Abstract
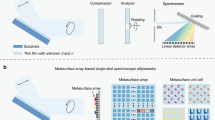
We propose a novel spectroscopic ellipsometry capable of measuring line profile of the film thicknesses with a single image at once. By adopting a polarization-pixelated CMOS camera and an imaging spectrometer, spatial, spectral and polarization information of the film structure can be acquired at the frame rate of the camera without any mechanical or electrical adjustments of polarizing optical components. The proposed system is beneficial not only to provide film thickness of the specimen with a single image acquisition, but also to analyze the spatial features of the film layers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothen, A. (1945). The ellipsometer, an apparatus to measure thicknesses of thin surface films. Review of Scientific Instruments, 16, 26–30.
Engelsen, D. D. (1971). Ellipsometry of anisotropic films. JOSA, 61, 1460–1466.
Jellison, G. E., Jr. (1998). Spectroscopic ellipsometry data analysis: measured versus calculated quantities. Thin Solid Films, 313, 33–39.
Boer, J. H. W. G., Kroesen, G. M. W., & Hoog, F. J. (1997). Spectroscopic rotating compensator ellipsometry in the infrared: retarder design and measurement. Measurement Science and Technology, 8, 484–492.
Chen, L. Y., & Lynch, D. W. (1987). Scanning ellipsometer by rotating polarizer and analyzer. Applied Optics, 26, 5221–5228.
Aspnes, D. E. (2004). Optimizing precision of rotating-analyzer and rotating-compensator ellipsometers. JOSA A, 21, 403–410.
Acher, O., Bigan, E., & Drévillon, B. (1989). Improvements of phase-modulated ellipsometry. Review of Scientific Instruments, 60, 65–77.
Kewu, L., Rui, Z., Ning, J., Youhua, C., Minjuan, Z., Liming, W., et al. (2017). Fast and full range measurements of ellipsometric parameters using a 45 dual-drive symmetric photoelastic modulator. Optics Express, 25, 5725–5733.
Asinovski, L., Beaglehole, D., & Clarkson, M. T. (2008). Imaging ellipsometry: quantitative analysis. Physica Status Solidi, 205, 764–771.
Okabe, H., Matoba, K., Hayakawa, M., Taniguchi, A., Oka, K., Naito, H., & Nakatsuka, N. (2005). New configuration of channeled spectropolarimeter for snapshot polarimetric measurement of materials. Advanced Characterization Techniques for Optics, Semiconductors, and Nanotechnologies II. In Proc. SPIE 5878, p. 58780H.
Okabe, H., Hayakawa, M., Naito, H., Taniguchi, A., & Oka, K. (2007). Spectroscopic polarimetry using channeled spectroscopic polarization state generator (CSPSG). Optics Express, 15, 3093–3109.
Kim, D. H., Yun, Y. H., & Joo, K.-N. (2017). SPARSE (spatially phase-retarded spectroscopic ellipsometry) for real-time film analysis. Optics Letters, 42, 3189–3192.
Vilas, J. L., Sanchez-Brea, L. M., & Bernabeu, E. (2013). Optimal achromatic wave retarders using two birefringent wave plates. Applied Optics, 52, 1892–1896.
Tompkins, H. G., & Irene, E. I. (2005). Handbook of ellipsometry. Berlin: Springer.
Millerd, J. E., & Brock, N. J. (2001). Methods and apparatus for splitting, imaging, and measuring wavefronts in interferometry. U. S. Patent 6,304,330.
Creath, K., & Goldstein, G. (2012). Dynamic quantitative phase imaging for biological objects using a pixelated phase mask. Biomedical Optics Express, 3, 2866–2880.
Funding
Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, 2018R1D1A1B07040434.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Park, H.M. & Joo, KN. Single Shot Line Profile Measurement of Multi-layered Film Thicknesses. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 21, 2089–2094 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00410-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00410-z