Abstract
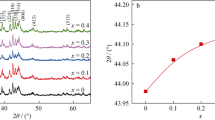
Melt-spun Y16Fe78B6 ribbons were prepared by the melt-spinning technique with pure elements Y, Fe and Fe–B alloy in argon. The ribbons are mainly composed of Y2Fe14B, YFe2 and α-Fe phases. Amorphous phase appears at the wheel velocity of >35 m·s−1. For the ribbons prepared at optimum wheel velocity and heat treatments, the coercivity, remanence and maximum energy product are 239.5 kA·m−1, 0.61 T and 32.7 kJ·m−3, respectively. By an investigation of Henkel plots of ribbons, it is found that intergrain exchange coupling leads to the enhancement of remanence. The coercivity mechanism of ribbons prepared at 35 m·s−1 is mainly controlled by inhomogeneous pinning of domain walls. The phase component and magnetic properties change with annealing temperature and time. The optimum magnetic properties are obtained with the ribbon quenched at 35 m·s−1 and annealed at 700 °C for 10 min.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coehoorn R, De Mooij DB, De Waard CD. Meltspun permanent magnet materials containing Fe3B as the main phase. J Magn Magn Mater. 1989;80(1):101.
Kneller EF, Hawig R. The exchange-spring magnet: a new material principle for permanent magnets. IEEE Trans Magn. 1991;27(4):3588.
Hadjipanayis GC. Nanophase hard magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 1999;200(1):373.
Li ZB, Zhang M, Shen BG, Sun JR. Non-uniform magnetization reversal in nanocomposite magnets. Appl Phys Lett. 2013;102(10):102405.
Li ZB, Shen BG, Niu E, Sun JR. Nucleation of reversed domain and pinning effect on domain wall motion in nanocomposite magnets. Appl Phys Lett. 2013;103(6):062405.
Stoner EC. A mechanism of magnetic hysterisis in heterogenous alloys. Trans Roy Soc. 1948;240(826):599.
Skomski R, Coey JMD. Giant energy product in nanostructured two-phase magnets. Phys Rev B. 1993;48(21):15812.
Qu H, Li J. Remanence enhancement in magnetically interacting particles. Phys Rev B. 2003;68(21):212402.
Li ZB, Zhang M, Wang LC, Shen BG, Zhang XF, Li YF, Hu FX, Sun JR. Investigation on intergranular exchange coupling effect in Pr9Fe85.5B5.5 ribbons. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;104(5):052406.
Zhang M, Ren WJ, Zhang ZD, Sun XK, Liu W, Geng DY, Zhao XG, Grössinger R, Triyono D. Magnetic properties and exchange coupling of nanocomposite (Nd, Y)2Fe14B/α-Fe. J Appl Phys. 2003;94(4):2602.
Coey JMD, Givord D, Liénard A, Rebouillat JP. Amorphous yttrium–iron alloys. I. Magnetic properties. J Phys F: Met Phys. 1981;11(12):2707.
Kronmüller H, Durst K-D, Sagawa M. Analysis of the magnetic hardening mechanism in RE-FeB permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 1988;74(3):291.
Tang W, Dennis KW, Wu YQ, Kramer MJ, Anderson IE, McCallum RW. Studies of new YDy-based R2Fe14B magnets for high temperature performance (R = Y+Dy + Nd). IEEE Trans Magn. 2004;40(4):2907.
Itoh T, Hikosaka K, Takahashi H, Ukai T, Mori N. Anisotropy energies for Y2Fe14B and Nd2Fe14B. J Appl Phys. 1987;61(8):3430.
Schrefl T, Fidler J, Kronmüller H. Remanence and coercivity in isotropic nanocrystalline permanent magnets. Phys Rev B. 1994;49(9):6100.
Liu YC, Li HW, Li KS, Jing JL, Luo Y, Quan NT. Magnetic properties optimization of nanocomposite Nd9Fe85B6 magnets by controlling microstructure of as-quenched ribbons. Rare Met. 2014;33(3):299.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51401028) and the Science and Technology Project of Xicheng District, Beijing (No. XCKJJH2013-33).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Li, KS., Li, HW. et al. Hard magnetic properties of melt-spun nanocomposite Y16Fe78B6 ribbons. Rare Met. 42, 602–605 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0750-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0750-3