Abstract
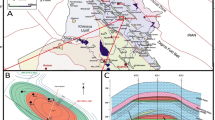
Continuous exploration has triggered a heated debate on hydrocarbon resource potential in the southern slope zone of the Kuqa foreland basin, and sources of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic oil and gas have become a key problem to be solved in this region. Composition and organic geochemical parameters of crude oil and natural gas from the southern slope zone of the Kuqa foreland basin were illustrated in order to reveal their origin by using a combination of gas chromatograph (GC), gas chromatogram-mass spectrum (GC-MS) and carbon isotope analyses. The characteristics of crude oil, such as low density, viscosity, solidification point and sulfur content, and high wax content, indicate that source of the crude oil is continental. The biomarker compositions of crude oil are characterized by low to medium molecular weight compounds (n-C12 to n-C20), high Pr/Ph ratios (>1.0), low phytane/n-C18 ratios (0.06–0.54), and predominant regular sterane C29. All biomarker parameters clearly indicate that the crude oil was derived mainly from algae and aquatic plankton and deposited under weak reduction-oxidation environment, and has the characteristics of mixed kerogens. The Cretaceous crude oil was mainly derived from the Triassic lacustrine source rocks, which also contributed to the Paleogene crude oil together with Jurassic coal source rocks. Natural gas is characterized by moderate methane content, high heavy hydrocarbon and nitrogen content, and no hydrogen sulfide. The methane and ethane in Paleogene natural gas are relatively rich in 13C with δ13C1 and δ13C2 values ranging from −37.3‰ to −31.2‰ (mean = −34.25‰) and from −25‰ to −21.3‰ (mean = −23.09‰), respectively, indicating the coal-derived gas from the Middle and Lower Jurassic strata. Hydrocarbon products in the southern slope zone of the Kuqa foreland basin are primarily generated from source rocks in the mature stage. The low-amplitude structural and lithologic traps with the updip pinch-out sand bodies or plugging secondary fault at relatively high tectonic positions are the most favorable areas for discovery and breakthrough in the study area. Results of this study will provide useful information for controlling factors of reservoirs and oil and gas exploration deployment in the southern slope zone of the Kuqa foreland basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bernard, B. B., Brooks, J. M., Sackett, W. M., 1978. Light Hydrocarbons in Recent Texas Continental Shelf and Slope Sediments. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 83(C8): 4053–4061. https://doi.org/10.1029/jc083ic08p04053
Berner, U., Faber, E., 1996. Empirical Carbon Isotope/Maturity Relationships for Gases from Algal Kerogens and Terrigenous Organic Matter, Based on Dry, Open-System Pyrolysis. Organic Geochemistry, 24(10/11): 947–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0146-6380(96)00090-3
Cheng, K. M., Jin, W. M., He, Z. H., et al., 1987. Composition Characteristics of Light Hydrocarbons in Continental Oil and Condensate and Their Geological Significance. Petroleum Expoloration and Development, 14(1): 34–43 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Dai, J. X., Qi, H. F., 1989. The Relations between δl3C and Ro of Coaliferous Natural Gases in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 9: 690–695 (in Chinese)
Didyk, B. M., Simoneit, B. R. T., Brassell, S. C., et al., 1978. Organic Geochemical Indicators of Palaeoenvironmental Conditions of Sedimentation. Nature, 272: 216–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/272216a0
Du, J. H., Wang, Z. M., Hu, S. Y., et al., 2012. Formation Conditions and Geological Characteristics of Deep Giant Gas Provinces in the Kuqa Foreland Thrust Belt. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(4): 413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1876-3804(12)60058-5
Feng, J., Gao, Z., Cui, J., et al., 2018. Reservoir Porosity Evolution Characteristics and Evaluation of the Jurassic Deep Reservoir from Dibei in Kuqa Depression: Insight from Diagenesis Modeling Experiments under the Influence of Burial Mode. Advances in Earth Science, 33(3): 305–320 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Jiang, Z. X., Li, L. X., Song, Y., et al., 2010. Control of Neotectonic Movement on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Kuqa Foreland Basin, West China. Petroleum Science, 7(1): 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12182-010-0006-z
Li, F., Jiang, Z. X., Li, Z., et al., 2015. Enriched Mechanism of Natural Gas of Lower Jurassic in Dibei Area, Kuqa Depression. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 40(9): 1538–1548. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2015.138 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, X. D., 1999. Geological Characters and Forming History of Yangtake Oil Field. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 26(6): 30–32, 7 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, Z., Jiang, Z. X., Pang, X. Q., et al., 2013. Genetic Types of the Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, NW China. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 38(1): 156–164. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2013.015 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liang, D. G., Zhang, S. C., Zhao, M. J., et al., 2002. Hydrocarbon Sources and Stages of Reservoir Formation in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(1): 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02902820
Liu, C., Xu, Z. P., Chen, G., et al., 2019. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Conditions and Evolution Process of ZQ1 Large Condensate Gas Field in Qiulitage Structural Belt, Tarim Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 39: 8–17 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, J. L., Jiang, Z. X., Liu, K. Y., et al., 2015. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Process of the Yaha Tectonic Belt, Kuqa Foreland Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 26(1): 43–53 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, J. L., Jiang, Z. X., Liu, K. Y., et al., 2016. Hydrocarbon Sources and Charge History in the Southern Slope Region, Kuqa Foreland Basin, Northwestern China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 74: 26–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.04.004
Liu, J. L., Liu, K. Y., Jiang, Z. X., et al., 2018. Cretaceous Hydrocarbon Accumulation Process in Yudong Area, Kuqa Foreland Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 39(6): 620–630 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lorant, F., Prinzhofer, A., Behar, F., et al., 1998. Carbon Isotopic and Molecular Constraints on the For-mation and the Expulsion of Thermogenic Hydrocarbon Gases. Chemical Geology, 147(3/4): 249–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(98)00017-5
Lu, X. S., Liu, K. Y., Zhuo, Q. G., et al., 2012. Palaeo-Fluid Evidence of the Multi-Stage Hydrocarbon Charges in Kela-2 Gas Field, Kuqa Foreland Basin, Tarim Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(5): 574–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1876-3804(12)60078-0
Luo, X., Jiang, Z. X., Li, Z., et al., 2015. The Properties of Petroleum Inclusions and Stages of Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Mesozoic — Cenozoic Reservoirs in Yingmaili Area of Tabei Uplift, Tarim Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(1): 60–66 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lü, X. X., Jin, Z. J., 2000. Ananysis on Reservoir Fomation Process in Yangtake Structural Belt of Tabei Uplift. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 24(1): 48–52 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lü, X. M., Pi, X. J., Ren, Z. L., et al., 2004. The Geological Characteristics of the Petroleum System in Kucha Foreland Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 15(3): 214–217 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Peters, K. E., Moldowan, J. M., 1993. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs. 363
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., Moldowan, J. M., 2005. The Biomarker Guide (2nd Ed.). Cambridge University Press, New York
Prinzhofer, A. A., Huc, A. Y., 1995. Genetic and Post-Genetic Molecular and Isotopic Fractionations in Natural Gases. Chemical Geology, 126 (3/4): 281–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(95)00123-9
Radke, M., Welte, D. H., Willsch, H., 1982. Geochemical Study on a Well in the Western Canada Basin: Relation of the Aromatic Distribution Pattern to Maturity of Organic Matter. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46(1): 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(82)90285-x
Tian, Z. J., Zhang, G. Y., Zou, H. Y., et al., 2001. The Major Controlling Factors and Pool-Forming Pattern of Oil and Gas Reservoirs in Kuqa Petroleum System, Tarim Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 28(5): 12–16 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, P. W., Pang, X. Q., Jiang, Z. X., et al., 2014. Critical Phyisical Conditions for Accumulation of Yinan 2 “Continuous” Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoir, Kuqa Depression. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(10): 1381–1390. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2014.130 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, Z. M., 2014. Formation Mechanism and Enrichment Regularities of Kelasu Subsalt Deep Large Gas Field in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(2): 153–166 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, Z. M., Li, Y., Xie, H. W., et al., 2016. Geological Understanding on the Formation of Large-Scale Ultra-Deep Oil-Gas Field in Kuqa Foreland Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 21(1): 37–43 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, Z. M., Long, H. S., 2010. Different Hydrocarbon Accumulation Histories in the Kelasu-Yiqikelike Structural Belt of the Kuqa Foreland Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica—English Edition, 84(5): 1195–1208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.2010.00290.x
Wang, Z., Tian, J., Wang, Q., 2004. Petroleum Exploration and Practice in Tarim Basin. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xiao, Z. Y., Huang, G. H., Lu, Y. H., et al., 2004. Rearranged Hopanes in Oils from the Quele 1 Well, Tarim Basin, and the Significance for Oil Correlation. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 31(2): 35–37 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, R. H., Zou, W. H., Chen, G., et al., 2018. Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Exploration Significance of the Huge Lower Cretaceous Lacustrine Sand Bar in the Northern Tarim Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 39(8): 845–857 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, S. C., Zhang, B., Zhu, G. Y., et al., 2011. Geochemical Evidence for Coal-Derived Hydrocarbons and Their Charge History in the Dabei Gas Field, Kuqa Thrust Belt, Tarim Basin, NW China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 28(7): 1364–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.02.006
Zhao, J. Z., Dai, J. X., 2003. Timing and Filling History of Natural Gas Reservoirs in Kuqa Foreland Thrust Belts, Tarim Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 23(2): 6–10 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhao, M. J., Lu, X. S., Zhuo, Q. G., et al., 2015. Characteristics and Distribution Law of Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Kuqa Foreland Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(4): 395–404 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhao, M. J., Wang, Z. M., Zhang, S. C., et al., 2005. Accumulation and Features of Natural Gas in the Kuqa Foreland Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(3): 414–422 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, G. Y., Yang, H. J., Zhang, B., et al., 2013. Ultra-Long Distance Migration of Hydrocarbon. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9): 3192–3212 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, Y. M., Weng, H. X., Su, A. G., et al., 2005. Geochemical Characteristics of Tertiary Saline Lacustrine Oils in the Western Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. Applied Geochemistry, 20(10): 1875–1889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.06.003
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by the National Science and Technology Major Project in the 13th Five-Year Plan (Nos. 2016ZX05003-001, 2017ZX05001-002), the Science and Technology Project of the China Petroleum and Natural Gas Co. Ltd. (No. KT2018-02-06). We sincerely thank the Tarim Oilfield Company of PetroChina for allowing the data to be published. We also acknowledge the colleagues of PetroChina Hangzhou Research Institute of Geology, Ge Chen, Qinglu Zeng, and Junpeng Wang, for their suggestions in the process of the paper’s completion. Sincere thanks goes to Yujuan Qin, Yuanyuan Hu, Dongxiao Wei and Wei Chen for their helps. Yue Liang and Xiaojing Wang from China University of Geoscience (Wuhan) are thanked for language polishing. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1412-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Chen, S., Zhao, J. et al. Geochemical Characteristics and Origin of Crude Oil and Natural Gas in the Southern Slope Zone, Kuqa Foreland Basin, NW China. J. Earth Sci. 33, 820–830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1412-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1412-4