Abstract
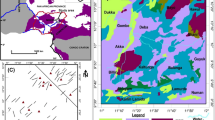
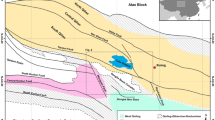
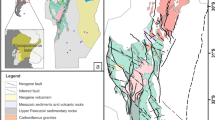
The Malani igneous suite, a terrain showing crustal formation as late as in Neoproterozoic, shows some pink and grey granites in the northeast of the desert city of Jodhpur, in northwestern, India. The average heat generation value of 15.925 HGU for these granites that is much higher than the average known value (3.8 HGU) for the continental crust has been reported here. The concentration of uranium determined is four times higher than the average continental crust. Thorium is still higher than U and K. The radioelement concentration (Ur) varies from 15.58 to 73.48 in the granites with an average of 45.671, clearly indicates a ‘hot crust’. Hence it is favourable for the formation of mineralization of HFS elements like, Nb, Ce, REE and U and Th, which need to be explored in the terrain as an economic deposit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashwal, L.D., Morgan, P., Kelly, S.A. and Preicival, G.A. (1987) Heat production in an Archean crustal profile and implications for heat flow and mobilization of heat producing elements. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.85, pp.439–450.
Bea, F. (1996) Residence of REE, Y, Th and U in granites and crustal protoliths implications for the chemistry of crustal melts. Jour. Petrol., v.37, pp.52l–552.
Bhandari, N. (2009) Mineral Exploration of the Moon. In Economic Mineralization, K.L. Shrivastava (Ed.), Sci. Publ. (India). pp.47–52.
Bhushan, S.K. and Chittora, V.K. (1999) Late Proterozoic bimodal volcanic assemblage of Siwana subsidence structure, Western Rajasthan India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.53, pp.433–452.
Bhushan, S.K. and Chandrasekaran, V. (2002) Geology and Geochemistry of rocks of the Malani Igneous Suite and tertiary Alkaline province of western Rajasthan. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.126, pp.1–181.
Birch, F. (1954) Heat from Radioactivity. In: Nuclear Geology, H. Faul (Ed.), John Wiley and Sons., pp.148–174.
Bonin, B. (1988) Peralkaline granites in Corsica: some petrological and geochemical constraints. Rendiconti Della Society Italiana Di Mineralgia E Petrologia, v.43(2), pp.281–306.
Boyle, R.W. (1982) Geochemical prospecting for uranium and thorium Deposits. Elsevier. pp.1–498.
Brown, G.C., Cassidy, J., Oxburgh, E.R., Plant, J., Sabine, P.A. and Watson, J.V. (1980) Basement heat flow and metalliferous mineralization in England and Wales. Nature, v.288(5792), pp.651–659.
Clark, A.H. and l0 others (1990) Geological and Geochronological constructions on the Metallogenic evolution of the Andes of Southeastern Peru. Econ. Geol., v.85, pp.1520–1583.
Dhana Raju, R., Singh, J.P., and Bhattacharya, T.K. (1983) A Preliminary study on Radioactive Heat Generation of Some Precambrian Granitic Rocks of India. Indian Jour. Earth Sci., v.10(2), pp.112–119.
Fehn, U., Cathies, L. M., and Holland, H. D., 1978: Hydrothermal convection and uranium deposits in abnormally radioactive plutons. Econ. Geol., v.73, pp.1556–1566.
Hollings, P., Fralick, P., and Kissin, S. (2004) Geochemistry and geodynamic implications of the Mesoproterozoic English Bay granite-rhyolite complex, Northeastern Ontario. Can. Jour. Earth Sci., v.41, pp.1329–1338.
Jackson, N.J., Drysdall, A.R. and Stoeser D.B. (1985) Alkali granites related Nb-Zr-REE-U-Th mineralization in the Arabian Shield. In: High heat production (HHP) granites, hydrothermal circulation and Ore genesis, Inst. Min. and Metallurgy., London, pp.479–488.
Kimberley, M.M. (1978) Uranium deposits, their mineralogy, and origin. Min. Assoc. Can., Short Course Handbook, v.3, pp.523.
Kinnaird, J.A., Batchelor, R.A., Whittely, J.E. and Mackenzie, A.B. (1985) Geochemistry, mineralization and hydrothermal alteration of the Nigerian high heat producing. In High heat producing (HHP) granites, hydrothermal alteration and Ore genesis. Inst. of Mining and Metallurgy, London, pp.169–199.
Kochhar, N. (1989) High heat producing granites of Malani Igneous Suite, Northern Peninsular India. Indian Minerals, v.43, pp.339–346.
Kochhar, N. (2012) The Malani Supercontinent: Siberia Mangolia Kazakhistan connections during Late Proterozoic. Inter. Geol. Cong. Brisbane, v.207.
Menuge, J.F., Brewer, T.S. and Seeger, C.M. (2002) Petrogenesis of Metaluminous A-type rhyolite from the St. Francois Mountains, Missouri and Mesoproterozoic evolution of the Southern Laurentian margin. Precambrian Res., v.113, pp.269–291.
Morgan, P. and Sass, J.H. (1984) Thermal Regime of the Continental Lithosphere. Jour. Geodyn., v.1, pp.143–166.
Morgan, P. (1985) Crustal Radiogenic Heat Production and the Selective Survival of Ancient Continental Crust. Proc. 15th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., Geophys. Res., v.90, pp.561–570.
Pagel, M. (1982) The mineralogy and geochemistry of uranium, thorium and rare earth elements in two radioactive granites of the Vosges, France. Min. Mag., v.46, pp.149–161.
Patwardhan, A.M. (2010) The Dynamic Earth system. Second editions, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd (New Delhi). p.422.
Plant, J.A., O’Brien, C., Terney, J. and Hurdley, J. (1985) Geochemical criteria for the recognition of heat production granites, in: High heat Production granite, hydrothermal alteration and ore genesis. Institute of Mining and Metallurgy London, pp.263–286.
Rogers, J.J.W. and Adams, J.A.S. (1969) Thorium in Handbook of Geochemistry. K.H., Wedepohl, (Ed.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp.11–14.
Roy, A. B., Kroner, A. Rathore, S., Laul, V., and Purohit, R. (2012) Tectonometamorphic and geochronological studies from Sandmata Complex, Northwest Indian Shield: Implications on exhumation of Late Palaeoproterozoic Granulites in an Archean-early Palaeoproterozoic granite-Gneiss terrane. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.19, pp.323–334.
Roy, A. B. (2009) Precambrian Crustal evolution and Metallogeny. In: Economic Mineralization, K.L. Shrivastava (Ed.), Scientific Publ., 545p.
Rybach, L., Werner, D., Mueller, S., and Berset, G. (1977) Heat flow, heat production and crustal dynamics in the Central Alps, Switzerland. Tectonophysics, v.41, pp.113–126.
Sharma R.S. (1994) High heat production granites of Jhunjhunu area, Rajasthan, India. Bull. Indian Geol. Assoc., v.27, pp.55–61.
Shrivastava, K.L., Prajapat, T., Mathur, A., Gaur, V., Dadhich, C.P., Chouhan, M. and Tripathi, B. (2013) High radioactive heat-producing, economically potential granites around jodhpur city, Malani Igneous Suite, Northwestern India. Jour. Appld. Geochem., v.15(4), pp.410–418.
Shrivastava, K. L., Mathur, A., Gaur, V., Prajapat, T., Dadhich, C. P., Chouhan, M. and Tripathi, B. (2014) Determination of High Heat Production to evaluate Radioactive Mineralization Potential of Granites of Mungeria Ring Complex of Malani Igneous Suite, Rajasthan, India. In: ‘Geo-Resources’ K.L. Shrivastava and Arun Kumar (Eds.), Scientific Publ., India. pp.264–269.
Singh, A.K. and Vallinayagam, G. (2009) Radioactive element distribution and rare-metal mineralization in anorogenic acid volcano-plutonic rocks of the Neo-Proterozoic Malani Felsic Province, western Peninsular, India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.73(6), pp.837–853.
Singh, H.K., Kumar, Y., Chandrasekharan, D., Gurav, T. and Singh, B. (2014) High Heat Producing Granites of East Dharwar Craton around Gugi, Karnataka and their possible influence on the evolution of Rajapur thermal springs, Deccan volcanic Province, India. Geother. Energy, v.2(2) doi:10.1186/s40517–014-0002–4
Singh, L. S. and Vallinayagam, G. (2012) High Heat Producing volcano-Plutonic Rocks of the Siner Area malani Igneous Suite, Western Rajasthan, India. Int. Jour. Geosci. Vol. 3. Pp 1137–1141. Doi:10.4236/ijg.2012.35115
Smith, R.L. and Shaw H.R. (1975) Igneous related thermal system assessment of geothermal resources of United States’. In: D.E. Whiten and D.C. Wiiliams, (Eds.), USGS, Washington, D.C. Circ., v.726, pp.58–83.
Srivastava, P.K. (2003) High heat producing granites of Degana, Rajasthan. Ind. Jour. Geochem., v.18, pp.149–155.
Taylor, S.R. and McLennan, S.M. (1985) The continent crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford, p.312.
Taylor, S. R. (1964) Trace element abundance and the chondritic earth model. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.28, pp.1989–1999.
Valdiya, K.S. (2010) The making of India Geodynamic Evolution. McMillan, p.816.
Vallinayagam, G. and Singh, L. G. (2011) Radioactive Heat Producing Felsic to Intermediate Volcano—Plutonic Rocks of Dhiran Area, Malani Igneous Suite, Western India. Indian Jour. Earth Sci., v.4(2), pp.68–97.
Wasserburg, G.G. (1964) Relative contribution of U, Th and K to heat production in the Earth’s Crust. Sci., v.143, pp.465–467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrivastava, K.L., Ram, D. & Gaur, V. High heat producing radioactive granites of malani igneous suite at northeast of Jodhpur, northwestern India. J Geol Soc India 89, 291–294 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0601-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0601-3