Abstract
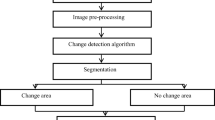
Urban areas are gaining attention globally with the implementation of the United Nations sustainable development agenda 2030 where more emphasis is given on making cities inclusive, resilient, safe, and sustainable. Hence, it is crucial to have precise data of urban built-up areas such as the shape, size, and spatial context. It is a challenging task to extract urban built-up features due to continuous modifications in land as well as heterogeneity in spatial and spectral extent of the urban surfaces. The present research attempts to extract urban built up structures using rule-based object-oriented classification. SEaTH, a tool used for feature analysis in eCognition software was applied to select the discrete features and optimum thresholds that allow more and more separability during classification. With respect to diversity in urban areas, two urban patches of Pune city were selected where one patch is the core part of the city with a congested network of roads and buildings and another patch is located in the outskirts comprises of modern multi-story buildings and relatively broad roads. Multiresolution segmentation with scale parameter of 5 with a shape 0.1 and compactness of 0.5 was finally accepted after a lot of trial iterations for both the areas. Using the SEaTH tool, some of the best object features such as shape properties, spectral bands, and indices (NDVI) were selected for the assessment of the separability and threshold. A rule-based classification was performed to acquire land use/land cover with an overall accuracy of 92% for the city core and 91% for the suburb. The k-hat value obtained was 0.81 and 0.88 for the city core and suburb area, respectively. With incorporating shape parameters in image classification, the SEaTH method applied hierarchically the shape features such as density, compactness, and shape index as the best features to separate the buildings and roads. The NDVI spectral index demonstrated in this study proved beneficial to classify vegetation features from other land use types. As a result of the present study, it has been concluded that rule-based object-oriented classification can help improve the classification of dynamic urban areas and update land use maps effectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Satellite data is procured from the National Remote Sensing Center (NRSC) by following standard procedure.
Code availability
For the analysis, ArcGIS 10.3, Definiens, and MS Excel are used. Code is not used from any platform.
References
Aguilar MA, Vicente R, Aguilar FJ, Fernández A, Saldaña MM (2012) Optimizing object based classification in urban environments using very high resolution Geoeye-1 imagery. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume I-7, 2012 XXII ISPRS Congress, 25 August – 01 September 2012, Melbourne, Australia
Baatz M and Schaepe A (1999) Object-oriented and multi-scale image analysis in semantic networks. 2nd International Symposium: Operationalization of Remote Sensing, 16-20August, ITC, The Netherlands
Baatz MC, Hoffmann, Willhauck G (2008) Progressing from object-based to object-oriented image analysis. In: Blaschke T, Lang S, Hay GJ (eds) Object-based Image Analysis- Spatial Concepts for Knowledge-driven remote sensing applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Bhattacharyya A (1943) On a measure of divergence between two statistical populations defined by probability distributions. Bull Calcutta Math Soc 35:99–109
Blaschke T, and Lang S (2006) Object based image analysis for automated information extraction a synthesis. In Proc. of Measuring the Earth II ASPRS Fall Conference, San Antonio, Texas, November 6-10
Blaschke TS, Lang, E, Lorup J, Strobl and Zeil P (2000) Object-oriented image processing in an integrated GIS/remote sensing environment and perspectives for environmental applications. In A. Cremers and K. Greve (Hrsg.): Umweltinformation fr Planung, Politik und ffentlichkeit / Environmental Information for Planning, Politics and the Public. Metropolis Verlag, Marburg 2: 555-570.
Buck AR, De Kok T, Schneider and Ammer U (1999) Improvement of a forest GIS by integration of remote sensing data for the observation and inventory of protective forests in the Bavarian Alps. In Proc. IUFRO Conference on Remote Sensing and Forest Monitoring, Rogow, Poland, June 1-3
De Kok RT, Schneider and Ammer U (1999) Object based classification and applications in the Alpine forest environment. In Proc. Joint ISPRS/EARSeL Workshop, Fusion of sensor data, knowledge sources and algorithms, Valladolid, Spain, June 3-4.
Definiens (2010) Definiens Developer Reference Guide. Definiens
Fakunaga K (1990) Introduction to statistical pattern recognition. Academic press, San Diego, CA second ed.
Hay GJ, Castilla G (2008) Geographic Object-based Image Analysis (GEOBIA): a new name for a new discipline. In: Blaschke T, Lang S, Hay GJ (eds) Object-based Image Analysis− Spatial Concepts for Knowledge-driven remote sensing applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Marpu PR, Niemeyer I, Nussbaum S, Gloaguen R (2006) A procedure for automatic object-based classification. In: Proc. 1st International Conference on Object-based Image Analysis (OBIA 2006), Salzburg, 4-5 July 2006, ISPRS Volume No. XXXVI - 4/C42.
Masek JG, Lindsay FE, Goward SN (2001) Dynamics of urban growth in the Washington DC metropolitan area 1973–1996 from Landsat observations. Int J Remote Sens 21(18):3473–3486
Niemeyer I, Canty MJ and Baatz M (1999) Fractal-hierarchical pattern recognition for safeguard purposes. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Operationalization of Remote Sensing, Enschede, ITC, August 1620, 1999
Nussbaum S, Niemeyer I and Canty MJ (2002) Feature recognition in the context of automated object-oriented analysis of remote sensing data monitoring the Iranian nuclear sites, Proceedings of Optics/Photonics in Security & Defence.
Salehi B, Yun Z, Ming Z, Dey V (2012) Object-based classification of urban areas using VHR imagery and height points ancillary data. Remote Sens 4(8):2256–2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs4082256
Wang Z, Wei W, Zhao S and Chen X (2004) Object-oriented classification and application in land use classification using SPOT-5 PAN imagery. IGARSS 2004. 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 5: 3158-3160. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2004.1370370
Wojtaszek MV, Ronczyk L, Mamatkulov Z, Reimov M (2021) Object-based approach for urban land cover mapping using high spatial resolution data. E3S Web Conf 227:01001 (2021) GI 2021. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202122701001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This research is part of dissertation work of post graduate program. Starting from the data collection to data analysis has been done by authors and self-sponsored. The authors conceived of the presented idea and developed framework of methodology, performed the analytic calculations with the help of literature. The authors read and approve the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
This research is original and conducted by author and co-authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhorde, A., Deshpande, G. & Datkhile, P. Automatic urban feature extraction using rule-based object-oriented classification: a case study of parts of Pune city, Maharashtra, India. Appl Geomat 15, 871–884 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-023-00527-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-023-00527-6