Abstract
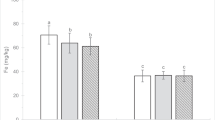
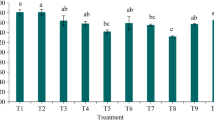
The use of machinery in vineyards is increasing soil compaction and erosion. However, there is a lack of information about the impacts of different management practices on soil conditions of vineyards. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess soil compaction in Croatian vineyards under four different management systems: no-tillage (NT) system, conventional tillage (CT), yearly inversed grass covered (INV-GC) and tillage managed (INV-T) treatments. Four key top-soil (0–20 cm) parameters were assessed in the different land uses: bulk density (BD), penetration resistance (PR), soil water content (SWC) and carbon dioxide (CO2) fluxes. Tractor traffic increased the BD and PR in all treatments, with exception of CT treatment, as consequence of tillage. SWC showed higher values in INV-GC treatment during the dry period; meanwhile, it was similar during the wet season in every management type. Lower CO2 fluxes were found in INV-GC and NT than in the CT and INV-T treatments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire SE, Lange SF, Lafond JA, Pelletier B, Cambouris AN, Dutilleul P (2012) Multiscale spatial variability of CO2 emissions and correlations with physico-chemical soil properties. Geoderma 170:251–260. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.11.019
Alvarez R, Steinbach HS (2009) A review of the effects of tillage systems on some soil physical properties, water content, nitrate availability and crops yield in the Argentine Pampas. Soil Tillage Res 104:1–15. doi:10.1016/j.still.2009.02.005
Ampoorter E, Schrijver AD, van Nevel L, Hermy M, Verheyen K (2012) Impact of mechanized harvesting on compaction of sandy and clayed soils: results of a meta-analysis. Ann For Sci 69:533–542. doi:10.1007/s13595-012-0199-y
Arnaez J, Lasanta T, Ruiz-Flaño P, Ortigosa L (2007) Factors affecting runoff and erosion under simulated rainfall in Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res 93:324–334. doi:10.1016/j.still.2006.05.013
Barik K, Aksakal EL, Islam KR, Sari S, Angin I (2014) Spatial variability in soil compaction properties associated with field traffic operations. Catena 120:122–133. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2014.04.013
Bauer PJ, Frederick JR, Novak JM, Hunt PG (2006) Soil CO2 flux from a Norfolk loamy sand after 25 years of conventional and conservation tillage. Soil Tillage Res 90:205–211. doi:10.1016/j.still.2005.09.003
Becerra AT, Botta GF, Bravo XL, Tourn M, Melcon FB, Vazquez J, Nardon G (2010) Soil compaction distribution under tractor traffic in almond (Prunus amigdalus L.) orchard in Almería España. Soil Tillage Res 107:49–56. doi:10.1016/j.still.2010.02.001
Biddoccu M, Ferraris S, Opsi F, Cavallo E (2016) Long-term monitoring of soil management effects on runoff and soil erosion in sloping vineyards in Alto Monferrato (North–West Italy). Soil Tillage Res 155:176–189. doi:10.1016/j.still.2015.07.005
Birkás M, Antos G, Neményi M, Szemők A (2008) Environmentally-sound adaptable tillage. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest
Botta GF, Jorajuria D, Balbuena R, Ressia M, Ferrero C, Rosatto H, Tourn M (2006) Deep tillage and traffic effects on subsoil compaction and sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) yields. Soil Tillage Res 91:164–172. doi:10.1016/j.still.2005.12.011
Botta GF, Tolon-Becerra A, Lastra-Bravo X, Tourn M (2010) Tillage and traffic effects (planters and tractors) on soil compaction and soybean (Glycine max L.) yields in Argentinean pampas. Soil Tillage Res 110:167–174. doi:10.1016/j.still.2010.07.001
Botta GF, Tolón-Becerra A, Rivero D, Laureda D, Ramírez-Roman M, Lastra-Bravo X, Agnes D, Flores-Parrac IM, Pelizzari F, Martiren V (2016) Compactión produced by combine harvest traffic: effect on soil and soybean (Glycine max L.) yields under direct sowing in Argentinean Pampas. Eur J Agron 74:155–163. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2015.12.011
Brevik EC, Cerdà A, Mataix-Solera J, Pereg L, Quinton JN, Six J, Van Oost K (2015) The interdisciplinary nature of SOIL. Soil 1:117–129. doi:10.5194/soil-1-117-2015
Buragienė S, Šarauskis E, Romaneckas K, Sasnauskienė J, Masilionytė L, Kriaučiūnienė Z (2015) Experimental analysis of CO2 emissions from agricultural soils subjected to five different tillage systems in Lithuania. Sci Total Environ 514:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.090
Carbonell-Bojollo R, González-Sánchez EJ, Veróz-González O, Ordóñez-Fernández R (2011) Soil management systems and short term CO2 emissions in a clayey soil in southern Spain. Sci Total Environ 409:2929–2935. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.003
Cheng-Fang L, Dan-Na Z, Zhi-Kui K, Zhi-Sheng Z, Jin-Ping W, Ming-Li C, Cou-Gui C (2012) Effects of tillage and nitrogen fertilizers on CH4 and CO2 emissions and soil organic carbon in paddy fields of central China. PLoS One 7:e34642. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034642
Dawson JJ, Smith P (2007) Carbon losses from soil and its consequences for land-use management. Sci Total Environ 382:165–190. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.03.023
De Moraes MT, Debiasi H, Carlesso R, Franchini JC, da Silva VR, da Luz FB (2016) Soil physical quality on tillage and cropping systems after two decades in the subtropical region of Brazil. Soil Tillage Res 155:351–362. doi:10.1016/j.still.2015.07.015
Defossez P, Richard G, Boizard H, O'Sullivan MF (2003) Modelling change in soil compaction due to agricultural traffic as function of water content. Geoderma 116:89–105. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00096-X
Dorner J, Sandoval P, Dec D (2010) The role of soil structure on the pore functionality of an ultisol. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10:495–508. doi:10.4067/S0718-95162010000200009
Duttmann R, Schwanebeck M, Nolde M, Horn R (2014) Predicting soil compaction risks related to field traffic during silage maize harvest. Soil Sci Soc Am J 78:408–421. doi:10.2136/sssaj2013.05.0198
Fabrizzi KP, Garcı́a FO, Costa JL, Picone LI (2005) Soil water dynamics, physical properties and corn and wheat responses to minimum and no-tillage systems in the southern Pampas of Argentina. Soil Tillage Res 81(1):57-69
Ferrero A, Usowicz B, Lipiec J (2005) Effects of tractor traffic on spatial variability of soil strength and water content in grass covered and cultivated sloping vineyard. Soil Tillage Res 84:127–138. doi:10.1016/j.still.2004.10.003
Galati A, Gristina L, Crescimanno M, Barone E, Novara A (2015) Towards more efficient incentives for agri-environment measures in degraded and eroded vineyards. Land Degrad Dev 26:557–564. doi:10.1002/ldr.2389
García-Díaz A, Allas RB, Gristina L, Cerdà A, Pereira P, Novara A (2016) Carbon input threshold for soil carbon budget optimization in eroding vineyards. Geoderma 271:144–149. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.02.020
García-Díaz A, Bienes R, Sastre B, Novara A, Gristina L, Cerdà A (2017) Nitrogen losses in vineyards under different types of soil groundcover. A field runoff simulator approach in central Spain. Agric Ecosyst Environ 236:256–267. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2016.12.013
García-Ruiz JM, Lana-Renault N (2011) Hydrological and erosive consequences of farmland abandonment in Europe, with special reference to the Mediterranean region—a review. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140:317–338. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2011.01.003
Grossman RB, Reinsch TG (2002) Methods of soil analysis, part 4. Physical methods: bulk density and linear extensibility. Soil Science Society of America Inc, Madison, pp 201–228
Håkansson I, Lipiec J (2000) A review of the usefulness of relative bulk density values in studies of soil structure and compaction. Soil Tillage Res 53:71–85. doi:10.1016/S0167-1987(99)00095-1
Hamza MA, Anderson WK (2005) Soil compaction in cropping systems: a review of the nature, causes and possible solutions. Soil Tillage Res 82:121–145. doi:10.1016/j.still.2004.08.009
Horn R, Domżżał H, Słowińska-Jurkiewicz A, Van Ouwerkerk C (1995) Soil compaction processes and their effects on the structure of arable soils and the environment. Soil Tillage Res 35:23–36. doi:10.1016/0167-1987(95)00479-C
IUSS, Working Group World reference base for soil resources (2014) World soil resources reports. FAO, Rome
Keller T, Arvidsson J (2006) Prevention of traffic-induced subsoil compaction in Sweden: experiences from wheeling experiments. Arch Agron Soil Sci 52:207–222. doi:10.1080/03650340600631540
Mahmood R, Littell A, Hubbard KG, You J (2012) Observed data-based assessment among soil moisture at various depths, precipitation, and temperature. Appl Geogr 34:255–264. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2011.11.009
Marquina S, Pérez T, Donoso L, Giuliante A, Rasse R, Herrera F (2015) NO, N2O and CO2 soil emissions from Venezuelan corn fields under tillage and no-tillage agriculture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 101:123–137. doi:10.1007/s10705-014-9659-0
Matthews GP, Laudone GM, Gregory AS, Bird NRA, Matthews AG, Whalley WR (2010) Measurement and simulation of the effect of compaction on the pore structure and saturated hydraulic conductivity of grassland and arable soil. Water Resour Res 46:W05501. doi:10.1029/2009WR007720
Moitinho MR, Padovan MP, Panosso AR, Teixeira DDB, Ferraudo AS, La Scala N (2015) On the spatial and temporal dependence of CO2 emission on soil properties in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) production. Soil Tillage Res 148:127–132. doi:10.1016/j.still.2014.12.012
Nawaz MF, Bourrie G, Trolard F (2013) Soil compaction impact and modelling. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 33:291–309. doi:10.1007/s13593-011-0071-8
Novara A, Gristina L, Guaitoli F, Santoro A, Cerdà A (2013) Managing soil nitrate with cover crops and buffer strips in Sicilian vineyards. Solid Earth 4:255–262. doi:10.5194/se-4-255-2013
Oorts K, Merckx R, Gréhan E, Labreuche J, Nicolardot B (2007) Determinants of annual fluxes of CO2 and N2O in long-term no-tillage and conventional tillage systems in northern France. Soil Tillage Res 95:133–148. doi:10.1016/j.still.2006.12.002
Prosdocimi M, Cerdà A, Tarolli P (2016) Soil water erosion on Mediterranean vineyards: a review. Catena 141:1–21. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2016.02.010
Rubinić V, Durn G, Husnjak S, Tadej N (2014) Composition, properties and formation of Pseudogley on loess along a precipitation gradient in the Pannonian region of Croatia. Catena 113:138–149. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2013.10.003
Ruiz-Colmenero M, Bienes R, Marques MJ (2011) Soil and water conservation dilemmas associated with the use of green cover in steep vineyards. Soil Tillage Res 117:211–223. doi:10.1016/j.still.2011.10.004
Saha D, Kukal SS (2015) Soil structural stability and water retention characteristics under different land uses of degraded lower Himalayas of North-West India. Land Degrad Dev 26:263–271. doi:10.1002/ldr.2204
Schwartz RC, Baumhardt RL, Evett SR (2010) Tillage effects on soil water redistribution and bare soil evaporation throughout a season. Soil Tillage Res 110:221–229. doi:10.1016/j.still.2010.07.015
Šimanský V, Balashov E, Horák J (2016) Water stability of soil aggregates and their ability to sequester carbon in soils of vineyards in Slovakia. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:177–197. doi:10.1080/03650340.2015.1048683
Six JΑΕΤ, Elliott ET, Paustian K (2000) Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: a mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol Biochem 32:2099–2103. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00179-6
Smart DR, Penuelas J (2005) Short-term CO2 emissions from planted soil subject to elevated CO2 and simulated precipitation. Appl Soil Ecol 28:247–257. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2004.07.011
Smith KA, Ball T, Conen F, Dobbie KE, Massheder J, Rey A (2003) Exchange of greenhouse gases between soil and atmosphere: interactions of soil physical factors and biological processes. Eur J Soil Sci 54:779–791. doi:10.1046/j.1351-0754.2003.0567.x
Tolon-Becerra A, Tourn M, Botta GF, Lastra-Bravo X (2011) Effects of different tillage regimes on soil compaction, maize (Zea mays L.) seedling emergence and yields in the eastern Argentinean Pampas region. Soil Tillage Res 117:184–190. doi:10.1016/j.still.2011.10.003
Tracy SR, Black CR, Roberts JA, Mooney SJ (2013) Exploring the interacting effect of soil texture and bulk density on root system development in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Environ Exp Bot 91:38–47. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.03.003
Van Dijck SJE, van Asch TW (2002) Compaction of loamy soils due to tractor traffic in vineyards and orchards and its effect on infiltration in southern France. Soil Tillage Res 63:141–153. doi:10.1016/S0167-1987(01)00237-9
Widen B, Lindroth A (2003) A calibration system for soil carbon dioxide – efflux measurement chambers: description and application. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:327–334. doi:10.2136/sssaj2003.3270
Yavuzcan HG, Matthies D, Auernhammer H (2005) Vulnerability of Bavarian silty loam soil to compaction under heavy wheel traffic: impacts of tillage method and soil water content. Soil Tillage Res 84:200–215. doi:10.1016/j.still.2004.11.003
Zhang S, Grip H, Lövdahl L (2006) Effect of soil compaction on hydraulic properties of two loess soils in China. Soil Tillage Res 90:117–125. doi:10.1016/j.still.2005.08.012
Ziadat FM, Taimeh AY (2013) Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad Dev 24:582–590. doi:10.1002/ldr.2239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogunovic, I., Bilandzija, D., Andabaka, Z. et al. Soil compaction under different management practices in a Croatian vineyard. Arab J Geosci 10, 340 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3105-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3105-y