Abstract
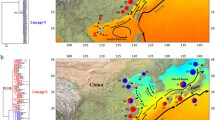
Patelloida pygmaea is one of the most abundantly distributed intertidal marine gastropods along the China coast. The mitochondrial (COI) and internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) DNA of P. pygmaea, one hundred and thirty-seven samples collected from 13 localities along its distribution along the China coast, were used to investigate the phylogeographic patterns of P. pygmaea. Phylogeographic analysis revealed three distinct phylogeographic clades, the South China Sea (SCSC), the Bohai and Yellow Sea (BYSC), and the East China Sea (ECSC) clades. The results of AMOVA showed significant genetic differentiation (P < 0.001) among the three clades. The vicariance of the three lineages was created by the glacial drop in sea level, the Changjiang Estuary, and the sea surface temperature gradient. Based on the ITS1 gene, the BYSC clade was split into two subclades, the north and south clades. We speculate that the Shandong Peninsula was another possible barrier limiting gene flow in the BYSC. Ocean currents played more roles in influencing gene flow within the three clades. The mismatch analysis confirmed the demographic population expansion (P > 0.05). Phylogeographic patterns of P. pygmaea have been primarily affected by Pleistocene climatic oscillations and environmental conditions. During the glacial periods, the sea regressed and moist and warm conditions, characterizing glacial refugia, became prevalent in the region and caused isolated P. pygmaea populations to expand.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BI:
-
Bayesian inference
- BYSC:
-
Bohai and Yellow Sea clade
- COI:
-
first subunit of cytochrome c oxidase
- ECS:
-
East China Sea
- ECSC:
-
Eastern China Sea clade
- Fst:
-
fixation index
- IBD:
-
isolation by distance
- ITS1:
-
internal transcribed spacer region 1
- MCMC:
-
Monte Carlo Markov chains
- ML:
-
maximum likelihood
- NBYS:
-
north clade
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PP:
-
posterior probabilities
- PSRF:
-
potential scale reduction factor
- SCS:
-
South China Sea
- SCSC:
-
South China Sea clade
- SSD:
-
sum of squared deviation
- RI:
-
raggedness index
- TL:
-
tree length
References
Aiyar A (2000) The use of CLUSTAL W and CLUSTAL X for multiple sequence alignment. Methods Mol Biol 132:221–241. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-192-2:221
Alvarez I, Wendel JF (2003) Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:417–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1055-7903(03)00208-2
Avise JC (2009) Phylogeography: retrospect and prospect. J Biogeogr 36:3–15. https://doi.org/10.2307/20488328
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036
Belfiori B, Riccioni C, Paolocci F, Rubini A (2013) Mating type locus of chinese black truffles reveals heterothallism and the presence of cryptic species within the T. indicum species complex. PLoS One 8:e82353. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082353
Borzée A, Santos JL, Sánchez-Ramírez S, Bae Y, Heo K, Jang Y, Jowers MJ (2017) Phylogeographic and population insights of the Asian common toad (Bufo gargarizans) in Korea and China: population isolation and expansions as response to the ice ages. Peerj 5:e4044. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4044
Caldeira RL, Vidigal TH, Paulinelli ST, Simpson AJ, Carvalho OS (1998) Molecular identification of similar species of the genus Biomphalaria (Mollusca: Planorbidae) determined by a polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Mem I Oswaldo Cruz 93(Suppl 1):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02761998000700039
Cheang CC, Chu KH, Ang J (2008) Morphological and genetic variation in the populations of Sargassum hemiphyllum (Phaeophyceae) in the northwestern Pacific. J Phycol 44:855–865. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2008.00532.x
Cheang CC, Chu KH, Ang P Jr (2010) Phylogeography of the marine macroalga Sargassum hemiphyllum (Phaeophyceae, Heterokontophyta) in northwestern Pacific. Mol Ecol 19:2933–2948. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04685.x
Cheang CC, Tsang LM, Ng WC, Williams GA, Chu KH, Chan BKK (2012) Phylogeography of the coldwater barnacle Chthamalus challengeri in the north-western Pacific: effect of past population expansion and contemporary gene flow. J Biogeogr 39:1819–1835. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2012.02742.x
Clark JS, Fastie C, Hurtt GC et al (1998) Reid’s paradox of rapid plant migration. BioScience 48:13–24. https://doi.org/10.2307/1313224
Cummings MP (2014) jModelTest. Dictionary of bioinformatics and computational biology, John Wiley and Sons, Ltd https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471650126.dob0959
David DC, Savini D (2011) Molecular approaches to bivalve population studies: a review. Analele tiinifice ale Universit_x0005_ii “Alexandru Ioan Cuza”, Seciunea Genetic_x0005_ i Biologie Molecular_x0005_, TOM XII
Dawson MN (2001) Phylogeography in coastal marine animals: a solution from California? J Biogeogr 28:723–736. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2699.2001.00572.x
Dong YW, Wang HS, Han GD, Ke CH, Zhan X, Nakano T, Williams GA (2012) The impact of Yangtze river discharge, ocean currents and historical events on the biogeographic pattern of Cellana toreuma along the China coast. PLoS One 7:e36178. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036178
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol 29:1969–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss075
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Eberl R, Mateos M, Grosberg RK, Santamaria CA, Hurtado LA (2013) Phylogeography of the supralittoral isopod Ligia occidentalis around the point conception marine biogeographical boundary. J Biogeogr 40:2361–2372. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12168
Excoffier L, Lischer H (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x
Fang JJ, Li YT, Sun ZH, Deng JY (2011) Analysis of runoff change characteristics at Datong station of Yangtze River. Water Resources and Power 333. [In Chinese with English abstract]
Feliner G, Rossello J (2007) Better the devil you know? Guidelines for insightful utilization of nrDNA ITS in species-level evolutionary studies in plants. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:911–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2007.01.013
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DDF.7.460
González-Wevar CA, Díaz A, Gerard K, Cañete JI, Poulin E (2012) Divergence time estimations and contrasting patterns of genetic diversity between Antarctic and southern South America benthic invertebrates. Rev Chil Hist Nat 85:445–456. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0716-078x2012000400007
González-Wevar CA, Nakano T, Cañete JI, Poulin E (2011) Concerted genetic, morphological and ecological diversification in Nacella limpets in the Magellanic Province. Mol Ecol 20:1936–1951. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05065.x
Grosberg RK, Vermeij GJ, Wainwright PC (2012) Biodiversity in water and on land. Curr Biol 22:900–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.09.050
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Hordijk W, Lefort V, Gascuel O (2009) PhyML: fast and accurate phylogeny reconstruction by maximum likelihood. Infect Genet Evol 9:384–385
Hewitt GM (2003) Ice ages: their impact on species distributions and evolution. In: Evolution on planet earth (eds Rothschild LJ, Lister AM), pp. 339–361, Academic Press, London
Hu Z, Fraser C (2016) Seaweed phylogeography - adaptation and evolution of seaweeds under environmental change. SpringerNature, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7534-2
Huang Z, Lin M (2012) Atlas of Chinese marine life. Ocean press, Beijing
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
Imbrie J, Boyle EA, Clemens SC et al (1992) On the structure and origin of major glaciation cycles. 1. Linear responses to Milankovitch forcing. Paleoceanography 7:701–738. https://doi.org/10.1029/92PA02253
Jablonski D, Belanger CL, Berke SK, Huang S, Krug AZ, Roy K, Tomasovych A, Valentine JW (2013) Out of the tropics, but how? Fossils, bridge species, and thermal ranges in the dynamics of the marine latitudinal diversity gradient. P Natl Acad Sci 110:10487–10494. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1308997110
Jensen JL, Bohonak AJ, Kelley ST (2005) Isolation by distance, web service. BMC Genet 6:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-6-13
Kitamura A, Kimoto K (2006) History of the inflow of the warm Tsushima current into the sea of Japan between 3.5 and 0.8 Ma. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 236:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.11.015
Kopelman NM, Mayzel J, Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA, Mayrose I (2015) Clumpak: a program for identifying clustering modes and packaging population structure inferences across K. Mol Ecol Resour 15:1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12387
Kyle CJ, Boulding EG (2000) Comparative population genetic structure of marine gastropods (Littorina spp.) with and without pelagic larval dispersal. Mar Biol 137:835–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270000412
Li S, Yeung C, Feinstein J, Han L, Manh H, Wang C, Ding P (2009) Sailing through the late pleistocene: unusual historical demography of an East Asian endemic, the Chinese Hwamei (Leucodioptron canorum canorum), during the last glacial period. Mol Ecol 18:622–633. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.04028.x
Li J, Foighil DÓ, Park JK (2013) Triton's trident: cryptic Neogene divergences in a marine clam (Lasaea australis) correspond to Australia's three temperate biogeographic provinces. Mol Ecol 22:1933–1946. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12220
Li J, Hu Z, Gao X et al (2016) Oceanic currents drove population genetic connectivity of the brown alga Sargassum thunbergii in the north-west Pacific. J Biogeogr 44:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12856
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Oxford University Press 25:1451–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Lindberg DR, Guralnick RP (2003) Phyletic patterns of early development in gastropod molluscs. Evol Dev 5:494–507. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-142X.2003.03055.x
Liu JX, Gao TX, Wu SF, Zhang YP (2007) Pleistocene isolation in the northwestern Pacific marginal seas and limited dispersal in a marine fish, Chelon haematocheilus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1845). Mol Ecol 16:275–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.03140.x
Liu R (2008) Checklist of marine biota of China seas. Science Press
Lomolino MV, Riddle BR, Brown JH (2006) Biogeography, 3rd edn. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA
Marko PB, Hoffman JM, Emme SA, Mcgovern TM, Keever CC, Cox LN (2010) The ‘expansion–contraction’ model of pleistocene biogeography: rocky shores suffer a sea change? Mol Ecol 19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04417.x
Matsuura N (1977) Molluscan fossils from the Late Pleistocene marine terrace deposits of Hokuriku region, Japan Sea side of Central Japan. Science Reports of Kanazawa University 22:117–162 https://core.ac.uk/display/14772699
Miller AD, Versace VL, Matthews TG, Montgomery S, Bowie KC (2013) Ocean currents influence the genetic structure of an intertidal mollusc in southeastern Australia-implications for predicting the movement of passive dispersers across a marine biogeographic barrier. Ecol Evol 3:1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.535
Miller KG, Browning JV, Aubry MP, Wade BS, Katz ME, Kulpecz AA, Wright JD (2008) Eocene-oligocene global climate and sea-level changes: St. Stephens Quarry, Alabama. Geol Soc Am Bull 120:34–53. https://doi.org/10.1130/B26105.1
Nakano T, Ozawa T (2005) Systematic revision of Patelloida pygmaea (gastropoda: lottiidae), with a description of a new species. J Molluscan Stud. https://doi.org/10.1093/mollus/eyi039
Ni G, Li Q, Kong L, Zheng X (2012a) Phylogeography of bivalve Cyclina sinensis: testing the historical glaciations and changjiang river outflow hypotheses in northwestern Pacific. PLoS One 7:e49487. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049487
Ni G, Li Q, Kong L, Zheng X (2012b) Phylogeography of the bivalve Tegillarca granosa in coastal China: implications for management and conservation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 452:119–130
Ni G, Li Q, Kong L, Yu H, (2015) Mitochondrial phylogeography of a surf clam Mactra veneriformis in the East China Sea: genetic homogeneity across two biogeographic boundaries. Biochem. Syst Ecol 61:493–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2015.07.026
Ni G, Li Q, Kong L, Yu H (2014) Comparative phylogeography in marginal seas of the northwestern Pacific. Mol Ecol 23:534. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12620
Ni L, Li Q, Kong L (2011) Microsatellites reveal fine-scale genetic structure of the Chinese surf clam Mactra chinensis (Mollusca, Bivalvia, Mactridae) in northern China. Mar Ecol 32:488–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0485.2011.00436.x
Nolasco-Soto J, González-Astorga J, Espinosa de los Monteros A, Galante-Patiño E, Favila ME (2017) a Neotropical dung beetle in the Mexican transition zone: insights on its origin and the impacts of Pleistocene climatic fluctuations on population dynamics. Mol Phylogenet Evol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2017.01.004
Nylander, JAA (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre Uppsala University
Palumbi SR (1996) What can molecular genetics contribute to marine biogeography? An urchin’s tale. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 203:75–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(96)02571-3
Polzin T, Daneshmand SV (2003) On Steiner trees and minimum spanning trees in hypergraphs. Oper Res Lett 31:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-6377(02)00185-2
Poulin R, de León G (2017) Global analysis reveals that cryptic diversity is linked with habitat but not mode of life. J Evol Biol 30:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeb.13034
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genet Mol Res 155:945–959
Qin Y, Shi G, Sun Y (2013) Evaluation of genetic diversity in Pampus argenteus using SSR markers. Genet Mol Res 12:5833–5841. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.November.22.10
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2013) Tracer v.1.6. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh. Available at: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree. Accessed 5 May 2014.
Rato C, Carranza S, Harris DJ (2011) When selection deceives phylogeographic interpretation: the case of the Mediterranean house gecko, Hemidactylus turcicus (Linnaeus, 1758). Mol Phylogenet Evol 58:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1046/10.1016/j.ympev.2010.12.004
Ren JF, Hou ZH, Wang HS, Ming A, Liu X, Liu B, Guo XM (2016) Intraspecific variation in mitogenomes of five Crassostrea species provides insight into oyster diversification and speciation. Mar Biotechnol 18:242–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-016-9686-8
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol Biol Evol 9:552–569. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040727
Rosenberg NA (2004) DISTRUCT: a program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol Ecol Resour 4:137–138. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2003.00566.x
Schneider S, Excoffier L (1999) Estimation of past demographic parameters from the distribution of pairwise differences when the mutation rates vary among sites: application to human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics 152:1079–1089
Shen KN, Jamandre BW, Hsu CC, Tzeng WN, Durand JD (2011) Plio-Pleistocene sea level and temperature fluctuations in the northwestern Pacific promoted speciation in the globally-distributed flathead mullet Mugil cephalus. BMC Evol Biol 11:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-83
Sponaugle S, Cowen RK, Shanks A, Morgan SG, Leis JM, Pineda J, Boehlert GW, Kingsford MJ, Lindeman KC, Grimes C, Munro JL (2002) Predicting self-recruitment in marine populations: biophysical correlates and mechanisms. Bull Mar Sci 70:341–375. https://doi.org/10.1515/BOT.2002.040
Voris HK (2000) Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time durations. J Biogeogr 27:1153–1167. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2699.2000.00489.x
Wang LJ (1994) Sea surface temperature history of the low latitude western Pacific during the last 5.3 million years. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 108:379–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/10.1016/0031-0182(94)90244-5
Wang M, Zhang X, Yang T, Han Z, Yanagimoto T, Gao T (2008) Genetic diversity in the mtDNA control region and population structure in the Sardinella zunasi Bleeker. Afr J Biotech 7:4384–4392
Wang P (1999) Response of Western Pacific marginal seas to glacial cycles: paleoceanographic and sedimentological features. Mar Geol 156:5–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-3227(98)00172-8
Wang J, Wan HU, Yang Y, Xiao K, Fan DM, Zhang ZY (2015a) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers for Eomecon chionantha, a monotypic species endemic to China. J Plant Sci 41:930–933. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02359.x
Wang H, Jun Z, Li DM (2015b) Structural investigation of an uronic acid-containing polysaccharide from abalone by graded acid hydrolysis followed by PMP-HPLC–MSn and NMR analysis. Carbohydr Res 402:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2014.10.010
Wang J, Tsang LM, Dong YW (2015c) Causations of phylogeographic barrier of some rocky shore species along the Chinese coastline. BMC Evol Biol 15:114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-015-0387-0
Wang X, Kong L, Chen J, Matsukuma A, Li Q (2017) Phylogeography of bivalve Meretrix petechialis in the northwestern Pacific indicated by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA data. PLoS One 12:e0183221. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183221
Wang Y, Tan ZM, Zhang DC, Murat C, Jeandroz S, Tacon FL (2006) Phylogenetic and populational study of the tuber indicum complex. Mycol Res 110:1034–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycres.2006.06.013
Yin J, Pan D, He C, Wang A, Yan J, Sun H (2013) Morphological and molecular data confirm species assignment and dispersal of the genus ligia, (crustacea: isopoda: ligiidae) along northeastern coastal China and East Asia. Zool J Linnean Soc 169:362–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/zoj.12068
Zhang SP (2008) China marine shellfish illustrated book. Ocean Press, Beijing, China
Zhao D, Li Q, Kong L, Yu H (2017) Cryptic diversity of marine gastropod Monodonta labio (Trochidae): did the early Pleistocene glacial isolation and sea surface temperature gradient jointly drive diversification of sister species and/or subspecies in the northwestern Pacific? Mar Ecol 38:e12443. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12443
Zhao Y, Li Q, Kong L, Mao Y (2009) Genetic and morphological variation in the venus clam Cyclina sinensis along the coast of China. Hydrobiologia 635:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9916-4
Zheng X, Qu X (2013) Atlas of chineseaquatic shellfish. Qingdao Publishing House, Qindao
Acknowledgments
We thank the Administration of Ocean and Fisheries and Professor Zhenxiang Dai for assistance with the collecting work. We are also grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions to improve this manuscript. We also thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31460562) and the Project of Yantai Double Hundred Talent and the Doctoral Science Research Foundation of Yantai University (SM15B01, SM19B70).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460562) and the Project of Yantai Double Hundred Talent and Doctoral Science Research Foundation of Yantai University (SM15B01 and SM19B70).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Q., Y.C., and X.W. collected the samples. B.S., J.Q., and X.W. wrote the manuscript. Y.X., B.S., R.L., X.S., X.G., and S.W. performed the molecular analysis. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No animal testing was performed during this study.
Sampling and field studies
All necessary permits for sampling were obtained by the authors from relevant authorities and are mentioned in the acknowledgements when applicable.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Editorial Responsibility: K. Kocot
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Shi, B., Xu, Y. et al. Phylogeography of Patelloida pygmaea along the China coast. Mar. Biodivers. 51, 38 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-021-01164-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-021-01164-1