Abstract
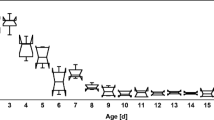
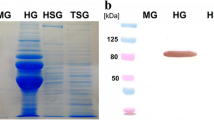
An API ZYM (Bio-Merieux, Lyon, France) test kit was used to examine the activity 19 hydrolases in in-hive bees and out-hive bees of worker Apis cerana. The study indicated that the activity of enzymes was changing in hypopharyngeal gland in in-hive and out-hive worker bees distinctly. The activities of most of the enzymes were observed. The protein hydrolases (acidic hydrolases) viz. leucine arylamidase, and valine arylamidase were more active in in-hive bees than out-hive bees. Rest of the tested enzymes were moderately present both in in-hive and out-hive bees. The hypopharyngeal gland and their secretion play important role affecting digestion of pollen, lipids and carbohydrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chrailsheim, K., L.H.W. Schneider, N. Hrassnigg, G. Buhlmann, U. Broasch, R. Gmeinbauer, and B. Schoffmann. 1992. Pollen consumption and utilization in worker honey bees (Apis mellifera carnica): Dependence on individual age and function. Journal of Insect Physiology 38: 409–419.
Costa, R.A., and C. Cruz-Landim. 2005. Hydrolases in the hypopharyngeal glands of workers of Scaptotrigona postica and Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera, Apinae). Genetics and Molecular Research 4: 616–623.
Deseyn, J., J. Billen, and J. Dziekonska-Rynko. 2005. Age-dependent morphology and ultra structure of the hypopharyngeal gland of Apis mellifera workers (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Apodologie 36: 49–57.
Haslett, J.R. 1983. A photographic account of pollen digestion by adult Hoverflies. Physiological Entomology 8: 167–171.
Klungness, L.M., and Y.S. Peng. 1984. A histochemical study of pollen digestion in the alimentary canal of honey bees. Journal of Insect Physiology 30: 511–521.
Kroon, G.H., J.P. VanPraagh, and H.H.W. Veltius. 1974. Osmotic shock as a prerequisite to pollen digestion in the alimentary tract of the worker honey bee. Journal of Apocalypse Research 13: 511–521.
Ohashi, K., S. Natori, and T. Kubo. 1999. Expression of amylase and glucose oxidase in the hypopharyngeal gland with age—Dependent role change of the worker honey bee (Apis mellifera L.). European Journal of Biochemistry 265: 127–133.
Schmolz, E., F. Kosece, and I. Lamprecht. 2005. Energetics of honey bee development isoperibol and combustion colorimetric investigation. Thermochimica Acta 437: 39–47.
Acknowledgments
The authors are deeply grateful to Professor Santi Gopal Pal, Retired Professor, Department of Zoology, University of Calcutta and Panchali Sengupta, Department of Zoology, West Bengal State University, for their help and advice during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naiya, S., Ghorai, N. Activity of Some Selected Hydrolases in Worker Honey Bees, Apis cerana (Fabr.). [Apidae:Insecta]. Proc Zool Soc 70, 42–45 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12595-015-0154-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12595-015-0154-7