Abstract
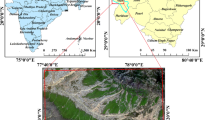
User-defined parameters (point density, interpolation, and pixel size) have a great influence on the accuracy of digital terrain model (DTM). Therefore, the optimal interpolation method (IM) and appropriate pixel size should be used to create a continuous surface. Pixel size or spatial resolution tends to be a compromise between the number of samples and the size of the study area, whereby input dataset is often devaluated. In this paper, the authors propose a new methodological approach to DTM production (hybrid DTM—HDTM) from an aero-photogrammetry dataset. Two different approaches to DTM production are presented: the usual (UDTM) and the hybrid (HDTM). HDTM is based on restructuring and refining the input dataset by generating contour lines, determining the optimal interpolation method and selecting the appropriate spatial resolution. The goal is to develop a qualitative DTM while minimalizing the devaluation of input data and error propagation. The accuracy of different IMs for UDTM was examined in a comparative analysis of six statistical parameters by applying cross-validation, with the focus on the root mean square error (RMSE) parameter. Four different methods of selecting optimal spatial resolution were tested for the same model. The UDTM and HDTM generated were compared by interior, exterior, and visual accuracy assessment and by the performance success of specific hydrological parameters: (1) flow accumulation—by applying a developed DNA concept and (2) watershed—by calculating volume and 3D surface. The reference value for exterior accuracy assessment was high-resolution airborne LiDAR DTM (LDTM). It was found that ordinary kriging (OK) was the best IM (RMSE, 1.9893 m). The spatial resolution of UDTM was calculated by combining two variants of the point pattern analysis method and was found to be 19 m. On the other hand, the complexity of terrain method was used to define the spatial resolution of HDTM (3 m). HDTM achieved better results than UDTM in all aspects of accuracy assessment. The exterior accuracy of HDTM was better by 1.483 m (RMSE). Finally, the results of the applied DNA concept showed that a stream generated from HDTM had a 2.587 m lower horizontal root mean square error (HRMSE) than the stream generated from UDTM.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The average nearest neighbor ratio is calculated as the observed average distance divided by the expected average distance. The expected distance is the average distance between neighbors in a hypothetical random distribution. If the index is less than 1, the pattern exhibits clustering; if the index is greater than 1, the trend is toward dispersion or competition. The average nearest neighbor method is very sensitive to the area value. The ANN tool is most effective for comparing different features in a fixed study area (ESRI 2016).
Autocorrelation is a mathematical representation of the degree of similarity between data at a given time and space (URL 8 2018).
A variogram is a description of the spatial continuity of the data. Experimental variogram is a discrete function calculated using a measure of variability between pairs of points at various distances.
A tool that automates the whole process was created in ModelBuilder.
References
Aguilar FJ, Agüera F, Aguilar MA, Carvajal F (2005) Effects of terrain morphology, sampling density, and interpolation methods on grid DTM accuracy. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 71(7):805–816. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.71.7.805
Albani M, Klinkenberg B, Andison DW, Kimmins JP (2004) The choice of window size in approximating topographic surfaces from digital elevation models. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 18(6):577–593. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810410001701987
Al-Yahyai S, Charabi Y, Gastli A (2013) Optimal micro-siting of small wind turbine using numerical simulation. In GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCC), 2013 7th IEEE (pp 28–32). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEEGCC.2013.6705743
Anders NS, Seijmonsbergen AC, Bouten W (2013) Geomorphological change detection using object-based feature extraction from multi-temporal LiDAR data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 10(6):1587–1591. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2013.2262317
Anderson ES, Thompson JA, Austin RE (2005) LiDAR density and linear interpolator effects on elevation estimates. Int J Remote Sens 26(18):3889–3900. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160500181671
Anderson DL, Ames DP, Yang P (2014) Quantitative methods for comparing different polyline stream network models. J Geogr Inf Syst 6:88–98. https://doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2014.62010
Aricak B (2015) Using remote sensing data to predict road fill areas and areas affected by fill erosion with planned forest road construction: a case study in Kastamonu Regional Forest Directorate (Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 187(7):417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4663-7
Barada M (2017) Utjecaj korisničko-definiranih parametara na točnost digitalnog modela reljefa. Master Thesis, Department of Geography, University of Zadar, Croatia
Barker DM, Lawler DM, Knight DW, Morris DG, Davies HN, Stewart EJ (2009) Longitudinal distributions of river flood power: the combined automated flood, elevation and stream power (CAFES) methodology. Earth Surf Process Landf 34:280–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1723
Bashfield A, Keim A (2011) Continent-wide DEM creation for the European Union. In: 34th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment. The GEOSS era: towards operational environmental monitoring. Sydney, Australia, pp 10–15
Bater CW, Coops NC (2009) Evaluating error associated with lidar-derived DEM interpolation. Comput Geosci 35(2):289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2008.09.001
Biron PM, Choné G, Buffin-Bélanger T, Demers S, Olsen T (2013) Improvement of streams hydro-geomorphological assessment using LiDAR DTMs. Earth Surf Process Landf 38:1808–1821. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3425
Bishop MP, James LA, Shroder JF, Walsh SJ (2012) Geospatial technologies and digital geomorphological mapping: concepts, issues and research. Geomorphology 137(1):5–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.06.027
Böer J, Gonzalez C, Wecklich C, Bräutigam B, Schulze D, Bachmann M, Zink M (2016) Performance assessment of the final TanDTM-X DTM. In: ESA living planet symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016
Burrough PA, McDonnell RA (1998) Principles of geographical information systems. Oxford University Press, New York
Callow JN, Van Niel KP, Boggs GS (2007) How does modifying a DTM to reflect known hydrology affect subsequent terrain analysis? J Hydrol 332(1–2):30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.06.020
Cavazzi S, Corstanje R, Mayr T, Hannam J, Fealy R (2013) Are fine resolution digital elevation models always the best choice in digital soil mapping? Geoderma 195:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.11.020
Chaplot V, Darboux F, Bourennane H, Leguédois S, Silvera N, Phachomphon K (2006) Accuracy of interpolation techniques for the derivation of digital elevation models in relation to landform types and data density. Geomorphology 77(1–2):126–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.12.010
Chase AF, Chase DZ, Weishampel JF, Drake JB, Shrestha RL, Slatton KC, Awe JJ, Carter WE (2011) Airborne LiDAR, archaeology, and the ancient Maya landscape at Caracol, Belize. J Archaeol Sci 38(2):387–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2010.09.018
Chu HJ, Wang CK, Huang ML, Lee CC, Liu CY, Lin CC (2014) Effect of point density and interpolation of LiDAR-derived high-resolution DEMs on landscape scarp identification. GIScience & remote sensing 51(6):731–747. https://doi.org/10.1080/15481603.2014.980086
Claessens L, Heuvelink GBM, Schoorl JM, Veldkamp A (2005) DTM resolution effects on shallow landslide hazard and soil redistribution modelling. Earth Surf Process Landf 30:461–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1155
Contreras M, Aracena P, Chung W (2012) Improving accuracy in earthwork volume estimation for proposed forest roads using a high-resolution digital elevation model. Croatian Journal of Forest Engineering 33(1):125–142
Data Sheet, RIEGL LMS-Q780, 24.3.(2015) (http://www.riegl.com/uploads/tx_pxpriegldownloads/DataSheet_LMS-780_2015-03-24.pdf, 29.6.2017)
DGU RH (2014) Specifikacija proizvoda - Digitalni model reljefa 2. DGU RH, Zagreb, p 0
Erdogan S (2009) A comparison of interpolation methods for producing digital elevation models at the field scale. Earth Surf Process Landf 34(3):366–376. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1731
ESRI (2016), ArcGIS Desktop 10.1 – Help, 2016
Evans DH, Fletcher RJ, Pottier C, Chevance JB, Soutif D, Tan BS, Im S, Ea D, Tin T, Kim S, Cromarty C, de Greef S, Hanus K, Baty P, Kuszinger R, Shimoda I, Boornazian G (2013) Uncovering archaeological landscapes at Angkor using lidar. Proceedings of the National AcaDTMy of Sciences 110(31):12595–12600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1306539110
Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T (2016) Assessing uncertainties associated with digital elevation models for object based landslide delination. In: GEOBIA 2016: solutions and synergies, 14 September 2016–16 September 2016, University of Twente Faculty of Geo-Information and Earth Observation. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3990/2.390
Fisher PF, Tate NJ (2006) Causes and consequences of error in digital elevation models. Prog Phys Geogr 30(4):467–489
Florinsky IV (2002) Errors of signal processing in digital terrain modelling. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 16(5):475–501. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810210129139
Gamba P, Dell’Acqua F, Houshmand B (2003) Comparison and fusion of LIDAR and InSAR digital elevation models over urban areas. Int J Remote Sens 24(22):4289–4300. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311603100009600
Gonçalves A, Almeida J, Rua H (2016) Assessment of the permeability of historical defensive systems: the case of the lines of Torres Vedras. Int J Hist Archaeol 20(2):229–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10761-016-0334-9
Goulding CJ (1977) Cubic spline curves and calculation of volume of sectionally measured trees. Forest Research Institute 9 (1): 89–99, New Zealand Forest Service, Rotorua
Grindle C, Lewis M, Glinton R, Giampapa J, Owens S, Sycara K (2004) Automating terrain analysis: algorithms for intelligence preparation of the battlefield. In: Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting (Vol. 48, No. 3, pp. 533–537), Sage CA: Los Angeles, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/154193120404800355
Guptill SC, Morrison JL (2002) Elementi kvalitete prostornih podataka, O’Alster, Ipswich. Translated by: D. Tutić and M. Lapaine, Hrvatsko kartografsko društvo, Zagreb, 1–11
Hengl T (2006) Finding the right pixel size. Comput Geosci 32(9):1283–1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2005.11.008
Hengl T, Evans IS (2009) Mathematical and digital models of the land surface. In: Hengl T, Reuter HI (eds) Geomorphometry: concepts, software, applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 31–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2481(08)00002-0
Hengl T, Gruber S, Shrestha DP (2003) Digital terrain analysis in ILWIS: lecture notes and user guide. In: International institute for geo-information science and earth observation (ITC). Enschede, Netherlands
Hoober D, Svoray T, Cohen S (2017) Using a landform evolution model to study ephemeral gullying in agricultural fields: the effects of rainfall patterns on ephemeral gully dynamics. Earth Surf Process Landf 42:1213–1226
Humme A, Lindenbergh R, Sueur C (2006) Revealing celtic fields from lidar data using kriging based filtering. In: Symposium V, Maas H-G, Schneider D (eds) Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission. Dresden, Germany, pp 25–27, 2006
Hutchinson MF (1989) A new procedure for gridding elevation and stream line data with automatic removal of spurious pits. J Hydrol 106:211–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(89)90073-5
Hutchinson MF (1996) A locally adaptive approach to the interpolation of digital elevation models. In: Third International Conference/Workshop on Integrating GIS and Environmental Modeling, Santa Fe, NM, January 21–26, 1996. Santa Barbara, CA: National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis
Hutchinson MF, Xu T, Stein JA (2011) Recent progress in the ANUDTM elevation gridding procedure. Geomorphometry 2011, 19–22. ISO 690
Hynek BM, Beach M, Hoke MR (2010) Updated global map of Martian valley networks and implications for climate and hydrologic processes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 115(E9). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JE003548
Ismail Z, Rahman MZA, Salleh MRM, Yusof ARM (2015) Accuracy assessment of LIDAR-derived elevation value over vegetated terrain in tropical region. Jornal Teknologi 73(5). DOI: https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v73.4335
James LA, Watson DG, Hansen WF (2007) Using LiDAR data to map gullies and headwater streams under forest canopy: South Carolina, USA. Catena 71(1):132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2006.10.010
Jonkman SN, Maaskant B, Boyd E, Levitan ML (2009) Loss of life caused by the flooding of New Orleans after hurricane Katrina: analysis of the relationship between flood characteristics and mortality. Risk Anal 29(5):676–698. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01190.x
Karel W, Pfeifer N, Briese C (2006) DTM quality assessment, in: ISPRS Technical Commission Symposium. In: ISPRS Technical Commission II Symposium (2006), International Archives of the ISPRS, XXXVI/2 (2006), Wien, 1682-1750, 7
Kienzle S (2004) The effect of DEM raster resolution on first order, second order and compound terrain derivatives. Trans GIS 8(1):83–111
Korzeniowska K, Łącka M (2011) Generating DEM from LiDAR data–comparison of available software tools. Archiwum Fotogrametrii, Kartografii i Teledetekcji, 22
Leitão JP, de Vitry MM, Scheidegger A, Rieckermann J (2016) Assessing the quality of digital elevation models obtained from mini unmanned aerial vehicles for overland flow modelling in urban areas. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20(4):1637. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-1637-2016
Li J, Heap AD (2008) A review of spatial interpolation methods for environmental scientists. Geoscience Australia, Record 2008/23, Canberra
Li J, Heap AD (2014) Spatial interpolation methods applied in the environmental sciences: a review. Environ Model Softw 53:173–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2013.12.008
Li Z, Zhu Q, Gold C (2005) Digital terrain modeling. CRC Press, London
Lin S, Jing C, Coles NA, Chaplot V, Moore NJ, Wu J (2013) Evaluating DTM source and resolution uncertainties in the soil and water assessment tool. Stoch Env Res Risk A 27(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0577-x
Liu X (2008) Airborne LiDAR for DEM generation: some critical issues. Prog Phys Geogr 32(1):31–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133308089496
Lo Curzio S, Magliulo P (2010) Soil erosion assessment using geomorphological remote sensing techniques: an example from southern Italy. Earth Surf Process Landf 35:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1905
Longley PA (2005) Geographical information systems and science, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Maio CV, Tenenbaum DE, Brown CJ, Mastone VT, Gontz AM (2013) Application of geographic information technologies to historical landscape reconstruction and military terrain analysis of an American Revolution Battlefield: preservation potential of historic lands in urbanized settings, Boston, Massachusetts, USA. J Cult Herit 14(4):317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2012.08.002
Malone BP, Minasny B, Odgers NP, McBratney AB (2014) Using model averaging to combine soil property rasters from legacy soil maps and from point data. Geoderma 232:34–44. ISO 690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.04.033
Malvić T (2008) Primjena geostatistike u analizi geoloških podataka, Udžbenici Sveučilišta u Zagrebu, INA-Industrija nafte d.d., Zagreb, 2008
McCullagh MJ (1988) Terrain and surface modelling systems: theory and practice. Fotogrammetric Record 12(72):747–779
Medved I, Pribicević B, Medak D, Kuzmanić I (2010) Usporedba metoda interpolacije batimetrijskih mjerenja za praćenje promjena volumena jezera. Geodetski List 64(2):71–86
Meng X, Currit N, Zhao K (2010) Ground filtering algorithms for airborne LiDAR data: a review of critical issues. Remote Sens 2(3):833–860. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs2030833
Milan DJ, Heritage GL. (2012) LiDAR and ADCP use in gravel bed rivers: advances since GBR6. Gravel-bed rivers: processes, tools, environments, 286–302. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119952497.ch22
Minasny B, McBratney AB (2007) Spatial prediction of soil properties using EBLUP with the Matérn covariance function. Geoderma 140(4):324–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.04.028
Mitas L, Mitasova H (1999) Spatial interpolation. In: Longley P, Goodchild MF, Maguire DJ, Rhind DW (eds) Geographical information systems: principles, techniques, management and applications, Second edn. Wiley, Chichester, pp 481–492
Nagesh H, Goil S, Choudhary A. (2001) Adaptive grids for clustering massive data sets. In Proceedings of the 2001 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (pp. 1–17). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
Nelson A, Reuter HI, Gessler P (2009) DTM production methods and sources. In: Hengl T, Reuter HI (eds) Geomorphometry: concepts, software, and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 65–85
Nitsche M, Turowski JM, Badoux A, Rickenmann D, Kohoutek TK, Pauli M, Kirchner JW (2013) Range imaging: a new method for high-resolution topographic measurements in small-and medium-scale field sites. Earth Surf Process Landf 38(8):810–825. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3322
Oliver MA, Webster R (1990) Kriging: a method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int J Geogr Inf Syst 4(3):313–332
Palata D (2003) Newton-Cotesove formule numericke integracije. https://www.google.hr/search?client=opera&q=palata+Newton+Cotesove+formule&sourceid=opera&ie=UTF-8&oe=UTF-8&gfe_rd=cr&ei=tjrLVePGKcaG8QeSiK0Y. Accessed 10 Jul 2017
Pajarola R, Gobbetti E (2007) Survey of semi-regular multiresolution models for interactive terrain rendering. Vis Comput 23(8):583–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-007-0163-2
Parrot JF, Nunez CR (2016) LiDAR DTM: artifacts, and correction for river altitudes. Investigaciones Geográficas. Boletín del Instituto de Geografía 2016(90):28–39
Passalacqua P, Belmont P, Foufoula Georgiou E (2012) Automatic geomorphic feature extraction from lidar in flat and engineered landscapes. Water Resour Res, 48(3): DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR010958
Pereira P, Oliva M, Misiune I (2016) Spatial interpolation of precipitation indexes in Sierra Nevada (Spain): comparing the performance of some interpolation methods. Theor Appl Climatol 126(3–4):683–698. ISO 690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1606-8
Petrie G, Toth C (2009) Introduction to laser ranging, profiling, and scanning. In: Shan J, Toth CK (ed)
Pike RJ (1995) Geomorphometry – progress, practice and prospect. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, Supplement band 101:221–238
Pike RJ (2000) Geomorphometry - diversity in quantitative surface analysis. Prog Phys Geogr 24(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1191/030913300674449511
Pike RJ, Evans IS, Hengl T (2009) Geomorphometry: a brief guide. In: Hengl T & Reuter H I (ed) Geomorphometry: concepts, software, applications (pp. 3.30). Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ser. Development in Soil Science, 3–30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2481(08)00001-9
Pirotti F, Tarolli P (2010) Suitability of LiDAR point density and derived landform curvature maps for channel network extraction. Hydrological Processes: An International Journal 24(9):1187–1197. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7582
Podobnikar T (2009) Methods for visual quality assessment of a digital terrain model, SAPIENS 2 (3)
Prosdocimi M, Calligaro S, Sofia G, Dalla Fontana G, Tarolli P (2015) Bank erosion in agricultural drainage networks: new challenges from structure-from-motion photogrammetry for post-event analysis. Earth Surf Process Landf 40:1891–1906. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3767
Qi P, Hu S, Cui Y (2013) On the suitability of the SRTM DTM for simulating potential insolation. In: Geoinformatics (GEOINFORMATICS) 2013, 21st International Conference on (pp. 1–5). IEEE. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/Geoinformatics.2013.6626144
Raaflaub LD, Collins MJ (2006) The effect of error in gridded digital elevation models on the estimation of topographic parameters. Environ Model Softw 21(5):710–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2005.02.003
Raber GT, Jensen JR, Hodgson ME, Tullis JA, Davis BA, Berglund J (2007) Impact of LiDAR nominal post-spacing on DEM accuracy and flood zone delineation. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 73(7):793–804. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.73.7.793
Remondino F (2003) From point cloud to surface: the modeling and visualization problem. International Archives of photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information sciences, 34
Saksena S, Merwade V (2015) Incorporating the effect of DTM resolution and accuracy for improved flood inundation mapping. J Hydrol 530:180–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.09.069
Sanders BF (2007) Evaluation of on-line DTMs for flood inundation modeling. Adv Water Resour 30(8):1831–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.02.005
Satge F, Denezine M, Pillco R, Timouk F, Pinel S, Molina J, Garnier J, Seyler F, Bonnet MP (2016) Absolute and relative height-pixel accuracy of SRTM-GL1 over the South American Andean Plateau. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 121:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.09.003
Schneider A, Gerke HH, Maurer T, Nenov R (2013) Initial hydro-geomorphic development and rill network evolution in an artificial catchment. Earth Surf Process Landf 38:1496–1512. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3384
Shannon CE (1949) Communication in the presence of noise. Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers 37(1):10–21
Shary PA, Sharaya LS, Mitusov AV (2002) Fundamental quantitative methods of land surface analysis. Geoderma 107(2):1–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(01)00136-7
Shi WZ, Tian Y (2006) A hybrid interpolation method for the refinement of a regular grid digital elevation model. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 20(1):53–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810500286943
Siebert S, Teizer J (2014) Mobile 3D mapping for surveying earthwork projects using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) system. Autom Constr 41:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2014.01.004
Šiljeg A (2013) Digitalni model reljefa u analizi geomorfometrijskih parametara–primjer PP Vransko jezero. Doktorski rad, PMF, Sveucilište u Zagrebu
Šiljeg A, Lozić S, Šiljeg S (2015) A comparison of interpolation methods on the basis of data obtained from a bathymetric survey of Lake Vrana, Croatia. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 9:3653–3666. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-3653-2015
Slattery KT, Slattery KD, Peterson JP (2012) Road construction earthwork volume calculation using three-dimensional laser scanning. J Surv Eng 138(2):96–99. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000073
Smelik RM, Tutenel T, de Kraker KJ, Bidarra R (2010) Declarative terrain modeling for military training games. International journal of computer games technology 2:2–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/360458
Steinitz C (2011) On scale and complexity and the need for spatial analysis, ArcNews (http://www.esri.com/news/arcnews/spring11articles/on-scale-and-complexityand-the-need-for-spatial-analysis.html)
Stereńczak K, Ciesielski M, Balazy R, Zawiła-Niedźwiecki T (2016) Comparison of various algorithms for DTM interpolation from LIDAR data in dense mountain forests. European Journal of Remote Sensing 49(1):599–621. https://doi.org/10.5721/EuJRS20164932
Su J, Bork E (2006) Influence of vegetation, slope, and lidar sampling angle on DEM accuracy. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 72(11):1265–1274. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.72.11.1265
Sulebak JR, Hjelle Ø (2003) Multiresolution spline models and their applications in geomorphology. Concepts and Modelling in Geomorphology: International Perspectives. 221–237
Tan Q, Xu X (2014) Comparative analysis of spatial interpolation methods: an experimental study. Sensors & Transducers 165:155–163
URL 5 (2018) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_lidar_dataset
URL 6 2018 https://www.researchgate.net/post/Which_EU_Countries_provide_free_access_to_LIDAR_data_files_in_2017
URL 7 (2018) https://www.geospatialworld.net/blogs/did-you-know-the-sources-for-free-lidar-data/
URL 8 (2018) https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/autocorrelation.asp
URL1 (2017) https://www.aaas.org/content/what-are-geospatial-technologies
URL2 (2017) https://planetcalc.com/5494/
URL3 (2017) http://surferhelp.goldensoftware.com
URL4 (2017) http://cijene-gradjevinskih-radova.blogspot.hr/
Van Haaren R, Fthenakis V (2011) GIS-based wind farm site selection using spatial multi-criteria analysis (SMCA): evaluating the case for New York state. Renew Sust Energ Rev 15(7):3332–3340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.04.010
Wang L, Wang K (2015) Impacts of DTM uncertainty on estimated surface solar radiation and extracted river network. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 96(2):297–304
Wasklewicz T, Staley DM, Reavis K, Oguchi T (2013) Digital terrain modeling. In: Shroder J, Bishop MP (eds) Treatise on geomorphology, vol 3. Academic Press, San Diego pp 130–61
Watson DF (1992) Contouring: a guide to the analysis and display of spatial data. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK
Wechsler SP (2003) Perceptions of digital elevation model uncertainty by DTM users, URISA Journal 15 (2), 57–64. Washington DC
Wilson J (2012) Digital terrain modelling. Geomorphology 137(1):269–297
Wilson JP, Bishop MP (2013) Geomorphometry. J. Shroder (editor in chief), M. P. Bishop (ed.), Treatise on Geomorphology 3: 162–186. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374739-6.00049-X
Wilson JP, Gallant JC (2000) Digital terrain analysis. In: Wilson JP, Gallant JC (eds) Terrain analysis: principles and applications. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 1–27
Wong WSD, Lee J (2005) Statistical analysis of geographic information with ArcView GIS and ArcGIS. Wiley, Hoboken
Yakar M, Yilmaz HM, Mutluoglu O (2010) Comparative evaluation of excavation volume by TLS and total topographic station based methods. Lasers in Engineering 19(5–6):331–345
Yan WY, Shaker A, El-Ashmawy N (2015) Urban land cover classification using airborne LiDAR data: a review. Remote Sens Environ 158:295–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.11.001
Yang CT, Stall JB (1971) Note on the map scale effect in the study of stream morphology. Water Resour Res 7(3):709–712. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR007i003p00709
Yang P, Ames PA, Fonseca A, Anderson D, Shrestha R, Glenn NF, Cao Y (2014) What is the effect of LiDAR-derived DTM resolution on large-scale watershed model results? Environ Model Softw 58:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.04.005
Yao X, Fu B, Lü Y, Sun F, Wang S, Liu M (2013) Comparison of four spatial interpolation methods for estimating soil moisture in a complex terrain catchment. PLoS One 8(1):e54660. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054660
Yilmaz HM (2007) The effect of interpolation methods in surface definition: an experimental study. Earth Surf Process Landf 32(9):1346–1361. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1473
Zhang P, Liu R, Bao Y, Wang J, Yu W, Shen Z (2014) Uncertainty of SWAT model at different DTM resolutions in a large mountainous watershed. Water Res 53:132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.01.018
Zhao C, Jensen J, Deng X, Dede-Bamfo N (2016) Impacts of LiDAR sampling methods and point spacing density on DEM generation. Papers in Applied Geography 2(3):261–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/23754931.2015.1121405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šiljeg, A., Barada, M., Marić, I. et al. The effect of user-defined parameters on DTM accuracy—development of a hybrid model. Appl Geomat 11, 81–96 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-018-0243-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-018-0243-1