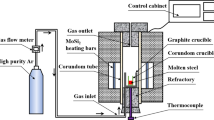
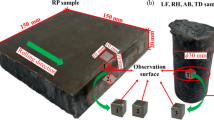
Abstract
In this paper, in order to identify the formation mechanism of duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions in steel, based on the two heats of commercial Ca-treated resulfurized steel, the characteristics of duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions in bars, blooms and CaO-Al2O3 oxides in molten steel were observed and analyzed. The results indicate that there are three types of duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions in steel. The first type with over 20% Ca in (Ca,Mn)S is named as “Type-C”, the second with 4–20% Ca in (Ca,Mn)S is named as “Type-MC” and the third with below 4% Ca in (Ca,Mn)S is named as “Type-M”. Their core oxides are mainly Ca-Mg–Al-O oxides. The aspect ratios of duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions in bars decrease as Ca content in (Ca,Mn)S increases. From Type-M to Type-C, CaO content in core oxides increases, and Ca content in wrapping (Ca,Mn)S increases. The shape of duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions can be controlled through controlling CaO content in core oxides. During solidification, CaO-Al2O3 oxides become as heterogeneous nucleation cores of MnS inclusions, duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions forming in this way, and Ca in wrapping (Ca,Mn)S come from CaO in core oxides. The higher CaO content in core oxides, the higher Ca content in wrapping (Ca,Mn)S. Under the condition with specific Ca/S ratio in steel, to obtain more duplex (Ca,Mn)S inclusions, numbers of Type-C should be decreased, and numbers of Type-MC and Type-M should be increased. To achieve this goal, the key is to obtain larger numbers of CaO-Al2O3 oxides with lower CaO and smaller sizes in molten steel.
Graphic abstract




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Lu, G. Cheng, J. Che, Met. Mater. Int. 25, 473 (2019)
A. Abyazi, A. Ebrahimi, Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 976 (2016)
C. Temmel, B. Karlsson, N. Ingesten, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 2995 (2006)
A. Wilson, Metall. 12, 233 (1979)
J. Jung, J. Shin, S. Lee, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24, 2658 (2015)
C. Temmel, B. Karlsson, N. Ingesten, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39, 1132 (2008)
N. Ånmark, A. Karasev, P. Jönsson, Mater. 8, 751 (2015)
N. Ånmark, T. Björk, Wear 368, 173 (2016)
N. Ånmark, A. Karasev, P. Jönsson, Steel Res. Int. 88, 1 (2017)
C. Leung, L. Vlack, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 12, 987 (1981)
N. Tsunekage, H. Tsubakino, ISIJ Int. 41, 498 (2001)
D. Froschhammer, H. Tensi, H. Zoller, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 11, 169 (1980)
S. Choudhary, A. Ghosh, ISIJ Int. 48, 1552 (2008)
R. Piao, H. Lee, Y. Kang, ISIJ Int. 53, 2132 (2013)
C. Blais, G.L.’ Espérance, H. LeHuy, Mater. Charact. 38, 25 (1997)
A. Larsson, S. Ruppi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 313, 160 (2001)
Y. Guo, S. He, G. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 2549 (2016)
J. Tian, T. Qu, D. Wang, Arch. Metall. Mater. 63, 1599 (2018)
X. Li, X. Long, L. Wang, Mater. 13, 619 (2020)
C. Cao, G. Wang, J. Li, Metall. Res. Technol. 118, 512 (2021)
T. Kano, T. Hanyuda, DENKI-SEIKO 75, 27 (2004)
T. Fujimatsu, N. Tsunekage, K. Hiraoka, Sanyo Techn. Rep. 11, 50 (2004)
D. Zhao, H. Li, C. Bao, ISIJ Int. 55, 2115 (2015)
Y. Chu, W. Li, Y. Ren, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50, 2047 (2019)
Q. Ren, W. Yang, L. Cheng, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51, 200 (2020)
H. Ahmad, B. Zhao, S. Lyu, Metals 11, 2051 (2021)
H. Kim, H. Lee, K. Oh, Met. Mater. Int. 6, 305 (2000)
F. Li, H. Li, D. Huang, Met. Mater. Int. 24, 1394 (2018)
Y. Ren, L. Zhang, Ironmaking Steelmaking 46, 558 (2019)
J. Guo, S. Cheng, Z. Cheng, Steel Res. Int. 84, 545 (2013)
J. Shin, J. Park, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49, 311 (2018)
C. Fincham, F. Richardson, Proc. R. Soc. A 223, 40 (1954)
G. Yan, Ph.D. thesis (University of Science and Technology, Beijing, 2006)
R. Geng, J. Li, C. Shi, ISIJ Int. 61, 1506 (2021)
S. Li, G. Cheng, Z. Miao, ISIJ Int. 58, 1781 (2018)
S. Gao, M. Wang, J. Guo, Met. Mater. Int. 27, 1306 (2021)
G. Zhang, K. Chou, U. Pal, ISIJ Int. 53, 761 (2013)
Y. Kang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 52, 2859 (2021)
B. Bramfitt, Metall. Trans. 1, 1987 (1970)
J. Lu, W. Qiu, G. Cheng, Iron. Steel 57, 118 (2022). ((Chinese))
Acknowledgements
The authors were grateful for support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51874034). The authors also appreciate the Shaoguan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd. for the technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Cheng, G., Lu, J. et al. Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Duplex (Ca,Mn)S Inclusions in Commercial Ca-Treated Resulfurized Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 29, 1019–1033 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01290-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01290-w