Abstract
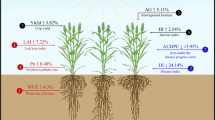
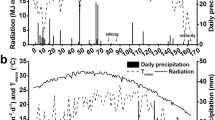
The yield and quality of maize grains are determined by genotype and environmental factors. Through a systematic comparison of the density effects of maize yield and quality of different plant-type varieties grown on land under four different ecological environments in a certain province, and the differences in maize yield and quality in different ecological regions, the reasons for the differences were analyzed. The results showed that differences in light, accumulated temperature, and precipitation are important reasons for yield differences, and these factors are also key factors affecting maize grain quality. Taking the southern ecological zone as an example, the effects of different planting densities on the content of nutrients such as protein, starch, and fat in maize grains were studied. The study found that with the increase of planting density, the grain protein content decreased significantly, while the increasing and decreasing trend of protein, fat, and starch content (PFSC) was more complicated. By formulating maize varieties, density, and other related control measures to make full use of ecological resources and give play to regional advantages, high-quality and high-yield maize can be achieved.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 November 2021
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09064-1
28 September 2021
An Editorial Expression of Concern to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08471-8
References
Altieri MA, Nicholls CI, Montalba R (2017) Technological approaches to sustainable agriculture at a crossroads: an agroecological perspective. Sustainability 9(3):349
Bajwa AA, Zulfiqar U, Sadia S, Bhowmik P, Chauhan BS (2019) A global perspective on the biology, impact and management of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale: two troublesome agricultural and environmental weeds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):5357–5371
Iqbal MA, Hamid A, Ahmad T, Siddiqui MH, Hussain I, Ali S, Ahmad Z (2019) Forage sorghum-legumes intercropping: effect on growth, yields, nutritional quality and economic returns. Bragantia 78(1):82–95
Kumar RK, Thilagaraj M (2021) Automated smoothie maker. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT) 12(10):1385–1397
Kumar R, Singh M, Meena BS, Kumar S, Yadav MR, Parihar CM, Kumar U (2017) Quality characteristics and nutrient yield of fodder maize (Zea mays) as influenced by seeding density and nutrient levels in Indo-Gangetic Plains. Indian J Agric Sci 87:1203–1208
Kumar RK, Thilagaraj M, Vengatesh P, Rajalakshmi J, Babul MM (2021) Remote transformer faults analyzing system using IoT. International Journal of Modern Agriculture 10(2):2390–2402
MacLaren C, Storkey J, Menegat A, Metcalfe H, Dehnen-Schmutz K (2020) An ecological future for weed science to sustain crop production and the environment. A review, Agronomy for Sustainable Development 40(4):1–29
Palamarchuk V, Krychkovskyi V, Honcharuk ІTN (2021) The modeling of the production process of high-starch maize hybrids of different maturity groups. European Journal of Sustainable Development 10(1):584–598
Sokolow J, Kennedy G, Attwood S (2019) Managing crop tradeoffs: a methodology for comparing the water footprint and nutrient density of crops for food system sustainability. J Clean Prod 225:913–927
Thapa S, Xue Q, Stewart BA (2020) Alternative planting geometries reduce production risk in maize and sorghum in water-limited environments. Agron J 112(5):3322–3334
Thilagaraj M, Krishna Kumar R (2021) Locating various license numbers in the wild: an effective approach. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT) 12(10):1440–1445
Thilagaraj M, Kumar RK, Krishnaraj M, Aravinth V, Mohanraj P, Akashkumar (2021) Design and implementation of coal mine safety monitoring and alerting system using IoT. International Journal of Modern Agriculture 10(2):2382–2389
Woli KP, Sawyer JE, Boyer MJ, Abendroth LJ, Elmore RW (2018) Maize era hybrid macronutrient and dry matter accumulation in plant components. Agron J 110(5):1648–1658
Youngerman CZ, DiTommaso A, Curran WS, Mirsky SB, Ryan MR (2018) Maize density effect on interseeded cover crops, weeds, and grain yield. Agron J 110(6):2478–2487
Zhang D, Sun Z, Feng L, Bai W, Yang N, Zhang Z, Zhang L (2020) Maize plant density affects yield, growth and source-sink relationship of crops in maize/peanut intercropping. Field Crop Res 257:107926
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by Hainan Natural Science Foundation. The agglomerate structure of red soil in Hainan province was improved by conservation tillage No. 519QN289; research on recognition method of maize crop nutrition status based on UVA Hyperspectral Imaging Technology No. ZRCPY202017; and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences No. 19CXTD-31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sheldon Williamson
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Environment and Low Carbon Transportation
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09064-1
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, L., Wang, C., Li, H. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Comparative analysis of nutritional components of maize with different planting densities from the perspective of ecological environment. Arab J Geosci 14, 1205 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07600-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07600-7