Abstract
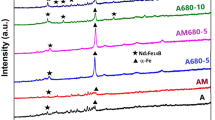
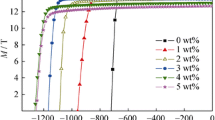
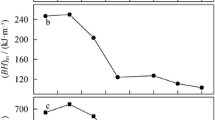
Anisotropic magnets were obtained by hot deformation with the partial crystallized precursor prepared via spark-plasma sintering (SPS). Amorphous powders with the nominal composition of Nd28.72FebalCo5.66Ga0.59B0.92 (wt%) were used as the starting material. The results show that the amorphous powders would suffer varying degrees of crystallization even below the crystallization point during the SPS process under high pressure. And the pre-crystallized grains in precursors have great impacts on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the hot-deformed magnets. The final obtained anisotropic magnets exhibit homogeneous microstructure consisting of well-aligned and platelet-shaped Nd2Fe14B grains without abnormal growth. It can be found that a reasonable proportion of pre-crystallized gains could promote the preferential orientation in the magnet, leading to the achievement of optimal magnetic properties among the magnets with identical composition and best magnetic performance is achieved in the magnet hot deformed from the 490 °C high-pressure hot-pressed precursor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu YP, Liu Y, Li J, Zheng Q, Wang RQ. Desorption-recombination behavior of as-disproportionated NdFeCoB compacts by reactive deformation. Rare Met. 2015;34(2):89.
Li YF, Zhu GM, Li AH, Feng HB, Huang SL, Li W, Du A, Qi Y. Relationship between controllable preparation and microstructure of NdFeB sintered magnets. J Rare Earth. 2014;32(7):628.
Sugimoto S. Current status and recent topics of rare-earth permanent magnets. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2011;44(6):064001.
Hadjipanayis GC, Liu JF, Gabay A, Marinescu M. Current status of rare-earth permanent magnet research in USA. J Iron Steel Res Int. 2006;13(S1):12.
Skomski R, Sellmyer DJ. Anisotropy of rare-earth magnets. J Rare Earth. 2009;27(4):675.
Zheng Q, Li J, Liu Y, Yu YP, Lian LX. Highly oriented NdFeCoB nanocrystalline magnets from partially disproportionated compacts by reactive deformation under low pressure. J Appl Phys. 2014;115(17):173511.
Hou YH, Huang YL, Liu ZW, Zeng DC, Ma SC, Zhong ZC. Hot deformed anisotropic nanocrystalline NdFeB based magnets prepared from spark plasma sintered melt spun powders. Mater Sci Eng B Adv. 2013;178(15):990.
Ma BM, Lee D, Smith B, Gaiffi S, Owens B, Bie H, Warren GW. Comparison of the corrosion behavior of die-upset and sintered NdFeB magnets. IEEE Trans Magn. 2001;37(4):2477.
Brown D, Ma BM, Chen ZM. Developments in the processing and properties of Nd–Fe–B-type permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2002;248(3):432.
Wang XC, Zhu MG, Li W, Li YF, Lai B, Du A. Microstructure and magnetic properties of anisotropic hot-deformed magnet of different magnetic particle sizes. Rare Met. 2015;34(4):255.
Li L, Graham CD Jr. Mechanism of texture formation by hot deformation in rapidly quenched FeNdB. J Appl Phys. 1990;67(9):4756.
Li L, Graham CD. The origin of crystallographic texture produced during hot deformation in rapidly-quenched NdFeB permanent magnets. IEEE Trans Magn. 1992;28(5):2130.
Liu WQ, Cui ZZ, Yi XF, Yue M, Jiang YB, Zhang DT, Zhang JX, Liu XB. Structure and magnetic properties of magnetically isotropic and anisotropic Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets prepared by spark plasma sintering technology. J Appl Phys. 2010;107(9):09A719.
Lin M, Wang HJ, Yi PP, Yan AR. Effects of excessive grain growth on the magnetic and mechanical properties of hot-deformed NdFeB magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2010;322(15):2268.
Harada T, Fujita M, Kuji T. Nd-Fe-B die upset magnets produced from amorphous bulk materials. J Alloy Compd. 1996;243(1–2):139.
Lee JI, Kwon HW, Choi GS. Texture in die-upset Nd–Fe–B magnet produced using HDDR-treated particles. Phys Status Solidi c. 2007;4(12):4617.
Wang L, Chen JW, Yue M, Liu RM, Liu WQ. Crystallographic alignment and magnetic anisotropy in melt-spun Nd-Fe-B/α-Fe composite ribbons with different neodymium contents. J Rare Earth. 2011;29(5):471.
Ma YL, Chen DM, Zhou AR, Sun JC, Cao PJ. Enhanced alignment and magnetic properties of die-upset nano-crystal Nd2Fe14B magnets with Nb addition. Phys B. 2012;407(23):4562.
Li XH, Gao ZS, Li W, Zhang KW, Zhang JW, Zhang XY. Study of the microstructure of α-Fe/Nd2Fe14B nanocomposites prepared by electropulsing heating amorphous NdFeCoB. Mater Lett. 2005;59(22):2782.
Li W, Li LL, Nan Y, Li XH, Zhang XY. Controllable nanocrystallization in amorphous Nd9Fe85B6 via combined application of severe plastic deformation and thermal annealing. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91(6):062509.
Liu YG, Xu L, Guo DF, Li W, Wang QF, Zhang XY. Bulk anisotropic Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe nanocomposite magnets prepared by hot deformation processing of amorphous alloys. J Appl Phys. 2009;106(11):113918.
Wu W, Li H, Xie YW, Zhang XY. Effect of high pressure on microstructure of crystallizing amorphous Nd9Fe85B6 alloy. J Rare Earth. 2008;26(5):741.
Liang BY, Xie YW, Li W, Wu W, Zhang XY. Microstructure and magnetic properties of bulk nanocomposite magnets prepared by crystallizing amorphous Nd3.6Pr5.4Fe80Co3B7Nb1 under high pressure. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41(19):195010.
Wu W, Li W, Sun HY, Li H, Li XH, Liu BT, Zhang XY. Pressure-induced preferential growth of nanocrystals in amorphous Nd9Fe85B6. Nanotechnology. 2008;19(28):285603.
Faupel F, Frank W, Macht MP, Mehrer H, Naundorf V, Raetzke K, Schober HR, Sharma SK, Teichler H. Diffusion in metallic glasses and supercooled melts. Rev Mod Phys. 2003;75(1):237.
Kwon HW, Kang YS, Choi GS, Yu JH. Effect of grain size and die-upset temperature on texture in die-upset Nd-Fe-B magnet. IEEE Trans Magn. 2009;45(6):2590.
Lee YI, Shih CW, Chang WC, Chang HW, Chen YJ. Inhomogeneity on texture, microstructure and magnetic properties of hot deformed R2Fe14B-typed magnet. Int J Mod Phys B. 2015;29(10):154007.
Lipiec W, Davies HA. The influence of the powder densification temperature on the microstructure and magnetic properties of anisotropic NdFeB magnets aligned by hot deformation. J Alloy Compd. 2010;491(1–2):694.
Sun Y, Gao RW, Feng WC, Han GB, Bai G, Liu T. Effect of grain size and distribution on the anisotropy and coercivity of nanocrystalline Nd2Fe14B magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2006;306(1):108.
Feng WC, Gao RW, Yan SS, Li W, Zhu MG. Effects of phase distribution and grain size on the effective anisotropy and coercivity of nanocomposite Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe magnets. J Appl Phys. 2005;98(4):044305.
Fischer R, Schrefl T, Kronmfiller H, Fidler J. Grain-size dependence of remanence and coercive field of isotropic nanocrystalline composite permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 1996;153(1–2):35.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51171122), and the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (Nos. 2014GZ0090 and 2016GZ0262).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Liu, Y., Li, J. et al. Microstructure and magnetic properties of hot-deformed anisotropic Nd–Fe–B magnets prepared from amorphous precursors with different crystallization proportions. Rare Met. 36, 268–276 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0894-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0894-9