Abstract
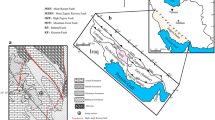
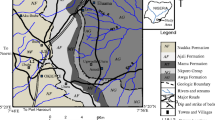
The Cretaceous-Paleogene sequence, including K-Pg transition, located 45 km from the South of Sari in the North of Iran was analyzed in regards to lithology, lithofacies, foraminifera, and palynology evaluation. The main aim of this study was the reconstruction of sedimentary environmental condition including relative sea level changes during the K-Pg transition. Seventy rock samples were collected from 133 m of sedimentary rocks, mainly comprising limestone, sandstone, siltstone, and evaporate. Two species of foraminifera, ten species of spore, and seven species of pollen grains have been identified. K/Pg boundary has been determined based on the first occurrence of Tricolpites phillipsii in the 133 m above the base of the studied section. Two palynofacies have been identified based on statistical analysis of palynofacies factors (SOM, MP, Ph). Palynofacies analysis suggests nearshore (inner ramp) as a sedimentary environment for these sequences. Our palynofacies data indicate sea-level regression near K/P which can be correlated to the global sea level trend.














Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ataabadi MM, Abbassi N (2007) Affinities and implications of new Miocene mammal footprints from Iran. Vertebrata Pal Asiatica 45(2):128–136
Beiranvand B, Zaghbib-Turki D, Ghasemi-Nejad E (2014) Integrated biostratigraphy based on planktonic foraminifera and dinoflagellates across the Cretaceous/Paleogene (K/Pg) transition at the Izeh section (SW Iran). C R Palevol 13:235–258
Berra F, Angiolini L (2014) The evolution of the Tethys region throughout the Phanerozoic: a brief tectonic reconstruction
Bujak JP, Williams GL (1979) Dinoflagellate diversity through time. Mar Micropaleontol 4:1–12
de Araujo Carvalho M, Mendonça Filho JG, Menezes TR (2006) Palynofacies and sequence stratigraphy of the Aptian–Albian of the Sergipe Basin, Brazil. Sediment Geol 192(1-2):57–74
Del Papa C, Quattrocchio M (2002) Sedimentary facies and palynofacies assemblages in an Eocene perennial lake, Lumbrera formation, northwest Argentina. J S Am Earth Sci 15(5):553–569
Etemad-Saeed N, Hosseini-Barzi M, Adabi MH, Miller NR, Sadeghi A, Houshmandzadeh A, Stockli DF (2016) Evidence for ca. 560 Ma Ediacaran glaciation in the Kahar formation, central Alborz Mountains, northern Iran. Gondwana Res 31:164–183
Federova VA (1977) The significance of the combined use of microphytoplankton, spores, and pollen for differentiation of multi-facies sediments IN SAMOILOVICH, SR & TIMOSHINA, NA (Eds.) Questions of Phytostratigraphy. Leningrad, Trudy Neftyanoinauchno-issledovatelskiigeologorazvedochnyi Institute (VNIGRI)
Handford CR, Loucks RG (1993) Carbonate depositional sequences and systems tracts--responses of carbonate platforms to relative sea-level changes: Chapter 1
Mohajer Soltani H, Shariat Zadeh M (1393) Geochemistry of source rock potential in South of Sari, North of Iran. Sci Propagative J Oil Gas Explor Prod (117):45–50
Oboh-Ikuenobe FE, de Villiers SE (2003) Dispersed organic matter in samples from the western continental shelf of Southern Africa: palynofacies assemblages and depositional environments of Late Cretaceous and younger sediments. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 201(1-2):67–88
Ocampo A, Vajda V, Buffetaut E (2006) Unravelling the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) turnover, evidence from flora, fauna and geology, Biological processes associated with impact events. Springer, Berlin, pp 197–219
Rezaeian M (2009) Coupled tectonics, erosion and climate in the Alborz Mountains, Iran. University of Cambridge, Cambridge
Schulte P, Alegret L, Arenillas I, Arz JA, Barton PJ, Bown PR, Bralower TJ, Christeson GL, Claeys P, Cockell CS (2010) The Chicxulub asteroid impact and mass extinction at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Science 327(5970):1214–1218
Stehlin HA (1931) una mandibula de giraffidae de tokoum (perse). Eclogae Geol Helv 24(2):275–279
Stöcklin J (1974) Northern Iran: Alborz Mountains. Geol Soc Lond, Spec Publ 4(1):213–234
Stover LE, Brinkhuis H, Damassa SP, De Verteuil L, Helby RJ, Monteil E, Partridge AD, Powell AJ, Riding JB, Smelror M, Williams GL (1996) Mesozoic-Paleogene dinoflagellates, acritarchs and prasinophytes. In: Palynology: principles and applications, vol 2, pp 641–750
Tappan H, Loeblich AR Jr (1970) Geobiologic implications of fossil phytoplankton evolution and time-space distribution. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap (127):247–340
Traverse A (2007) Paleopalynology. Springer, Dordrecht, p 813
Tyson RV (1993) Palynofacies analysis. In: Jenkins DJ (ed) Applied Micropalaeontology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 153–191
Tyson RV (1995) Sedimentary organic matter: organic facies and palynofacies. Chapman & Hall, London, p 615
Tyson RV (1996) Sequence-stratigraphical interpretation of organic facies variations in marine siliciclastic systems; general principles and application to the onshore Kimmeridge Clay Formation, UK. In: Hesselbo SP, Parkinson DN (eds) Sequence stratigraphy in British Geology, vol 103. Geological Society Special Publication, pp 75–96
Vahdati Daneshmand F (2003) Geological map of Pol-e Sefid: Geological Survey of Iran
Vajda V, Raine JI (2003) Pollen and spores in marine Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary sediments at mid-Waipara River, North Canterbury, New Zealand. N Z J Geol Geophys 46(2):255–273
Willumsen PS, Vajda V (2010) A new early paleogene dinoflagellate cyst species, Trithyrodinium partridgei: its biostratigraphic significance and palaeoecology. Alcheringa 34(4):523–538
Wood SE, Gorin GE (1998) Sedimentary organic matter in distal clinoforms of Miocene slope sediments: Site 903 of ODP Leg 150, onshore New Jersey (USA). J Sediment Res 68:856–868
Zaghbib-Turki D, Beiranvand B (2014) Planktonic foraminiferal extinction pattern, evolution, turnover, and geochemical anomalies across the Cretaceous/Paleogene boundary (K/Pg) in Izeh (Zagros Basin, SW Iran). Arab J Geosci 10(20):443
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Khazar Exploration and Production Company (Kepco) and the University of Zanjan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Beatriz Badenas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabbani, J., Emamgholi, R., Abbassi, N. et al. Late Cretaceous to Early Paleogene global sea level fluctuations and the sedimentary environment in central Alborz (Northern Iran). Arab J Geosci 13, 1258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06262-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06262-1