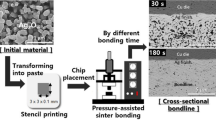
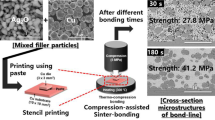
Abstract
To accomplish rapid chip attachment and produce a bondline between Cu finishes that provides both high-temperature thermo-mechanical reliability and superior thermal conductance, compression-assisted sinter bonding at 300 ℃ was performed in air through the in situ formation of active Ag atoms by the decomposition of 200 nm Ag2O during a redox reaction in the bonding paste. The remarkable sinterability of the generated Ag atoms and the effect of the reducing agent, which was added to the paste to remove the oxide layer on the Cu finish, induced extremely rapid sinter bonding between Cu finishes. Accordingly, the bonding under compression of 2 and 5 MPa resulted in a sufficient shear strength exceeding 27.0 MPa with a dense bondline microstructure even after a significantly short bonding time of 30 s. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that the bonding between the bondline and Cu finish was accomplished through the overlapping of Ag and Cu lattices by inter-diffusion of Ag and Cu atoms without the formation of any compound. Therefore, high-speed chip attachment was successfully achieved even for low-cost Cu finishes.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.S. Chin, K.Y. Cheong, A.B. Ismail, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41, 824 (2010)
H. Zhang, C. Chen, J. Jiu, S. Nagao, K. Suganuma, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 8854 (2018)
D. Kim, C. Chen, S. Noh, S.-J. Lee, Z. Zhang, Y. Kimoto, T. Sugahara. K. Suganuma, Microelectron. Reliab. 100–101, 113380 (2019)
W.S. Hong, M.S. Kim, C. Oh, Y. Joo, Y. Kim, K.-K. Hong, JOM 72, 889 (2020)
T.F. Chen, K.S. Siow, J. Alloys Compd. 866, 158783 (2021)
S. Zhang, Q. Wang, T. Lin, P. Zhang, P. He, K.-W. Paik, J. Manuf. Process 62, 546 (2021)
E.B. Choi, J.-H. Lee, Met. Mater. Int. 27, 5278 (2021)
D. Namgoong, K.S. Siow, J.-H. Lee, Met. Mater. Int. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01224-6
E. Ide, S. Angata, A. Hirose, K.F. Kobayashi, Acta Mater. 53, 2385 (2005)
J. Yan, G. Zou, A. Wu, J. Ren, J. Yan, A. Hu, Y. Zhou, Scr. Mater. 66, 582 (2012)
T. Morita, Y. Yasuda, E. Ide, Y. Akada, A. Hirose, Mater. Trans. 49, 2875 (2008)
S. Takata, T. Ogura, E. Ide, T. Morita, A. Hirose, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 507 (2013)
T. Ogura, T. Yagishita, S. Takata, T. Fujimoto, A. Hirose, Mater. Trans. 54, 860 (2013)
T. Ogura, S. Takata, M. Takahashi, A. Hirose, Mater. Trans. 56, 1030 (2015)
F. Mu, Z. Zhao, G. Zou, H. Bai, A. Wu, L. Liu, D. Zhang, Y.N. Zhou, Mater. Trans. 54, 872 (2013)
T. Matsuda, K. Inami, K. Motoyama, T. Sano, A. Hirose, Sci. Rep. 8, 10472 (2018)
K. Asama, T. Matsuda, T. Ogura, T. Sano, M. Takahashi, A. Hirose, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 702, 398 (2017)
K. Motoyama, T. Matsuda, T. Sano, A. Hirose, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 5780 (2018)
H. Zhang, Y. Gao, J. Jiu, K. Suganuma, J. Alloys Compd. 696, 123 (2017)
L. He, J. Li, X. Wu, F. Mu, Y. Wang, Y. Lu, T. Suga, Metals 10, 315 (2020)
Y.-J. Lee, J.-H. Lee, Electron. Mater. Lett. 18, 94 (2022)
N.L. Yong, A. Ahmad, A.W. Mohammad, Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 4, 155 (2013)
E.B. Choi, Y.-J. Lee, J.-H. Lee, J. Alloys Compd. 897, 163223 (2022)
E.B. Choi, J.-H. Lee, Appl. Surf. Sci. 580, 152347 (2022)
K.P. Jayadevan, N.V. Kumer, R.M. Mallya, K.T. Jacob, J. Mater. Sci. 35, 2429 (2000)
I. Kim, S. Chun, J. Electron. Mater. 40, 1977 (2011)
G.B. Hoflund, Z.F. Hazos, Phys. Rev. B 62, 11126 (2000)
K. Suganuma, S.-J. Kim, K.-S. Kim, JOM 61, 64 (2009)
S. Zhang, Q. Wang, T. Lin, P. Zhang, P. He, K.-W. Paik, J. Manuf. Process. 62, 546 (2021)
J.H. Kim, J.-H. Lee, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 06JG01 (2016)
Y. Liu, S. Lin, H. Zhang, S. Nagao, C. Chen, K. Suganuma, Scr. Mater. 184, 1 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No: 2021R1A2C1007400). This paper was also supported by a Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P0008458, HRD Program for Industrial Innovation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YJ., Lee, JH. Ultrafast Sinter Bonding Between Cu Finishes Under Moderate Compression Using In Situ Derived Ag Formed via Low-Temperature Decomposition of Ag2O in the Bonding Paste. Met. Mater. Int. 29, 1775–1785 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01320-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01320-7