Abstract
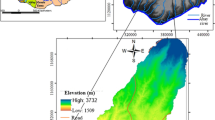
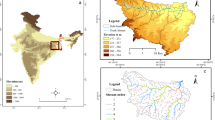
Groundwater resources have been under enormous strain due to over-exploitation and significant climate change. Due to its spatiotemporal diversity in distribution and occurrence, understanding the nature of these depleting resources is crucial for long-term adoption and development. A dry semi-arid climate prevails in this research area; farming is the most regular occupation, and they rely on groundwater due to a lack of surface water sources and erratic rainfall patterns. Therefore, an integrated approach of remote sensing, GIS and analytic hierarchical processes is used in the current research to help evaluate groundwater potential zones in the Boranakanive reservoir catchment. This analysis was carried out using twelve thematic layers, such as Lithology, Geomorphology, land use land cover, lineament density, drainage density, rainfall, groundwater level, soil, slope, curvature, Roughness Index, and Topographic Wetness Index. Each class is weighted in all thematic layers in accordance with its characteristics and water-holding capacity. Then, the groundwater potential index was prepared and added to the weighted-over analysis to generate the groundwater potential map. Finally, groundwater potential is categorized into five zones: very good (7.87%), good (28.81%), moderate (50.35%), poor (6.73%) and very poor (6.21%). The study results will enable future research and proposals for appropriate groundwater development planning and management.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Dar MA, Andualem TG, Teka AH (2020) GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation of groundwater potential of the Beshilo River basin. Ethiopia J Afr Earth Sci 164:103747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.103747
Aju CD, Achu AL, Raicy MC, Reghunath R (2021) Identification of suitable sites and structures for artificial groundwater recharge for sustainable water resources management in Vamanapuram River Basin, South India. HydroResearch 4:24–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2021.04.001
Andualem TG, Demeke GG (2019) Groundwater potential assessment using GIS and remote sensing: a case study of Guna tana landscape, upper blue Nile Basin. Ethiopia J Hydrol: Reg Stud 24:100610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2019.100610
Arulbalaji P, Gurugnanam B (2016) An integrated study to assess the groundwater potential zone using the geospatial tool in Salem District, South India. J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng of 7:2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2325-9647.1000136
Arulbalaji P, Padmalal D, Sreelash K (2019) GIS and AHP techniques based delineation of groundwater potential zones: a case study from the southern Western Ghats India. Sci Reports 9(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38567-x
Beven K (1997) TOPMODEL: a critique. Hydrol Process 11:1069–1085
Chaudhry AK, Kumar K, Alam MA (2021) Mapping of groundwater potential zones using the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and geospatial technique. Geocarto Int 36(20):2323–2344. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1695959
Das S (2019) Comparison among influencing factors, frequency ratio, and analytical hierarchy process techniques for groundwater potential zonation in Vaitarna basin, Maharashtra, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 8:617–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.03.003
Das S (2021) Hydro-geomorphic characteristics of the Indian (Peninsular) catchments: based on morphometric correlation with hydro-sedimentary data. Adv Space Res 67(8):2382–2397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.01.043
Das B, Pal SC (2019) Combination of GIS and fuzzy-AHP for delineating groundwater recharge potential zones in the critical Goghat-II block of West Bengal, India. HydroResearch 2:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.10.001
Das B, Pal SC, Malik S, Chakrabortty R (2019) Modeling groundwater potential zones of Puruliya district, West Bengal, India using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Geol Ecol Landsc 3(3):223–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1555740
Díaz-Alcaide S, Martínez-Santos P (2019) Advances in groundwater potential mapping. Hydrogeol J 27(7):2307–2324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-019-02001-3
Doke AB, Zolekar RB, Patel H, Das S (2021) Geospatial mapping of groundwater potential zones using multi-criteria decision-making AHP approach in a hard rock basaltic terrain in India. Ecol Ind 127:107685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107685
Etikala B, Golla V, Li P, Renati S (2019) Deciphering groundwater potential zones using MIF technique and GIS: a study from Tirupati area, Chittoor District, Andhra Pradesh, India. HydroResearch 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.04.001
Goitsemang T, Das DM, Raul SK, Subudhi CR, Panigrahi B (2020) Assessment of groundwater potential in the Kalahandi district of Odisha (India) using remote sensing, geographic information system, and analytical hierarchy process. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48(12):1739–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01188-3
Ifediegwu SI (2022) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS and AHP techniques: a case study of the Lafia district, Nasarawa State Nigeria. Appl Water Sci 12(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01556-5
Igwe O, Ifediegwu SI, Onwuka OS (2020) Determining the occurrence of potential groundwater zones using integrated hydro-geomorphic parameters, GIS, and remote sensing in Enugu State, Southeastern Nigeria. Sustain Water Resour Manag 6(3):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00397-5
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Magesh NS (2014) Identification of potential groundwater recharge zones in Vaigai upper basin, Tamil Nadu, using GIS-based analytical hierarchical process (AHP) technique. Arab J Geosci 7:1385–1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0849-x
Kordestani MD, Naghibi SA, Hashemi H, Ahmadi K, Kalantar B, Pradhan B (2019) Groundwater potential mapping using a novel data-mining ensemble model. Hydrogeol J 27(1):211–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1848-5
Machiwal D, Jha MK, Mal BC (2011) Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS, and MCDM techniques. Water Resour Manage 25(5):1359–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9749-y
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS, and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3(2):189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.007
Mokarram M, Roshan G, Negahban S (2015) Landform classification using topography position index (case study: the salt dome of Korsia-Darab plain, Iran). Model Earth Syst Environ 1(4):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0055-9
Mukhopadhyay BP, Barua S, Bera A, Mitra AK (2020) Study on the quality of groundwater and its impact on human health: a case study from Murshidabad district, West Bengal. J Geol Soc India 96(6):597–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1608-8
Naghibi SA, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghi ZS, Rezaei A (2015) Groundwater qanat potential mapping using frequency ratio and Shannon’s entropy models in the Moghan watershed Iran. Earth Sci Inform 8(1):171–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-014-0145-7
Naghibi SA, Pourghasemi HR, Dixon B (2016) GIS-based groundwater potential mapping using boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and random forest machine learning models in Iran. Environ Monit Assess 188(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5049-6
Nair HC, Padmalal D, Joseph A, Vinod PG (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in river basins using geospatial tools—an example from Southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. J Geovisualization Spatial Anal 1(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-017-0003-5
Owolabi ST, Madi K, Kalumba AM, Orimoloye IR (2020) A groundwater potential zone mapping approach for semi-arid environments using remote sensing (RS), geographic information system (GIS), and analytical hierarchical process (AHP) techniques: a case study of Buffalo catchment, Eastern Cape South Africa Arabian. J Geosci 13(22):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06166-0
Panikkar P, Saha A, Prusty AK, Sarkar UK, Das BK (2022) Assessing hydrogeochemistry, water quality index (WQI), and seasonal pattern of plankton community in different small and medium reservoirs of Karnataka India. Arab J Geosci 15(1):82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09291-6
Pourtaghi ZS, Pourghasemi HR (2014) GIS-based groundwater spring potential assessment and mapping in the Birjand Township, southern Khorasan Province Iran. Hydrogeol J 22(3):643–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-013-1089-6
Pradhan B (2009) Groundwater potential zonation for basaltic watersheds using satellite remote sensing data and GIS techniques. Central Eur J Geosci 1(1):120–129. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10085-009-0008-5
Raju RS, Raju GS, Rajasekhar M (2019) Identification of groundwater potential zones in Mandavi River basin, Andhra Pradesh, India using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. HydroResearch 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.09.001
Rakesh CJ, Govindaraju, Lokanath S, Kumar AK (2023) Prioritization of soil erosion prone sub-watersheds through morphometric analysis using geospatial and weighted sum approach: a case study of Boranakanive reservoir catchment in Tumkur district, Karnataka India. Environ Earth Sci 82(12):306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10996-y
Riley SJ, DeGloria SD, Elliot R (1999) The index quantifies topographic heterogeneity. Intermountain J Sci 5(1–4):23–27
Roy S, Hazra S, Chanda A, Das S (2022) Land suitability analysis using AHP-based multi-criteria decision model for sustainable agriculture in red and lateritic zones of West Bengal India. J Earth Syst Sci 131(4):201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01941-x
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Shao Z, Huq ME, Cai B, Altan O, Li Y (2020) Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach using Fuzzy-AHP to delineate and identify groundwater potential zones in semi-arid Shanxi Province China. Environ Model Software 134:104868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104868
Shruthi R, Ramakrishna S (2020) Heterogeneity of Zooplanktons in Boranakanive reservoir of Tumakuru District, Karnataka, India. Eco Env Cons S204-S209
Swain KC, Singha C, Nayak L (2020) Flood susceptibility mapping through the GIS-AHP technique using the cloud. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 9(12):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120720
Yadav SK, Dubey A, Szilard S, Singh SK (2018) Prioritization of sub-watersheds based on earth observation data of agricultural dominated northern river basin of India. Geocarto Int 33(4):339–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1265592
Yalew SG, Van Griensven A, Mul ML, van der Zaag P (2016) Land suitability analysis for agriculture in the Abbay basin using remote sensing, GIS and AHP techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0167-x
Yeh HF, Cheng YS, Lin HI, Lee CH (2016) Mapping groundwater recharge potential zone using a GIS approach in Hualian River Taiwan. Sustain Environ Res 26(1):33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2015.09.005
Yesilnacar E, Topal TAMER (2005) Landslide susceptibility mapping: a comparison of logistic regression and neural networks methods in a medium scale study, Hendek region (Turkey). Eng Geol 79(3–4):251–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.02.002
Yıldırım Ü (2021) Identification of groundwater potential zones using GIS and multi-criteria decision-making techniques: a case study upper Coruh River basin (NE Turkey). ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 10(6):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060396
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rakesh, C.J., Govindaraju, Lokanath, S. et al. Geospatial and AHP technique in assessment of groundwater potential zones—a case study of Boranakanive reservoir catchment in India. Arab J Geosci 16, 664 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11780-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11780-9