Abstract
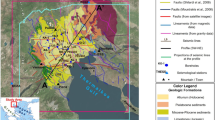
Digboi oil field, the oldest continuously producing oil field in India, is known to occur in an anticlinal trap (Digboi anticline) in the hanging wall of the frontal most thrust (Naga thrust) of Assam Arakan fold thrust belt. Since its discovery in 1890, about a thousand wells have been drilled in the Digboi anticline. The kinematic evolution of the Digboi anticline, however, is not well understood. In this article a geometrically valid balanced cross section and derive an internally consistent evolutionary model for the Naga thrust and related Digboi anticline are presented. It is shown that the Digboi anticline is a ramp anticline and can be best modelled as a fault-propagation fold with a high-angle breakthrough. There are two possible solutions (Model 1 and Model 2) to model the seismic events (sub-thrust high) in the footwall of Naga thrust. Model 1 considers the sub-thrust high to be real and conjectures a buried ramp anticline (Kusijan Anticline). Model 2 considers sub-thrust high to be a velocity pull up and the footwall rocks are undeformed. Both the models are geometrically and kinematically valid. Model 1 accommodates a total shortening of 32.9% while Model 2 accommodates a total shortening of 30.1%. From the present structural work and interpretation of seismic profiles, possible loci of branch line of Naga thrust along Digboi oil field is also traced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhandari, L.L., Fuloria, R.C., Sastri, V.V. (1973) Stratigraphy of Assam Valley, India. AAPG Bull., v.57, pp.642–654.
Corps, E.V. (1949) Digboi Oil Field, Assam. AAPG Bull., v.33, pp.1–21.
Dahlstrom, C.D.A., 1970. Structural geology in the eastern margin of the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Bull. Can. Pet. Geol. 18, 332–406.
Dahlstrom, C.D.A., 1969. Balanced cross sections. Canadian. Jour. Earth Sci., v.6, pp.743–757.
Dasgupta, A.B., Biswas, A.K. (2000) Geology of Assam. Geological Society of India, Bangalore.
Dasgupta, U., Majumdar, P., Mishra, P., Mehta, S. (2006) Geochemical characteristics of oil- clue to evidence of arrested seeps vis-a-vis extent of biodegradation in the Jaipur Anticline. Indian Jour. Petrol. Geol., v.15, pp.53–66.
Evans, P. (1964) Tectonic framework of Assam. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.5, pp.80–96.
Ghosh, T., Basu, S., Hazra, S. (2014) Geological mapping of the Schuppen belt of north-east India using geospatial technology. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.79, pp.97–111.
Ghosh, T., Hazra, S., 2020. Subsurface Modeling of Digboi Dilli Ghat Oil Bearing Structures (India) Using 2D Move. Geotectonics, v.54, pp.862–874.
Haproff, P.J., Odlum, M.L., Zuza, A. V., Yin, A., Stockli, D.F. (2020) Structural and Thermochronologic Constraints on the Cenozoic Tectonic Development of the Northern Indo-Burma Ranges. Tectonics, v.39.
Kent, W.N., Dasgupta, U., 2004. Structural evolution in response to fold and thrust belt tectonics in northern Assam. A key to hydrocarbon exploration in the Jaipur anticline area. Mar. Petrol. Geol., v.21, pp.785–803.
Kent, W.N., Hickman, R.G., Dasgupta, U. (2002) Application of a ramp/flat-fault model to interpretation of the Naga thrust and possible implications for petroleum exploration along the Naga thrust front. AAPG. Bull., v.86, pp.2023–2045.
Marshak, S., Mitra, G., 1988. Basic Methods of structural geology. New Jersey, Prentice Hall.
Mathur, L.P., Evans P. (1964) Oil in India. 22nd Int. Geol. Congr. Proceedings, New Delhi, pp.7–52.
Maurin, T., Rangin, C. (2009) Structure and kinematics of the Indo-Burmese Wedge: Recent and fast growth of the outer wedge. Tectonics, v.28.
Mitra, S. (1990) Fault-Propagation Folds: Geometry, Kinematic Evolution, and Hydrocarbon Traps. AAPG Bull., v.74, pp.921–945.
Mitra, S., Priestley, K., Bhattacharyya, A.K., Gaur, V.K. (2005) Crustal structure and earthquake focal depths beneath northeastern India and southern Tibet. Geophys. Jour. Int., v.160, pp.227–248.
Morley, C.K. (1986) A Classification of Thrust Fronts. AAPG Bull., v.70, pp.12–25.
Rangarao, A. (1983) Geology and hydrocarbon potential of a part of Assam-Arakan Basin and its adjacent region. Petrol. Asia Jour., v.6, pp.127–158.
Rangarao A., Samanta M.K. (1987) Structural style of the Naga overthrust belt and its implication on exploration. Bull. ONGC, v.24, pp.69–109.
Rangin, C., Maurin, T., Masson, F. (2013) Combined effects of Eurasia/Sunda oblique convergence and East-Tibetan crustal flow on the active tectonics of Burma. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.76, pp.185–194.
Srinivasan, V. (2007) Regional Structural Configuration and Seismic Pattern of Belt of Schuppen’in Northeast India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.70, pp.801–814.
Suppe, J. (1983) Geometry and kinematics of fault-bend folding. Amer. Jour. Sci., v.283, pp.684–721.
Suppe, J., Medwedeff, D.A. (1990) Geometry and kinematics of fault-propagation folding. Eclogae Geol. Helv., v.83, pp.409–454.
Tearpock, D.J., Bischke, R.E. (2002) Applied subsurface geological mapping with structural methods. Pearson Education.
Verma, R.K., Mukhopadhyay, M. (1977) An analysis of the gravity field in northeastern India. Tectonophysics, v.42, pp.283–317.
Wandrey, C.J. (2004) Sylhet-Kopili / Barail-Tipam Composite Total Petroleum System, Assam Geologic Province, India. US Dep. Inter. USGS.
Woodward, N.B., Boyer, S.E., Suppe, J. (1989) Balanced Geological Cross-Sections: An Essential Technique in Geological Research and Exploration, American Geophysical Union. American Geophysical Union.
Acknowledgements
The work was carried out with financial aid from IIT Roorkee in the form of MHRD fellowship to the first author. Help provided by the geoscientists of the Oil India Ltd. is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, D.P.M., Mukhopadhyay, D.K. & Mishra, P. Balanced Cross Sections and Kinematic Evolution Across Digboi Oil Field, Northeast India. J Geol Soc India 98, 487–495 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2006-1