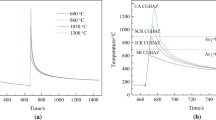
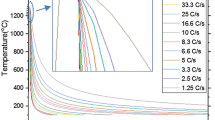
Abstract
Simulated heat-affected zone continuous cooling transformation diagram was developed for advanced fireresistant steel. Over a wide range of cooling rates, corresponding to t8/5 from 6 s to 150 s, granular bainite was the dominant transformation constituent, while the morphology of less dominant martensite-austenite (M-A) constituent changed from film-like to block-type constituent; but the hardness remained similar to the average value of 190-205 HV (0.2). The start and finish transformation temperature was high at 700 °C and 500 °C, and is different from the conventional high strength low alloy steels. It is believed that the high-content (0.09 wt%) of Nb may promote bainite transformation at relatively high temperatures. Martenistic matrix was not observed at high cooling rate and the film-like M-A constituent and blocky M-A constituent with thin film of retained austenite and lath martensite were observed on slow cooling. Excellent impact toughness was obtained in the heat-affected zone with 15-75 kJ/cm welding heat input.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Wan, F. Sun, L. Zhang, and A. Shan, Mater. Design 36, 227 (2012).
R. Chijiwa, H. Tamehiro, Y. Yoshida, K. Funato, R. Uemori, and Y. Horii, Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 58, 48 (1993).
Y. Mizutani, K. Ishibashi, K. Yoshii, Y. Watanabe, R. Chijiiwa, and Y. Yoshida, Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 90, 45 (2004).
R. Hattingh and G. Pienaar, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip. 75, 661 (1998).
J. R. Yang, C. Y. Huang, and C. S. Chiou, Mater. T. JIM 40, 199 (1999).
H. Kawan, M. Shibata, S. Okano, Y. Kobayashi, and Y. Okazaki, R&D Kobe Steel Engineering Rep. 54, 110 (2004).
A. D. Bate and P. R. Kirkwood, Proc. Microalloying’88 Held in Conjunction with the 1988 World Materials Congress, p. 175, ASM Int., Chicago, USA (1988).
Y. Q. Zhang, H. Q. Zhang, J. F. Li, and W. M. Liu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 16, 73 (2009).
C. Miao, C. Shang, X. Wang, L. Zhang, and M. Subramanian, Acta Metall. Sin. 46, 541 (2010).
Z. X. Zhu, L. Kuzmikova, H. J. Li, L. Chen, B. D. Jong, and F. Barbaro, Mater. Sci. Forum 753, 325 (2013).
F. Barbaro, Z. X. Zhu, L. Kuzmikova, H. J. Li, and H. Jian, Proc. Int. Conf. of Microalloying 2015 & Offshore Engineering Steels, pp.453–457, The Chinese Society for Metals (CSM) and Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE), Changzhou, China (2015).
N. C. Wu, Iron & Steel 49, 82 (2014).
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, Bainite in Steels, 2 nd ed., pp.223–224, IOM Communication Ltd, London, UK (2001).
X. Yue, J. C. Lippold, B. T. Alexandrov, and S. S. Babu, Weld. J. 91, S67 (2012).
Y. T. Zhao, S. W. Yang, C. J. Shang, X. M. Wang, W. Liu, and X. L. He, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 454-455, 695 (2007).
L. Yu, H. H. Wang, T. P. Hou, X. L. Wang, X. L. Wan, and K. M. Wu, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joi. 19, 708 (2014).
G. I. Rees, J. Perdrix, T. Maurickx, and H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 194, 179 (1995).
S. Lee, H. Na, B. Kim, D. Kim, and C. Kang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 2523 (2013).
T. Jia and M. Militzer, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46, 614 (2015).
X.-W. Chen, G.-Y. Qiao, X.-L. Han, X. Wanga, F.-R. Xiao, and B. Liao, Mater. Design 53, 888 (2014).
F. R. de Boer, R. Boom, W. C. M. Mattens, A. R. Miedema, and A. K. Niessen, Cohesion in Metals, pp.219–385, Elsevier Science Publishers, New York, USA (1988).
E. A. Simielli, S. Yue, and J. J. Jonas, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 23, 597 (1992).
N. Maruyama, G. D. W. Smith, and A. Cerezo, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 353,126 (2003).
T. D. Xu, Scripta Mater. 37, 1643 (1997).
K. C. Russel, Acta Metall. Mater. 17, 1123 (1969).
R. R. de Avillez, Niobium Technical Report, p. 1, CBMM, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (1982).
C. Fossaert, G. Rees, T. Maurickx, and H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26, 21 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H.H., Qin, Z.P., Wan, X.L. et al. Continuous cooling transformation behavior and impact toughness in heat-affected zone of Nb-containing fire-resistant steel. Met. Mater. Int. 23, 848–854 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-6776-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-6776-8