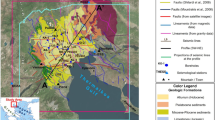
Abstract
There are multiple hydrocarbon-generating sags on the peripheral plane of Baijiahai Uplift, and there are multiple layers of source rocks in the vertical direction. How to identify which sags and source rocks are the sources of oil and gas in Baijiahai Uplift is the focus of oil and gas exploration. In this paper, based on the geochemical characteristics of oil and gas, the genesis of multi-source oil and gas is identified and summarizes the law of oil and gas enrichment. The results show that the carbon isotope of crude oil in this area is -26.73‰ to -29.51‰, Pr/nC17 and Ph/nC18 are low, sterane and light hydrocarbon parameters indicating that crude oil is a mixture of Permian and Jurassic source rocks. Using the formula: (δ13Coil) = (δ13Coil)C46 X + (δ13Coil)C1 (1-X). It is concluded that the mixed source oil and gas mainly come from Jurassic source rocks, and there is a small amount of mixture of Permian source rocks. The dry coefficient of natural gas in Baijiahai Uplift is between 0.92 and 0.98, most of which are dry gas. The average carbon isotope of ethane is about -26‰, which is similar to natural gas in Kelameili gasfield, and both are derived from Carboniferous source rocks in Dongdaohaizi Sag. The distribution of faults has a certain control effect on the migration and accumulation of oil and gas. Oil and gas are mainly distributed in Dongdaohaizi fault zone and Baijiahai fault zone. The next exploration direction should be close to the faulted structural belt of the hydrocarbon-generating sag.








source rocks and crude oil in studied area





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang ZY, Zhang WF, Ge X, Zhu SK (2018) Use of light hydrocarbons for the oil-oil correlation in Pearl River Mouth Basin. South China Sea Fuel 221(1):179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.089
Cheng L, Wang ZQ, Chen Y (2015) Reservoir forming model and exploration direction of jurassic petroleum, Baijiahai swell Junggar basin. Science Technology and Engineering 15(025):115–119. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.25.021
Chen JP, Deng CP, Liang DG, Wang XL, Zhong NN, Song FQ, Shi XP, Jin T, Xiang SZ (2003) Mixed oils derived from multiple source rocks in the Cainan oilfield, Junggar Basin, Northwest China. Part II: artificial mixing experiments on typical crude oils and quantitative oil-source correlation. Organic Geochemistry 34(7):911–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(03)00031-7
Dai JX, Gong DY, Ni YY, Huang SP, Wu W (2014) Stable carbon isotopes of coal-derived gases sourced from the Mesozoic coal measures in China. Org Geochem 74:123–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.04.002
Jia CZ, Zou CN, Yang Z, Zhu RK, Chen ZX, Zhang B, Jiang L (2018) Significant progress of continental petroleum geology theory in basins of Central and Western China. Pet Explor Dev 45(4):546–560. https://doi.org/10.11698/PED.2018.04.02
Jin J, Fu H, Yu JW, Qi LQ, Shang L, Wen HG, Xu WL (2018) Sedimentary evolution of the Lower Jurassic Sangonghe formation in Baijiahai uplift, Junggar basin and its significance in oil and gas exploration. China Petroleum Exploration 23(001):81–90. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.009
Li Y, Chen SJ, Lu JG, Wang G, Zou XL, Xiao ZL, Su KM, He QB, Luo XP (2020a) The logging recognition of solid bitumen and its effect on physical properties, AC, resistivity and NMR parameters. Mar Pet Geol 112:104070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104070
Li Y, Chen SJ, Wang YX, Su KM, He QB, Qiu W, Xiao ZL (2020b) Relationships between hydrocarbon evolution and the geochemistry of solid bitumen in the Guanwushan Formation, NW Sichuan Basin. Mar Pet Geol 111:116–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo2019.08.018
Lu JG, Luo ZY, Zou HL, Li YP, Hu ZZ, Zhou ZY, Zhu J, Han MM, Zhao LP, Lin ZH (2021) Geochemical characteristics, origin, and mechanism of differential accumulation of natural gas in the carboniferous kelameili gas field in Junggar basin, China. J Petrol Sci Eng 203:108658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108658
Luo ZY, Lu JG, Zou HL, Li YP, Hu ZZ (2020a) Inversion of hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism by geochemical characteristics: a case study of well DN 7, Junggar Basin, China. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1818893
Luo ZY, Lu JG, Zou HL, Li YP, Hu ZZ (2020b) Influence of methane diffusion on geochemical characteristics of natural gas: a case study of the Shiqiantan area in Junggar Basin, China. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects (1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1812771
Pei LX, Gang WZ, Zhu CZ, Liu YZ, He WJ, Dong Y, Xiang BL (2018) Carbon isotope and origin of the hydrocarbon gases in the Junggar Basin China. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience 3(5):253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnggs.2018.11.002
Peter KE, Moldowan MJ, Driscole AR, Demaison GJ (1989) Origin of beatrice oil by co-sourcing from devonian and middle jurassic source rocks, inner moray firth United Kingdom. AAPG Bulletin 73(4):454–471. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB094iB04p04697
Peters KE, Moldowan MJ (1991) Effects of source, thermal maturity, and biodegradation on the distribution and isomerization of homohopanes in petroleum. Org Geochem 17:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6380(91)90039-M
Su KM, Chen SJ, Hou YT, Zhang HF, Zhang XL, Zhang WX, Liu GL, Hu C, Han MM (2021) Geochemical characteristics, origin of the Chang 8 oil and natural gas in the southwestern Ordos Basin, China. J Petrol Sci Eng 200:108406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108406
Su KM, Lu JG, Zhang GW, Chen SJ, Li Y, Xiao ZL, Wang P, Qiu W (2018) Origin of natural gas in Jurassic Da’anzhai Member in the western part of central Sichuan Basin, China. J Petrol Sci Eng 167:890–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.04.014
Thompson KFM (1979) Light hydrocarbons in subsurface sediments. Geochem Cosmochim Acta 43:657–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(79)90251-5
Wang YZ, Lin MR, Xi KL, Cao YC, Wang J, Yuan GH, Kashif M, Song MS (2018) Characteristics and origin of the major authigenic minerals and their impacts on reservoir quality in the Permian Wutonggou Formation of Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin, western China. Mar Pet Geol 97:241–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.07.008
Wei ZF, Wang YL, Wu CJ, Wu BX, Sun ZP, Li SX, Wei W (2015) Geochemical characteristics of source rock from Upper Permian Longtan Formation in Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience 26(8):1613–1620. https://doi.org/10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2015.08.1613
Xu ZJ, Liu LF, Jiang S, Wang TG, Wu KJ, Feng YJ, Xiao F, Chen YY, Chen YT, Feng CY (2019) Migration model of hydrocarbons in the slope of the superimposed foreland basin: A study from the South Junggar, NW China. J Petrol Sci Eng 182:106337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106337
Xiao ZL, Chen SJ, Liu CW, Lu ZX, Zhu J, Han MM (2021) Lake basin evolution from early to Middle Permian and origin of Triassic Baikouquan oil in the western margin of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China: Evidence from geochemistry. J Petrol Sci Eng 203:108612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108612
Yang L, Jin ZJ (2019) Global shale oil development and prospects. China Petroleum Exploration 24(5):553–559. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.002
Zhang L, He DF, Li D, Ji DS, Liang YS, Zheng ML, Wu ST, Zhou G (2019) Geological structure and genesis model of the Baijiahai uplift in the Junggar Basin. Earth Sci Front 26(1):1005–2321. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.sf.2018.12.1
Zhao WZ, Hu SY, Hou LH, Yang T, Li X, Guo BC, Yang Z (2020) Types and resource potential of continental shale oil in China and its boundary with tight oil. Pet Explor Dev 47(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.11698/PED.2020.01.01
Zhou ZY, Lu JG (2020) Origin of heavy crude oil in the northern segment of the Zhangbei fault-bundling belt, eastern Junggar Basin, China. Energy Sources, Part a: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1813850
Zhou ZY, Lu JG, Wu H, Liu Y (2021) NMR response of maturity parameters and biodegradation grade of heavy oil. Pet Sci Technol 39(11):441–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2021.1925694
Zou HL, Lu JG, Qiu W, Yuan B, Wu BY, Hu ZZ, Yang DS (2017) The source of gas and oil in Cainan oilfield Jurassic layers of Junggar Basin. Pet Sci Technol 35(19):1873–1878. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2017.1369112
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41872165, No. 42072185).
Funding and/or Conflicts of interests/Competing interests: There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Lu, J. Identification of multi-source hydrocarbon genesis: a case study of Baijiahai Uplift, Junggar Basin, China. Arab J Geosci 15, 149 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09478-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09478-5