Abstract
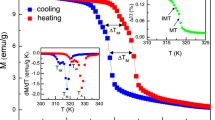
In present work, the effect of Ge substitution for Mn on crystal structure and martensitic transformation was carefully investigated in magnetic shape memory Ni50Mn36−xGexSn14 (x = 0, 1) alloys. From X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, it can be found that each sample possesses cubic austenitic structure (L21) at room temperature and the main peak (220) shifts to higher degree with Ge doping, indicating that the cell volume of austenitic phase shrinks. With Ge content increasing, martensitic transformation (MT), temperature shifts to higher temperature region and the difference of magnetization between martensitic and austenitic phases (ΔM) also increases. In addition, the magnetocaloric effect (MCE) and phase transition strain (ΔL/L) were investigated in Ni50Mn35GeSn14 alloy. The maximal magnetic entropy change (ΔS m) associated with martensitic transition is 3.9 J·kg−1·K−1 with applied magnetic field change of 5 T and the maximal ΔL/L reaches 0.18% in this alloy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutou Y, Imano Y, Koeda N, Omori T, Kainuma R, Ishida K, Oikawa K. Magnetic and martensitic transformations of NiMnX (X = In, Sn, Sb) ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2004;85(19):4358.
Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann EF. Martensitic transitions and the nature of ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni–Mn–Sn alloys. Phys Rev B. 2005;72(1):014412.
Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann EF. Ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni–Mn–In alloys. Phys Rev B. 2006;73(17):174413.
Krenke T, Duman E, Acet M, Wassermann EF, Moya X, Mañosa L, Planes A. Inverse magnetocaloric effect in ferromagnetic Ni–Mn–Sn alloys. Nat Mater. 2005;4(6):450.
Emre B, Bruno NM, Emre SY, Karaman I. Effect of niobium addition on the martensitic transformation and magnetocaloric effect in low hysteresis NiCoMnSn magnetic shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;105(23):231910.
Planes A, Mañosa L, Acet M. Magnetocaloric effect and its relation to shape-memory properties in ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. J Phys: Condens Matter. 2009;21(23):233201.
Kainuma R, Imano Y, Ito W, Sutou Y, Morito H, Okamota S, Kitakami O, Oikawa K, Fujita A, Kanomata T, Ishida K. Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation. Nature. 2006;439(7079):959.
Krenke T, Duman E, Acet M, Wassermann EF. Magnetic superelasticity and inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In. Phys Rev B. 2007;75(10):104414.
Li Z, Xu K, Zhang YL, Jing C. Reproducible magnetostrain behavior induced by structure transformation for Ni46Co4Mn39Sn11 Heusler alloy. J Appl Phys. 2015;117(2):023902.
Muthu SE, Rao NVR, Raja MM, Kumar DMR, Radheep DM, Arumugam S. Influence of Ni/Mn concentration on the structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties in Ni50−xMn37+xSn13 Heusler alloys. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2010;43(42):425002.
Xuan HC, Zheng YX, Ma SC, Cao QQ, Wang DH, Du YW. The martensitic transformation, magnetocaloric effect, and magnetoresistance in high-Mn content Mn47+xNi43−xSn10 ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J Appl Phys. 2010;108(10):103920.
Liu FS, Wang QB, Li SP, Ao WQ, Li JQ. The martensitic transition and magnetocaloric properties of Ni51Mn49−xSnx. Phys B. 2013;412:47.
Pramanick S, Chatterjee S, Giri S, Majumdar S. Excess Ni-doping induced enhanced room temperature magneto-functionality in Ni–Mn–Sn based shape memory alloy. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;105(11):112407.
Dan NH, Duc NH, Yen NH, Thanh PT, Bau LV, An NM, Anh DTK, Bang NA, Mai NT, Anh PK, Thanh TD, Phan TL, Yu SC. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–Sn alloys. J Magn Magn Mater. 2015;374:372.
Zhao XG, Tong M, Shih CW, Li B, Chang WC, Liu W, Zhang ZD. Microstructure, martensitic transitions, magnetocaloric, and exchange bias properties in Fe-doped Ni–Mn–Sn melt-spun ribbons. J Appl Phys. 2013;113(17):17A913.
Liao P, Jing C, Zheng D, Li Z, Kang BJ, Deng DM, Cao SX, Lu B, Zhang JC. Tuning martensitic transformation, large magnetoresistance and strain in Ni50−xFexMn36Sn14 Heusler alloys. Solid State Commun. 2015;217:28.
Huang L, Cong DY, Suo HL, Wang YD. Giant magnetic refrigeration capacity near room temperature in Ni40Co10Mn40Sn10 multifunctional alloy. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;104(13):132407.
Emre B, Bruno NM, Emre SY, Karaman I. Effect of niobium addition on the martensitic transformation and magnetocaloric effect in low hysteresis NiCoMnSn magnetic shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;105(23):231910.
Ghosh A, Mandal K. Large inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni48.5−xCoxMn37Sn14.5 (x = 0, 1 and 2) with negligible hysteresis. J Alloys Compd. 2013;579:295.
Yang LH, Zhang H, Hu FX, Sun JR, Pan LQ, Shen BG. Magnetocaloric effect and martensitic transition in Ni50Mn36−xCoxSn14. J Alloys Compd. 2014;588:46.
Wang DH, Zhang CL, Xuan HC, Han ZD, Zhang JR, Tang SL, Gu BX, Du YW. The study of low-field positive and negative magnetic entropy changes in Ni43Mn46−xCuxSn11 alloys. J Appl Phys. 2007;102(1):013909.
Das R, Sarma S, Perumal A, Srinivasan A. Effect of Co and Cu substitution on the magnetic entropy change in Ni46Mn43Sn11 alloy. J Appl Phys. 2011;109(7):07A901.
Raji GR, Uthaman B, Thomas S, Suresh KG, Varma MR. Magnetocaloric properties, exchange bias, and critical behavior of Ge substituted Ni50Mn36Sn14 Heusler alloys. J Appl Phys. 2015;117(10):103908.
Chen J, Han ZD, Qian B, Zhang P, Wang DH, Du YW. The influence of Al substitution on the phase transition and magnetocaloric effect in Ni43Mn46Sn11−xAlx alloys. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323(2):248.
Muthu SE, Kanagaraj M, Singh S, Sastry PU, Ravikumar G, Rao NVR, Raia MM, Arumugam S. Hydrostatic pressure effects on martensitic transition, magnetic and magnetocaloric effect in Si doped Ni–Mn–Sn Heusler alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;584:175.
Wang DH, Zhang CL, Han ZD, Xuan HC, Gu BX, Du YW. Large magnetic entropy changes and magnetoresistance in Ni45Mn42Cr2Sn11 alloy. J Appl Phys. 2008;103(3):033901.
Zhang Y, Liu J, Zheng Q, Zhang J, Xia WX, Du J, Yan A. Large magnetic entropy change and enhanced mechanical properties of Ni–Mn–Sn–C alloys. Scr Mater. 2014;75:26.
Saha R, Nigam AK. Room temperature inverse magnetocaloric effect in Pd substituted Ni50Mn37Sn13 Heusler alloys. Phys B. 2014;448:263.
Zhang P, Phan TL, Dan NH, Thanh TD, Yu SC. Magnetocaloric and critical behavior in the austenitic phase of Gd-doped Ni50Mn37Sn13 Heusler alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;615:S335.
Phan TL, Thanh PT, Dan NH, Zhang P, Thanh TD, Phan MH, Yu SC. Influence of Pr-doping on the magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect of Ni50−xPrxMn37Sn13 alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;615:S261.
Chen F, Tong YX, Tian B, Li L, Zheng YF. Martensitic transformation and magnetic properties of Ti-doped NiCoMnSn shape memory alloy. Rare Met. 2014;33(5):511.
Webster PJ, Ziebeck KRA, Town SL, Peak MS. Magnetic order and phase transformation in Ni2MnGa. Philos Mag B. 1984;49(3):295.
Aksoy S, Acet M, Deen PP, Mañosa L, Planes A. Magnetic correlations in martensitic Ni–Mn-based Heusler shape-memory alloys: neutron polarization analysis. Phys Rev B. 2009;79(21):212401.
Buchelnikov VD, Entel P, Taskaev PSV, Sokolovskiy VV, Hucht A, Ogura M, Akai H, Gruner ME, Nayak SK. Monte Carlo study of the influence of antiferromagnetic exchange interactions on the phase transitions of ferromagnetic Ni–Mn–X alloys (X = In, Sn, Sb). Phys Rev B. 2008;78(18):184427.
Mañosa L, Moya X, Planes A, Gutfleisch O, Lyubina J. Effects of hydrostatic pressure on the magnetism and martensitic transition of Ni–Mn–In magnetic superelastic alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92(1):012515.
Krenke T, Moya X, Aksoy S, Acet M, Entel P, Mañosa L, Planes A, Elermanc Y, Yuceld A, Wassermann EF. Electronic aspects of the martensitic transition in Ni–Mn based Heusler alloys. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;310(2):2788.
Sharma VK, Chattopadhyay MK, Nath SK, Sokhey KJS, Kumar R, Tiwari P, Roy SB. The effect of substitution of Mn by Fe and Cr on the martensitic transition in the Ni50Mn34In16 alloy. J Phys: Condens Matter. 2010;22(48):486007.
Wang RL, Yan JB, Xiao HB, Xu LS, Marchenkov VV, Xu LF, Yang CP. Effect of electron density on the martensitic transition in Ni–Mn–Sn alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2011;509(3):6834.
Xuan HC, Han PD, Wang DH, Du YW. The influence of Ge substitution on the magnetostructure transition and magnetocaloric effect of Mn–Ni–Sn–Ge alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;582:369.
Xu K, Li Z, Zhang YL, Jing C. An indirect approach based on Clausius–Clapeyron equation to determine entropy change for the first-order magnetocaloric materials. Phys Lett A. 2015;379(47–48):3149.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51371111, 11364035 and 11404186), the Key Basic Research Program of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 13JC1402400), the Project for Applied Basic Research Programs of Yunnan Province (No. 2013FZ110) and the Project for Innovation Research Team of Qujing Normal University (No. TD201301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, D., Jing, C., Lu, B. et al. Martensitic transformation, magnetocaloric effect and phase transition strain in Ni 50 Mn 36− x Ge x Sn 14 Heusler alloys . Rare Met. 41, 4217–4222 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0820-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0820-6