Abstract
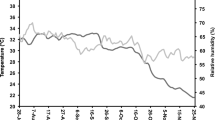
Participatory on-farm trials were conducted to assess effectiveness of Purdue Improved Crop Storage (PICS™) bags for storage of maize in small-scale farmers’ stores in rural villages in eastern Kenya. A PICS bag is a three-layered hermetic bag-system that forms a barrier against the influx of oxygen and the escape of carbon dioxide. Jute, woven polypropylene or PICS bags were filled with shelled maize grain, purchased from the participating farmers, and the three sets of bags kept in the farmers’ own stores for 35 weeks. Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the PICS bags were monitored, as well as the temperature and relative humidity in all the bags. Grain moisture, live insect population, grain damage and weight loss were examined at intervals of seven weeks. Oxygen and carbon dioxide composition demonstrated that PICS bags are capable of sustaining good air-barrier properties under farmer storage conditions. Moreover, moisture content of maize stored in PICS bags did not change throughout the storage period whereas the moisture content of maize stored in polypropylene and jute bags decreased significantly in the final 14 weeks. Maize stored in PICS bags remained free from insect infestation and the weight loss due to insect damage was below 1 %. On the contrary, polypropylene and jute bags permitted profuse build-up of insect populations. At 35 weeks, grain damage reached 77.6 % and 82.3 % corresponding to 41.2 % and 48.5 % weight loss in the polypropylene and jute bags respectively. These findings demonstrate that PICS bags are effective in controlling losses caused by storage pests under farmer storage conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe, F., Tefera, T., Mugo, S., Beyene, Y., & Vidal, S. (2009). Resistance of maize varieties to the maize weevil (Sitophilus zeamais) (motsch.) (coleoptera: curculionidae). African Journal of Biotechnology, 8, 5937–5943.
Affognon, H., Mutungi, C., Sanginga, P., & Borgemeister, C. (2015). Unpacking postharvest losses in sub-Saharan Africa. A Meta -Analysis. World Development., 66, 49–68.
Amoson, J. T., Conh de Beysac, B., Phlogene, B. J. R., Bergvision, D., Serratos, J. A., & Mihm, J. A. (1997). Mechanisms of resistance in maize grain to maize weevil and larger grain borer. Crop Science, 43, 2043–2049.
Anankware, P. J., Fatunbi, A. O., Afreh-Nuamah, K., Obeng-Ofori, D., & Ansah, A. F. (2012). Efficacy of the multiple-layer hermetic storage bag for biorational management of primary beetle pests of stored maize. Academic Journal of Entomology., 5, 47–53.
Annis, P. C. (1986). Towards rational controlled atmosphere dosage schedules: a review of current knowledge. In E. Donahaye & S. Navarro (Eds.), Stored Products Protection. Proceedings of the 4th International Working Conference on Stored-Product Protection (pp. 128–148). Jerusalem, Israel: Tel Aviv, Israel. Maor-Wallach Press.
Bailey, S. W., & Banks, H. J. (1980). A review of recent studies of the effects of controlled atmospheres on stored product pests. In J. Shejbal (Ed.), Controlled atmosphere storage of grains (pp. 101–118). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company.
Banks, H. J., & Annis, P. C. (1990). Comparative advantage of high CO2 and low O2 types of controlled atmospheres for grain storage. In M. Calderon & R. Barkai-Golan (Eds.), Food preservation by modified atmospheres (pp. 93–119). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press Inc.
Baoua, I. B., Margam,V., Amadou, L., & Murdock, L. L. (2012a). Performance of triple bagging hermetic technology for postharvest storage of cowpea grain in Niger. Journal of Stored Products Research 51: 81–85.
Baoua, I. B., Amadou, L., Ousmane, B., Baributsa, D., & Murdock, L. L. (2014). PICS bags for post-harvest storage of maize grain in West Africa. Journal of Stored Products Research, 58, 20–28.
Baributsa, D., Djibo, K., Lowenberg-DeBoer, J., Moussa, B., & Baoua, I. (2014). The fate of triple-layer plastic bags used for cowpea storage. Journal of Stored Products Research, 58, 97–102.
Biliwa, A., & Richter, J. (1990). Efficacité des insecticides binaries en poudre sur du maïs stocké en sacs. In F. Fleurat-Lessard & P. Ducom (Eds.), Stored Products Protection. Proceedings of the 5th International Working Conference on Stored-Product Protection (pp. 1577–1536). Bordeaux, France: Imprimerie du Médoc.
Birkinshaw, L. A., Hodges, R. J., Addo, S., & Riwa, W. (2002). Can ‘bad’ years for damage by Prostephanus truncatus be predicted? Crop Protection, 21, 783–791.
Boxall, R. (1986). A critical review of the methodology for assessing farm-level grain losses after harvest. tropical Development and Research Institute. London: Great Britain.
Boxall, R. A. (2002). Damage and loss caused by the larger grain borer Prostephanus truncatus. Integrated Pest Management Reviews, 7, 105–121.
Clevo, W., & Clem, T. (2001). Why farmers continue to use pesticides despite environmental, health and sustainability costs. Ecological Economics, 39, 449–462.
Cofie-Agblor, R., Muir, W. E., Sinicio, R., Cenkowski, S., & Jayas, D. S. (1995). Characteristics of carbon dioxide sorption by stored wheat. Journal of Stored Products Research, 31, 317–324.
Compton, J. A. F., Floyd, S., Magrath, P. A., Addo, S., Gbedevi, S. R., Agbo, B., Bokor, G., Amekupe, S., Motey, Z., Penni, H., & Kumi, S. (1998). Involving grain traders in determining the effect of post-harvest insect damage on the price of maize in African markets. Crop Protection, 17, 483–489.
De Groote, H., Kimenju, C. S., Likhayo, P., Kanampiu, F., Tefera, T., & Hellin, J. (2013). Effectiveness of hermetic systems in controlling maize storage pests in Kenya. Journal of Stored Products Research, 53, 27–36.
Denloye, A. A., Tesilim, K. O., Negbenebor, H., & Makanjuola, W. A. (2008). Assessment of the efficacy of actellic and sumithion in protecting grains from insect infestation during storage. Journal of Entomology, 5, 24–30.
Donahaye, E. (1990). Laboratory selection of resistance by the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum (herbst) to an atmosphere of low oxygen concentration. Phytoparasitica, 18, 189–202.
Fiedler, L. A. (1994). Rodent Pest Management in East Africa. In Plant Production and Protection Paper No. 123. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
Friedlander, A., Navarro, S., & Silhacek, D. L. (1984). The effect of carbon dioxide on NADPH production in Ephestia cautella (wlk.) pupae. Comparative Biochemistry Physiology. B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology., 77B, 839–842.
Gitonga, Z. M., De Groote, H., Kassie, M., & Tadele, T. (2013). Impact of metal silos on households’ maize storage, storage losses and food security: An application of a propensity score matching. Food Policy, 43, 44–55.
Golob, P., & Hanks, C. (1990). Protection of farm stored maize against infestation by Prostephanus trancatus (horn) and Sitophilus species in Tanzania. Journal of Stored Products Research, 26, 187–198.
Hodges, R. J. (2002). Detection and monitoring of the larger grain borer, Prostephanus truncatus (horn) (coleoptera: bostrichidae). Integrated Pest Management Reviews, 7, 223–243.
Jay, E. G. (1983). Imperfections in our current knowledge of insect biology as related to their response to controlled atmospheres. In B. E. Ripp, H. J. Banks, E. J. Bond, D. J. Calverley, E. G. Jay, & S. Navarro (Eds.), Controlled atmosphere and fumigation in Grain storage, 11–22 April 1983, Perth (pp. 493–508). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Western Australia. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company.
Kimenju, S.C., and De Groote, H. (2010). Economic Analysis of Alternative Maize Storage Technologies in Kenya Cape Town, South Africa. African Association of Agricultural Economists (AAAE) and 48th Agricultural Economists Association of South Africa (AEASA)
Lamboni, Y., & Hell, K. (2009). Propagation of mycotoxigenic fungi in maize stores by postharvest insects. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 29(1), 31–39.
Lea, T. J., & Ashley, C. C. (1978). Increase in free Ca2+ in muscle after exposure to CO2. Nature, 275, 236–238.
Madrid, F. J., White, N. D. G & Loschiavo, S. R. (1990). Insects in stored cereals, and their association with farming practices in Southern Manitoba. Canadian Entomologist 122, 515–523.
Makundi, R. H., Mbise, T. J., & Kilonzo, B. S. (1991). Observations on the role of rodents in crop losses in Tanzania and control strategies. Beiträge Zur Tropischen Landwirtschaft Und Vertirinärmedizin., 29, 465–474.
Meikle, W. G., Markham, R. H., Nansen, C., Holst, N., Degbey, P., Azoma, K., & Korie, S. (2002). Pest management in traditional maize stores in West Africa: a farmer’s perspective. Journal of Economic Entomology, 95, 1079–1088.
Moreno-Martinez, E., Jimenez, A. S., & Vazquez, M. E. (2000). Effect of Sitophilus zeamais and Aspergillus chevalieri on the oxygen level in maize stored hermetically. Journal of Stored Products Research, 36, 25–36.
Murdock, L. L., Dogo, S. D., Ntoukam, G., Kitch, L., & Shade, R. E. (2003). Preservation of cowpea grain in sub-Saharan Africa-Bean/Cowpea CRSP contributions. Field Crops Research, 82, 169–178.
Murdock, L. L., Margam, V. M., Baoua, I., Balfe, S., & Shade, R. E. (2012). Death by desiccation: effects of hermetic storage on cowpea bruchids. Journal of Stored Products Research, 49, 166–170.
Mutambuki, K., & Ngatia, C. M. (2012). Assessment of grain damage and weight loss on farm stored maize in highlands areas of Bungoma district, Kenya. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, B 2, 349–361.
Mutiro, C. F., Giga, D. P., & Chetsanga, P. (1992). Postharvest damage in small farmers’ stores. Zimbabwe. Journal of Agricultural Research, 30, 49–59.
Ngatia, C. M., & Kimondo, M. (2011). Comparison of three methods of weight loss determination on maize stored in two farmer environments under natural infestation. Journal of Stored Products and Postharvest Research, 254–260.
Nicolas, G., & Sillans, D. (1989). Immediate and latent effects of carbon dioxide on insects. Annual Review of Entomology, 34, 97–116.
Njoroge, A. W., Affognon, H. D., Mutungi, C. M., Manono, J., Lamuka, P. O., & Murdock, L. L. (2014). Triple bag hermetic storage delivers a lethal punch to Prostephanus truncatus (horn) (coleoptera: bostrichidae) in stored maize. Journal of Stored Products Research, 58, 12–19.
Nukenine, E. N., Monglo, B., Awasom, I., Tchuenguen, F. F. N., & Ngassoum, M. B. (2002). Farmers’ perception on some aspects of maize production and infestation level of stored maize by Sitophilus zeamais in the ngaoundere region of Cameroon. CJBBS, 12, 18–30.
Obeng-Ofori, D. (2011). Protecting grain from insect pest infestations in Africa: producer perceptions and practices. Stewart Postharvest Reviews., 3, 1–8.
Ognakossan, K. E., Tounou, A. K., Lamboni, Y., & Hell, K. (2013). Post-harvest insect infestation in maize grain stored in woven polypropylene and in hermetic bags. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 33, 71–81.
Ortega, C.A. (1987). Insect Pests of Maize: a Guide for Field Identification. CIMMYT, Mexico, D.F. Retrieved on 23/01/2015 from: http://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PNAAX152.pdf
Schwartz, B. E., & Burkholder, W. E. (1991). Development of the granary weevil (coleoptera: curculionidae) on barley, corn, oats, rice, and wheat. Journal of Economic Entomology, 84, 1047–1052.
Sori, W., & Ayana, A. (2012). Storage pests of maize and their status in jimma zone, Ethiopia. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 28, 4056–4060.
Stathers, T. E., Riwa, W., Mvumi, B. M., Mosha, R., Kitandu, L., Mngara, K., Kaoneka, B., & Morris, M. (2008). Do diatomaceous earths have potential as grain protectants for small-holder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa? The case of Tanzania. Crop Protection, 27, 44–70.
Subramanyam, B., & Hagstrum, D. W. (1996). Resistance measurement and management. In B. Subramanyam & D. W. Hagstrum (Eds.), Integrated Management of Insects in Stored Products (pp. 331–397). New York, USA: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Tadele, T., Kanampiu, F., De Groote, H., Hellin, J., Mugo, S., Kimenju, S., Beyene, Y., Boddupalli, P. M., Shiferaw, B., & Banziger, M. (2011). The metal silo: An effective grain storage technology for reducing post-harvest insect and pathogen losses in maize while improving smallholder farmers’ food security in developing countries. Crop Protection, 30, 240–245.
Vachanth, M. C., Subbu Rathinam, K. M., Preethi, R., & Loganathan, M. (2010). Controlled atmosphere storage technique for safe storage of processed little millet. Academic Journal of Entomology., 3, 12–14.
Vales, M. I., Rao, G. V. R., Sudini, S. B., Patil, S. B., & Murdock, L. L. (2014). Effective and economic storage of pigeonpea seed in triple layer plastic bags. Journal of Stored Products Research, 58, 29–38.
Williams, S. B., Baributsa, D., & Woloshuk, C. (2014). Assessing Purdue Improved Crop Storage (PICS) bags to mitigate fungal growth and aflatoxin contamination. Journal of Stored Products Research, 59, 190–196.
World Bank, (2010). Missing food: the case of postharvest grain losses in sub-Saharan Africa. Washington, DC: World Bank, 116 pp
Yamamoto, A., & Mitsuda, H. (1980). Characteristics of carbon dioxide gas adsorption by grain and its components. In J. Shejbal (Ed.), Controlled atmosphere storage of grains international symposium, 12–15 may 1980 (pp. 247–258). Rome, Italy: Castelgandolfo.
Zia-Ur-Rehman (2006). Storage effects on nutritional quality of commonly consumed cereals. Food Chemistry, 95, 53–57.
Acknowledgments
C. Mutungi is thankful to Grand Challenges Canada for a grant (GCC-0423-01) to conduct this study. The authors thank the International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology (icipe) for institutional support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng’ang’a, J., Mutungi, C., Imathiu, S.M. et al. Low permeability triple-layer plastic bags prevent losses of maize caused by insects in rural on-farm stores. Food Sec. 8, 621–633 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-016-0567-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-016-0567-9