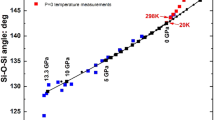
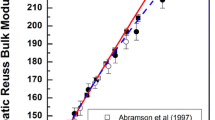
Abstract
The structure, elasticity and conductivity of hydrous fayalite (Fe2SiO4Hx (x= 0.25, 0.5, 0.75)) are discussed based on the First-principles. Fe2SiO4Hx (x= 0.25, 0.5, 0.75) models are established by hydrogen atoms occupying the interstice space of the fayalite (Fe2SiO4) unit cell. The optimized results show that hydrogen atoms form hydroxyl (OH−) with the surrounding oxygen atoms in the modeling course, which is consistent with the experimental conclusion that water exists in fayalite in the form of OH−. The calculated results of the elastic constants for Fe2SiO4Hx (x= 0.25, 0.5, 0.75) show that the elastic constants increase as the pressure increases and decrease as the water content increases at 0\(\sim \)30 GPa. Compared to Fe2SiO4, the ranges of compression wave velocity (Vp) of Fe2SiO4Hx (x= 0.25, 0.5, 0.75) are 1.02\(\sim \)3.52%, 3.06\(\sim \)4.30%, 3.63\(\sim \)6.93%; in the meanwhile, the ranges of shear wave velocity (Vs) are 0.01\(\sim \)7.01%, 0.40\(\sim \)8.85%, and 2.50\(\sim \)3.13%; this is in line with the wave velocity, which was observed to experimentally reduce to 2\(\sim \)5% in the low-velocity layer of the mantle. The decrease of wave velocity due to water may be the formation mechanism of low velocity layer. When analyzing the conductivity, the conductivity per relaxation time σ/τ gradually increases with the rise of temperature, while different pressures have little influence on σ/τ. At the same temperature, σ/τ increases with the water content of fayalite. The result theoretically explains why the upper mantle transition zone has the phenomenon of high conductivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artemieva IM (2003) Lithospheric structure, composition, and thermal regime of the east european craton: implications for the subsidence of the russian platform. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 213 (3-4):431–446. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x%2803%2900327-3
Beran A, Putnis A (1983) A Model of the OH positions in olivine, derived from infrared-spectroscopic investigations. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals 9(2):57–60. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00308148
Chmielowski R, Péré D, Bera C, Opahle I, Xie W, Jacob S (2015) Theoretical and experimental investigations of the thermoelectric properties of bi2s3. Journal of Applied Physics 117(12):125103. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4916528
Cococcioni M, Gironcoli S (2005) Linear response approach to the calculation of the effective interaction parameters in the LDA+Umethod. Physical Review B, 71(3). Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.71.035105
Dai L, Karato SI (2014) High and highly anisotropic electrical conductivity of the asthenosphere due to hydrogen diffusion in olivine. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 408:79–86. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.10.003
Dennler G, Chmielowski R, Jacob S, Capet F, Roussel P, Zastrow S (2014) Are binary copper sulfides/selenides really new and promising thermoelectric materials? Advanced Energy Materials 4 (9):1301581. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201301581
Frost D, Dolejs D (2007) Experimental determination of the effect of h2o on the 410-km seismic discontinuity. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 256(1-2):182–195. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.01.023
Gung Y, Panning M, Romanowicz B (2003) Global anisotropy and the thickness of continents. Nature 422(6933):707–711. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01559
Hill R (1952) The elastic behaviour of a crystalline aggregate. Proceedings of the Physical Society. Section A 65(5):349–354. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1088/0370-1298%2F65%2F5%2F307
Holzapfel C, Chakraborty S, Rubie D, Frost D (2007) Effect of pressure on fe-mg, ni and mn diffusion in (FexMg1-x)2sio4 olivine. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 162(3-4):186–198. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2007.04.009
Huang X, Xu Y, Karato SC (2005) Water content in the transition zone from electrical conductivity of wadsleyite and ringwoodite. Nature 434(7034):746–749. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03426
Inoue T, Ueda T, Tanimoto Y, Yamada A, Irifune T (2010) The effect of water on the high-pressure phase boundaries in the system mg2sio4-fe2sio4. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 215:012101. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596%2F215%2F1%2F012101
Ishii T, Kojitani H, Akaogi M (2018) Phase relations and mineral chemistry in pyrolitic mantle at 1600-2200 ∘c under pressures up to the uppermost lower mantle: phase transitions around the 660-km discontinuity and dynamics of upwelling hot plumes. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 274:127–137. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2017.10.005
Jacobsen SD, Jiang F, Mao Z, Duffy TS, Smyth JR, Holl CM (2008) Effects of hydration on the elastic properties of olivine. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(14). Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1029/2008gl034398
Katsura T, Sato K, Ito E (1998) Electrical conductivity of silicate perovskite at lower-mantle conditions. Nature 395(6701):493–495. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1038/26736
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficient iterative schemes forab initiototal-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B 54(16):11169–11186. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.54.11169
Li B (2003) Compressional and shear wave velocities of ringwoodite g-mg2sio4to 12 GPa. American Mineralogist 88(8-9):1312–1317. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2003-8-913
Liu Q, Liu W, Whitaker ML, Wang L, Li B (2010) In situ ultrasonic velocity measurements across the olivine-spinel transformation in fe2sio4. American Mineralogist 95(7):1000–1005. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2010.3369
Madsen GK, Carrete J, Verstraete MJ (2018) BoltzTraP2, a program for interpolating band structures and calculating semi-classical transport coefficients. Computer Physics Communications 231:140–145. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2018.05.010
Madsen GK, Singh DJ (2006) BoltzTraP. a code for calculating band-structure dependent quantities. Computer Physics Communications 175(1):67–71. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2006.03.007
Manthilake M, Matsuzaki T, Yoshino T, Yamashita S, Ito E, Katsura T (2009) Electrical conductivity of wadsleyite as a function of temperature and water content. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 174(1-4):10–18. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2008.06.001
Morozova E, Morozov I, Smithson S, Solodilov L (2000) Lithospheric boundaries and upper mantle heterogeneity beneath russian eurasia: evidence from the DSS profile QUARTZ. Tectonophysics 329 (1-4):333–344. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-1951%2800%2900202-x
Nong ZS, Wang HY, Zhu JC (2020) First-principles calculations of structural, elastic and electronic properties of (TaNb)0.67(HfZrTi)0.33 high-entropy alloy under high pressure. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials 27(10):1405–1414. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2095-z
Pontevivo A, Thybo H (2006) Test of the upper mantle low velocity layer in siberia with surface waves. Tectonophysics 416(1-4):113–131. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2005.11.015
Qin T, Wentzcovitch RM, Umemoto K, Hirschmann MM, Kohlstedt DL (2018) Ab initio study of water speciation in forsterite: importance of the entropic effect. American Mineralogist 103(5):692–699. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2018-6262
Shankland T (1975) Electrical conduction in rocks and minerals: parameters for interpretation. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 10(3):209–219. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9201%2875%2990047-3
Shi H, Parker D, Du MH, Singh DJ (2015) Connecting thermoelectric performance and topological-insulator behavior:bi2te3andbi2te2sefrom first principles. Physical Review Applied, 3(1). Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevapplied.3.014004
Thybo H, Perchu E, Zhou S (2000) Intraplate earthquakes and a seismically defined lateral transition in the upper mantle. Geophysical Research Letters 27(23):3953–3956. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1029/2000gl011636
Wang DJ, Mookherjee M, Xu YS, Karato SI (2006) The effect of water on the electrical conductivity of olivine. Nature 443(7114):977–980. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05256
Wei Y, Yang Y, Cen W, Li R, Lv L (2016) The effect on the electric structure and optical properties of ca2ge bulk with sr-doping. Journal of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering 04(11):20–26. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.4236/msce.2016.411003
Wu Y, Wang YB, Zhang YF, Jin ZM, Wang C, Zhou CY (2011) An experimental study of phase transformations in olivine under pressure and temperature conditions corresponding to themantle transition zone. Chinese Science Bulletin 57(8):894–901. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4884-2
Xu Y (1998) Electrical conductivity of olivine, wadsleyite, and ringwoodite under upper-mantle conditions. Science 280(5368):1415–1418. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5368.1415
Yang X, Hou H, Zhao Y, Yang L, Han P (2014) First-principles investigation of the structural, electronic and elastic properties of al2ca and al4sr phases in mg-alca(sr) alloy. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater Sci Ed 29(5):1049–1056. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-014-1042-0
Ye Y, Brown DA, Smyth JR, Panero WR, Jacobsen SD, Chang YY (2012) Compressibility and thermal expansion of hydrous ringwoodite with 2.5(3) wt% h2o. AmericanMineralogist 97(4):573–582. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2012.4010
Yoshino T, Katsura T (2009) Reply to comments on “electrical conductivity of wadsleyite as a function of temperature and water content” by manthilake et al. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 174 (1-4):22–23. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2009.01.012
Zhang JS, Hu Y, Shelton H, Kung J, Dera P (2016) Single-crystal x-ray diffraction study of fe2sio4 fayalite up to 31 GPa. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals 44(3):171–179. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-016-0846-1
Zhang L (1998) Single crystal hydrostatic compression of (mg,mn,fe,co) 2 SiO 4 olivines. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals 25(4):308–312. Disponible sur https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050119
Funding
This work is financed by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41930112, 91755215 and 11804238), National University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of China (Grant No. 202010616015). Great appreciation goes to the editorial board and the reviewers of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by:Domenico M. Doronzo
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Zhang, C., Zhu, H. et al. First-principles investigations of structural, elastic and electronic properties of hydrous fayalite. Arab J Geosci 15, 1108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09919-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09919-1