):509.
Zhou SZ, Dong QF, Gao XX. Sintered NdFeB Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Materials and Technology. 2nd ed. Beijing: Metall. Industry Press; 2012. 39.
Herbst JF, Croat JJ, Pinkerton PE. Relationships between crystal structure and magnetic properties in Nd2Fe14B. Phys Rev B. 1984;29(7):4176.
Herbst JF. R2Fe14B materials: intrinsic properties and technology aspects. Rev Mod Phys. 1991;63(63):819.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by State High-Tech Development Plan (No. 2011AA061901), the Technology Landing Project of Jiangxi Province (No. KJLD13041), the Science and Technology Plan of Ganzhou (No. [2014]131) and the Research Support Plan of Jiangxi University of Science and Technology (No. jxxjbs15001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, MN., Wang, H., Hu, YF. et al. Relating atomic local structures and Curie temperature of NdFeB permanent magnets: an X-ray absorption spectroscopic study. Rare Met. 37, 983–988 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0918-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0918-5