Abstract
A mold steel for plastic injection was subjected to low cycle fatigue (LCF) tests at temperatures of 25, 200, and 250 °C. LCF tests were carried out at a total strain amplitude (Δεt/2) from 0.004 to 0.012 under a constant strain rate of 0.01 s–1. Transmission electron microscope images showed that cyclic loading accelerated dislocation recovery as the LCF test temperature increased. The LCF life increased as a result of improvement in the ductility associated with dislocation recovery as the test temperature increased. The LCF behavior at the test temperature range followed the Coffin–Manson equation. Empirical equation was proposed to predict the LCF life of the mold steel within the test temperature range.
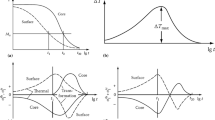
Graphic Abstract
Empirical equation was proposed to predict the LCF life of the mold steel considering the total strain amplitude and test temperature, and the calculated LCF life was in good agreement well with the experimental results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Kim, J. Jung, E. Baek, Y. Choi, K. Euh, Met. Mater. Int. 25, 353–363 (2019)
I. Khoubrou, B. Nami, S.M. Miresmaeili, Met. Mater. Int. 26, 196–204 (2020)
T. Mayer, L. Balogh, C. Solenthaler, E. Müller-Gubler, S.R. Holdsworth, Acta Mater. 60, 2485–2496 (2012)
P. Marmy, T. Kruml, J. Nucl. Mater. 377, 52–58 (2008)
M. Sauzay, H. Brillet, I. Monnet, M. Mottot, F. Barcelo, B. Fournier, A. Pineau, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 400–401, 241–244 (2005)
M.N. Batista, S. Hereñú, I. Alvarez-Armas, Procedia Eng. 74, 228–231 (2014)
D. Kim, S. Kim, Int. J. Fatigue 36, 24–29 (2012)
S. Hong, S. Lee, T. Byun, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 457, 139–147 (2007)
C.D. Lee, S.J. Yoo, Met. Mater. Int. 20, 601–612 (2014)
D. Firrao, P. Matteis, P.R. Spena, R. Gerosa, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 559, 371–383 (2013)
D. Firrao, R. Matteis, G. Scavino, G. Ubertalli, M.G. Ienco, M.R. Pinasco, E. Stagno, R. Gerosa, B. Rivolta, A. Silvestri, G. Silva, A. Ghidini, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 468–470, 193–200 (2007)
L.F. Coffin Jr., ASME Trans. 76, 931 (1954)
Y. Luo, C. Huang, R. Tian, Q. Wang, J. Iron Steel Inst. 20, 50–56 (2013)
Q. Zhou, L. Qian, J. Meng, L. Zhao, F. Zhang, Mater. Des. 85, 487–496 (2015)
J. Shin, Y. Kim, J. Lee, Met. Mater. Int. 24, 1412–1421 (2018)
P. Guo, L. Qian, J. Meng, F. Zhang, L. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 584, 133–142 (2013)
S. Hong, S. Lee, Int. J. Fatigue 26, 899–910 (2004)
C. Kanchanomai, Y. Mutoh, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 381, 113–120 (2004)
N. Costa, F.S. Silva, Int. J. Fatigue 33, 624–631 (2011)
S.R. Holdsworth, A.K.F. Maschek, L. Binda, E. Mazza, Procedia Eng. 2, 379–386 (2010)
C. Laird, Z. Wang, T. Ma, H.F. Chai, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 113, 245–257 (1989)
Acknowledgements
This paper was financially supported by Engineering Research Center (ERC) program (2011-0030058) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, JH., Lee, J. Effects of Test Temperature on Low Cycle Fatigue Behaviors in Large Mold Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 2292–2299 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00760-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00760-3