Abstract
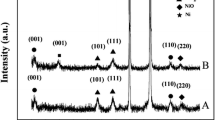
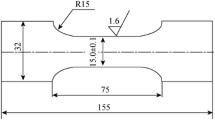
Smooth and compact nickel layers were successfully prepared in the ionic liquid of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BMIMBF4) by constant current electrodeposition method. The effects of temperature, additive content, current density, and deposition time on the performance of the nickel layers were systematically analyzed. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to analyze the surface morphology and composition of the nickel layers. Meanwhile, the tensile strengths of the nickel layers were tested by universal tensile testing machine. The results show that different process conditions have a great effect on morphology and performance of the electrodeposited nickel layer. The optimization of process parameters is as follows: BMIMBF4 to ethylene glycol (EG) volume ratio of 2:1, deposition temperature of 120 °C, and current density of 1.2 mA·cm−2. Current density has a greater influence on the tensile strength of the nickel layer, and the maximum value of tensile strength is 1275 MPa.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Zhai YC, Wang H. Research on production process of Nickel. Mater Rev. 2006;20(3):79.
Wang RY, Long JM, Pei HZ. Research progress on electroforming nickel and nickel alloys. Electroplat Finish. 2009;28(3):10.
Dibari GA. Nickel plating. Met Finish. 1995;93(1):259.
Watt GW, Hazlehurst DA. Mechanism of electrodeposition of nickel from liquid ammonia solutions of spin-free nickel(II) complexes. J Electrochem Soc. 1959;106(2):117.
Ebrahimi F, Bourne GR, Kelly MS, Matthews TE. Mechanical properties of nano-crystalline nickel produced by electrodeposition. Nanostruct Mater. 1999;11(3):343.
Matsui I, Takigawa Y, Uesugi T, Higashi K. Enhanced tensile ductility in bulk nanocrystalline nickel electrodeposited by sulfamate bath. Mater Lett. 2011;65(15):2351.
Ohno H. Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids. Hoboken: Wiley; 2005. 110.
Simka W, Puszczyk D, Nawrat G. Electrodeposition of metals from non-aqueous solutions. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54(23):5307.
Bonhote P, Dias AP, Papageorgiou N, Kalyanasundaram K, Grätzel M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg Chem. 1996;35(5):1168.
Abedin SZE, Endres F. Ionic liquids: the link to high-temperature molten salts. Acc Chem Res. 2007;40(11):1106.
Armand M, Endres F, MacFarlane DR, Ohno H, Scrosati B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat Mater. 2009;8(8):621.
Yang PX, An MZ, Li HX, Li JD, Wang FP. Study on electrodeposition of pure nickel. In: Proceedings of the National Electronic Electroplating Academic Annual Conference. Hangzhou; 2007, 208.
Freyland W, Zell CA, Zein El Abedin S, Endres F. Nanoscale electrodeposition of metals and semiconductors from ionic liquids. Electrochim Acta. 2003;48(20):3053.
Deng MJ, Sun I, Chen PY, Chang JK, Tsai WT. Electrodeposition behavior of nickel in the water-and air-stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide room-temperature ionic liquid. Electrochim Acta. 2008;53(19):5812.
Mann O, Freyland W. Electrocrystallization of distinct Ni nanostructures at the ionic liquid/Au(111) interface: an electrochemical and in situ STM investigation. J Phys Chem C. 2007;111(27):9832.
Mann O, Pan GB, Freyland W. Nanoscale electrodeposition of metals and compound semiconductors from ionic liquids. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54(9):2487.
Zhu YL, Katayama Y, Miura T. Effects of acetonitrile on electrodeposition of Ni from a hydrophobic ionic liquid. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55(28):9019.
Gu C, Tu J. One-step fabrication of nanostructured Ni film with lotus effect from deep eutectic solvent. Langmuir. 2011;27(16):10132.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Aerospace Science Foundation of China (No. 2012ZE51058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, JG., Li, TJ., Li, X. et al. Constant current electrodeposition preparation of nickel layer and its mechanical properties in ionic liquid. Rare Met. 42, 1752–1759 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0855-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0855-8