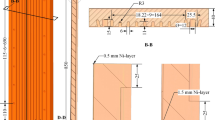
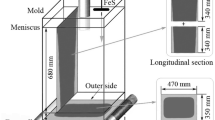
Abstract
A plane stress model was developed to study the coupled effect of mold taper and corner radius on the thermal–mechanical behavior of a 250 mm × 280 mm continuously cast bloom for a given special steel. Good agreement was obtained in both shell thickness and the off-corner cracking location from modeling and trial experiment. The results show that increasing mold taper results in the obvious decrease of surface temperature near the corner, while enlarging mold corner radius makes the shell surface temperature at the corner region more even with the mold taper between 0 and 1.5% m−1. It is also found that both the mold corner radius and taper are the key factors influencing the shell crack sensitivity but with different mechanism. For the internal crack, the mold taper takes more dominant effect for its corner radius between 0–10 mm, as the hoop strain at the solidification front decreases with increasing mold taper. For the surface crack, more sensitivity is noticed to the mold corner radius. Increasing mold corner radius leads to the increase of the surface hoop strain in the corner region, almost regardless of mold taper. The proper mold taper and corner radius for the present bloom casting should be 1.0–1.5% m−1 and 15–25 mm respectively.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρ :
-
Density of steel (kg m−3)
- C ceff :
-
Equivalent specific heat (J kg−1 °C−1)
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 °C−1)
- T :
-
Temperature (°C)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- f s :
-
Solid fraction
- x :
-
Coordinate along the width direction (m)
- y :
-
Coordinate along the thickness direction (m)
- h W :
-
Heat transfer coefficient of cooling water in the mold (W m−2 °C−1)
- T MC :
-
Temperature of the cold mold wall (°C)
- T W :
-
Temperature of the cooling water (°C)
- h T :
-
Heat transfer coefficient between the hot mold wall (W m−2 °C−1)
- T MH :
-
Temperature of hot the mold wall (°C)
- T S :
-
Temperature of the strand surface (°C)
- D :
-
Equivalent diameter of the water slot (m)
- u :
-
Average velocity of cooling water (m s−1)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (N s m−2)
- c :
-
Special heat of the water (J kg−1 °C−1)
- h Mold :
-
Heat transfer coefficient between mold wall surface and the mold flux (W m−2 °C−1)
- D Air :
-
Thickness of air gap (m)
- k Air :
-
Thermal conductivity of the air (W m−1 °C−1)
- D Sol :
-
Thickness of solid flux layer (m)
- k Sol :
-
Thermal conductivity of the solid flux layer (W m−1 °C−1)
- D Liq :
-
Thickness of liquid flux layer (m)
- k Liq :
-
Thermal conductivity of the liquid flux layer (W m−1 °C1)
- D gap :
-
Thickness of total flux film (m)
- h Shell :
-
Heat transfer coefficient between the mold flux and the strand surface (W m−2 °C−1)
- \(\dot{\varepsilon }\) :
-
Strain rate (s−1)
- α :
-
Thermal liner expansion coefficient (°C−1)
- E :
-
Young’s modulus (GPa)
- v :
-
Passion’s ratio
- ε :
-
Hoop strain
- σ:
-
Hoop stress (Pa)
References
J.K. Park, B.G. Thomas, I.V. Samarasekera, Ironmak. Steelmak. 29, 59 (2002)
Z.Z. Cai, M.Y. Zhu, ISIJ Int. 53, 1818 (2013)
S. Chakraborty, S. Ganguly, P. Talukdar, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 270, 132 (2019)
L.G. Zhu, R.V. Kumar, Ironmak. Steelmak. 34, 76 (2007)
T.M. Wang, S.W. Cai, J. Xu, Ironmak. Steelmak. 37, 341 (2010)
C. Chow, I.V. Samarasekera, B.N. Walker, Ironmak. Steelmak. 29, 61 (2002)
B.G. Thomas, O. Ojeda, in ISSTech Steelmaking Conference 295, Indianapolis (2003)
M.R. Ridolfi, A. Gotti, J.J. Laraudogoitia, Ironmak. Steelmak. 31, 371 (2004)
Y. Li, H. Li, P. Lan, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 24, 1159 (2017)
C. Chow, I.V. Samarasekera, B.N. Walker, Ironmak. Steelmak. 29, 61 (2002)
J. Heilemann, M. Jünemann, K. Schwerdtfeger, Ironmak. Steelmak. 43, 659 (2016)
Y.M. Won, T. Yeo, K.H. Oh, ISIJ Int. 38, 53 (1998)
M.L.S. Zappulla, Master Thesis (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2016)
J. Cho, H. Shibata, T. Emi, ISIJ Int. 38, 440 (1998)
B.G. Thomas, C.S. Li, Key Eng. Mater. 233, 827 (2003)
Y. Ueshima, S. Mizoguchi, T. Matsumiya, Metall. Mater. Trans. 17B, 845 (1986)
D. Zhang, S. Lei, S. Zeng, ISIJ Int. 54, 336 (2014)
M.L.S. Zappulla, L.C. Hibbeler, B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. 48A, 3777 (2017)
H. Mizukami, K. Murakami, Y. Miyashita, Tetsu. Hagane 63, 562 (1977)
M. Uehara, I.V. Samarasekera, J.K. Brimacombe, Ironmak. Steelmak. 13, 138 (1986)
C.S. Li, B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. 35B, 1151 (2004)
H. Zhu, PhD Thesis (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1996)
P.F. Kozlowski, B.G. Thomas, J.A. Azzi, Metall. Mater. Trans. 23A, 903 (1992)
Acknowledgements
The authors express their thanks to the financial support by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51604021, U1860111, 51874033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, P., Li, L., Tie, Z. et al. Combined Study on Mold Taper and Corner Radius in Bloom Continuous Casting by FEM Simulation and Trial Experiment. Met. Mater. Int. 25, 1603–1615 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00311-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00311-5