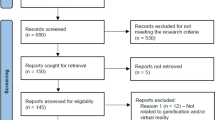
Abstract
Augmented reality (AR) technology is playing an important role in the preschool education. AR provides cost-effective learning systems which improve the attention skills of preschool children. In AR technology, the marker is used as an open-source computer tracking object to create AR applications that overlay virtual imagery on the physical world. Therefore, through augmented reality (AR) technology, learning materials, and knowledge can be visualized, and preschool children can learn interactively with the virtual model in an enjoyable manner and provide a stress-free teaching environment. This paper presents an ABCD AR Game for autistic children to learn the English alphabet innovatively. In the proposed system, a simple marker is used to recognize each character of the English alphabet to teach autistic children. After marker recognition, the ABCD AR-Game displays the corresponding image, helping students understand of English alphabets and their pronunciation, that provides multi-level gaming for reading, speaking, coloring, and writing under the teacher’s and parent’s supervision. The proposed system also provides game-based learning such as preview, question, read, self-recite, and test (PQRST) statistical method to optimize autistic children’s reading and learning of English alphabets. For evaluations, seventy-two (72) autistic children, their parents, and ten teachers participated and were divided into two groups for the assessment. Evaluation results indicated that autistic children, parents, and teachers reacted positively to the ABCD AR-Game. These results showed that ABCD AR-Game enhances autistic children’s learning and their motivation to learn about the English alphabet.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abualigah L et al (2021) The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 376:113609
Abualigah L et al (2022) Reptile search algorithm (RSA): a nature-inspired meta-heuristic optimizer. Expert Syst Appl 191:116158
Alaswad Z, Nadolny L (2015) Designing for game-based learning: the effective integration of technology to support learning. J Educ Technol Syst 43(4):389–402
Ali N, Ullah S, Muhammad R (2022) Interactive cube for effective demonstration of virtual periodic table. Educ Inf Technol 27:1635–1654
Bacca Acosta JL, Baldiris Navarro SM, Fabregat Gesa R, Graf S et al (2014) Augmented reality trends in education: a systematic review of research and applications. J Educ Technol Soc 17(4):133–149
Bhadra A, Brown J, Ke H, Liu C, Shin E-J, Wang X, Kobsa A (2016) Abc3d-using an augmented reality mobile game to enhance literacy in early childhood. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communication workshops (PerCom workshops), IEEE, pp 1–4
Billinghurst M, Kato H, Poupyrev I (2001) The magicbook: a transitional AR interface. Comput Graph 25(5):745–753
Bitter G, Corral A (2014) The pedagogical potential of augmented reality apps. Int J Eng Sci Invent 3(10):13–17
Chen RW, Chan KK (2019) Using augmented reality flashcards to learn vocabulary in early childhood education. J Educ Comput Res 57(7):1812–1831
Chen CH, Ho C-H, Lin J-B (2015) The development of an augmented reality game-based learning environment. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 174:216–220
Chen S-Y, Hung C-Y, Chang Y-C, Lin Y-S, Lai Y-H (2018) A study on integrating augmented reality technology and game-based learning model to improve motivation and effectiveness of learning English vocabulary. In: 2018 1st International Cognitive Cities Conference (IC3)
Cieza E, Lujan D (2018) Educational mobile application of augmented reality based on markers to improve the learning of vowel usage and numbers for children of a kindergarten in trujillo. Procedia Comput Sci 130:352–358
Clark A, Dünser A (2012) An interactive augmented reality coloring book. In: 2012 IEEE symposium on 3D user interfaces (3DUI), IEEE, pp 7–10
Diegmann P, Schmidt-kraepelin M, Eynden S Van Den, Basten D (2015) Benefits of augmented reality in educational environments—a systematic literature review. Benefits 3(6(2015)):1542–1556
Ewais A, Troyer OD (2019) A usability and acceptance evaluation of the use of augmented reality for learning atoms and molecules reaction by primary school female students in palestine. J Educ Comput Res 57(7):1643–1670
Feng L, Yang X, Xiao S (2017) Magictoon: a 2D-to-3D creative cartoon modeling system with mobile AR. In: 2017 IEEE Virtual Reality (VR), IEEE, pp 195–204
Gogula SK, Gogula SD, Puranam C (2015) Augmented reality in enhancing qualitative education. Int J Comput Appl 132(14):41–45
Hwang G-J, Wu P-H (2012) Advancements and trends in digital game-based learning research: a review of publications in selected journals from 2001 to 2010. Br J Edu Technol 43(1):E6–E10
Jason Z (2017) Bored out of their minds. https://www.gse.harvard.edu/news/ed/17/01/bored-out-their-minds. Accessed 08 Jan 2022
Klopfer E, Osterweil S, Salen K et al (2009) Moving learning games forward. The Education Arcade, Cambridge
Lam MC, Tee HK, Nizam SSM, Hashim NC, Suwadi NA, Tan SY, Abd Majid NA, Arshad H, Liew SY (2020) Interactive augmented reality with natural action for chemistry experiment learning. TEM J 9(1):351
Liu Z-Y, Shaikh Z, Gazizova F (2020) Using the concept of game-based learning in education. Int J Emerg Technol Learn (iJET) 15(14):53–64
López-Faican L, Jaen J (2020) Emofindar: evaluation of a mobile multiplayer augmented reality game for primary school children. Comput Educ 149:103814
Lu S-J, Liu Y-C (2015) Integrating augmented reality technology to enhance children’s learning in marine education. Environ Educ Res 21(4):525–541
Malia N, Yasin A (2015) Using PQRST strategy to improve students’ reading comprehension of hortatory exposition texts at grade XI IPS of MA Diniyah Puteri, Pekanbaru. English Language Teaching (ELT) 3(1):1–7
Merchant Z, Goetz ET, Cifuentes L, Keeney-Kennicutt W, Davis TJ (2014) Effectiveness of virtual reality-based instruction on students’ learning outcomes in k-12 and higher education: a meta-analysis. Comput Educ 70:29–40
Mokhtar MK, Mohamed F, Sunar MS, Arshad MAM, Sidik MKM (2018) Development of mobile-based augmented reality colouring for preschool learning. In: 2018 IEEE Conference on e-Learning, e-Management and e-Services (IC3e), IEEE, pp 11–16
Rambli DRA, Matcha W, Sulaiman S (2013) Fun learning with AR alphabet book for preschool children. Procedia Comput Sci 25:211–219
Salman AG, Antonius C (2017) Interactive educational game, an android mobile app for children learning alphabets. Libr Hi Tech News 35(5):20–22
Squire KD, Jan M (2007) Mad city mystery: Developing scientific argumentation skills with a place-based augmented reality game on handheld computers. J Sci Educ Technol 16(1):5–29
Tobar-Muñoz H, Baldiris S, Fabregat R (2017) Augmented reality game-based learning: enriching students’ experience during reading comprehension activities. J Educ Comput Res 55(7):901–936
Tsai C-W, Fan Y-T (2013) Research trends in game-based learning research in online learning environments: a review of studies published in ssci-indexed journals from 2003 to 2012. Br J Edu Technol 44(5):E115–E119
Weng C, Otanga S, Christianto SM, Chu RJ-C (2020) Enhancing students’ biology learning by using augmented reality as a learning supplement. J Educ Comput Res 58(4):747–770
Wu G, Qiu M, Zhang Y, Zheng Y (2019)Research and development of augmented reality children’s puzzle game based on Vuforia. In: 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Science and Education (ICCSE), IEEE, pp 354–359
Yilmaz RM (2016) Educational magic toys developed with augmented reality technology for early childhood education. Comput Hum Behav 54:240–248
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Najran University for funding this work under the National Research Priorities funding program grant code (NU/NRP/SERC/11/32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the techniques brought under use in the concerned study with the code of conduct and with the proper ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual articles included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sulaiman, A., Rahman, H., Ali, N. et al. An augmented reality PQRST based method to improve self-learning skills for preschool autistic children. Evolving Systems 14, 859–872 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-022-09472-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-022-09472-y