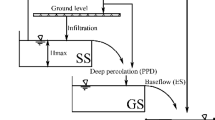
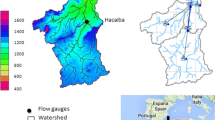
Abstract
In this paper, the lumped quasi-distributed hydrological model HEC HMS is used to simulate the rainfall–runoff process of the Mekerra watershed, located in the northwest of Algeria. The model parameters’ uncertainty and the predictive intervals were evaluated with the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) approach. According to the results, good simulations were obtained with different values of variables for many sets of parameters generated randomly by the Monte Carlo procedure, which is known as Equifinality. After the analysis, only the hydraulic conductivity at saturation parameter appears well defined, taking values within a limited range. In addition, results indicated that combinations of likelihood measures associated with multiple and different periods of observations reduce a posterior uncertainty of estimated parameters and predictive intervals in some degree. Overall, the GLUE analysis showed that there is a significant uncertainty associated with hydrological modelling of watershed Mekerra, to a great extent due to multiple sources of errors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC, Johnson CA, Van Genuchten MT (2004) Estimating uncertain flow and transport parameters using a sequential uncertainty fitting procedure. Vadose Zone J 3(4):1340–1352
Ali M, Khan SJ, Aslam I, Khan Z (2011) Simulation of the impacts of land-use change on surface runoff of Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Landsc Urban Plan 102(4):271–279
Bennabi F, Hamel L, Bouiadjra SEB, Ghomari S (2012) Ressources hydriques sous tension et enjeux de développement durable dans la wilaya de Sidi Bel Abbes (Algérie occidentale). Méditerranée 1:105–111
Bennabi F, Ghomari S, Bennabi L, Hamel L, Megharbi A, Toumi F (2016) Approche de gestion des ressources en eau: cas de la région de Sidi Bel Abbés. Afrique SCIENCE 12(1):205–213
Beven K, Binley A (1992) The future of distributed models: model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol Process 6(3):279–298
Beven K, Freer J (2001) Equifinality, data assimilation, and uncertainty estimation in mechanistic modelling of complex environmental systems using the GLUE methodology. J Hydrol 249(1):11–29
Blasone RS, Vrugt JA, Madsen H, Rosbjerg D, Robinson BA, Zyvoloski GA (2008) Generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) using adaptive Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling. Adv Water Resour 31(4):630–648
Borrell V, Chorda J, Dartus D (2005) Prévision des crues éclair. Comptes Rendus Géoscience 337:1109–1119
Cantón Y, Domingo F, Solé-Benet A, Puigdefábregas J (2001) Hydrological and erosion response of a badlands system in semiarid SE Spain. J Hydrol 252(1):65–84
Caruso BS, Rademaker M, Balme A, Cochrane TA (2013) Flood modelling in a high country mountain catchment, New Zealand: comparing statistical and deterministic model estimates for ecological flows. Hydrol Sci J 58(2):328–341
Castillo VM, Gomez-Plaza A, Martınez-Mena M (2003) The role of antecedent soil water content in the runoff response of semiarid catchments: a simulation approach. J Hydrol 284(1):114–130
Cherif EA, Errih M, Cherif HM (2009) Modélisation statistique du transport solide du bassin versant de l'Oued Mekerra (Algérie) en zone semi-aride méditerranéenne. Hydrol Sci J 54(2):338–348
Choi HT, Beven K (2007) Multi-period and multi-criteria model conditioning to reduce prediction uncertainty in an application of TOPMODEL within the GLUE framework. J Hydrol 332(3):316–336
Dotto CB, Kleidorfer M, Deletic A, Rauch W, McCarthy DT, Fletcher TD (2011) Performance and sensitivity analysis of stormwater models using a Bayesian approach and long-term high resolution data. Environ Model Softw 26(10):1225–1239
Fonseca A, Ames DP, Yang P, Botelho C, Boaventura R, Vilar V (2014) Watershed model parameter estimation and uncertainty in data-limited environments. Environ Model Softw 51:84–93
Freer J, Beven K, Ambroise B (1996) Bayesian estimation of uncertainty in runoff prediction and the value of data: an application of the GLUE approach. Water Resour Res 32(7):2161–2173
Halwatura D, Najim M (2013) Application of the HEC-HMS model for runoff simulation in a tropical catchment. Environ Model Softw 46:155–162
Heidari A, Saghafian B, Maknoon R (2006) Assessment of flood forecasting lead time based on generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation approach. Stoch Env Res Risk A 20(5):363–380
Jin X, Xu CY, Zhang Q, Singh VP (2010) Parameter and modeling uncertainty simulated by GLUE and a formal Bayesian method for a conceptual hydrological model. J Hydrol 383(3):147–155
Kizza M, Rodhe A, Xu CY, Ntale HK (2011) Modelling catchment inflows into Lake Victoria: uncertainties in rainfall–runoff modelling for the Nzoia River. Hydrol Sci J 56(7):1210–1226
Korichi K, Hazzab A (2012) Hydrodynamic investigation and numerical simulation of intermittent and ephemeral flows in semi-arid regions: Wadi Mekerra, Algeria. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics 60(2):125–142
Mantovan P, Todini E (2006) Hydrological forecasting uncertainty assessment: incoherence of the GLUE methodology. J Hydrol 330(1):368–381
McMichael CE, Hope AS, Loaiciga HA (2006) Distributed hydrological modelling in California semi-arid shrublands: MIKE SHE model calibration and uncertainty estimation. J Hydrol 317(3):307–324
Meddi M, Abbes ASB (2014) Analyse statistique et prévision des débits de crues dans le bassin versant de l'Oued Mekerra (Ouest de l'Algérie). Nature & Technology 10:21
Mediero L, Garrote L, Martín-Carrasco FJ (2011) Probabilistic calibration of a distributed hydrological model for flood forecasting. Hydrol Sci J 56(7):1129–1149
Mirzaei M, Galavi H, Faghih M, Huang YF, Teang Shui L, El-Shafie A (2013) Model calibration and uncertainty analysis of runoff in the Zayanderood River basin using generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) method. J Water Supply Res Technol 62.5:309–320
Mirzaei M, Huang YF, El-Shafie A, Chimeh T, Lee J, Vaizadeh N, Adamowski J (2015) Uncertainty analysis for extreme flood events in a semi-arid region. Nat Hazards 78(3):1947–1960
Montanari A (2005) Large sample behaviors of the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) in assessing the uncertainty of rainfall-runoff simulations. Water Resour Res 41(8). doi:10.1029/2004WR003826
Mousavi SJ, Abbaspour KC, Kamali B, Amini M, Yang H (2012) Uncertainty-based automatic calibration of HEC-HMS model using sequential uncertainty fitting approach. J Hydroinf 14(2):286–309
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290
Nourali M, Ghahraman B, Pourreza-Bilondi M, Davary K (2016) Effect of formal and informal likelihood functions on uncertainty assessment in a single event rainfall-runoff model. J Hydrol 540:549–564
Quintero F, Sempere-Torres D, Berenguer M, Baltas E (2012) A scenario-incorporating analysis of the propagation of uncertainty to flash flood simulations. J Hydrol 460:90–102
Rankinen K, Karvonen T, Butterfield D (2006) An application of the GLUE methodology for estimating the parameters of the INCA-N model. Sci Total Environ 365(1):123–139
Rawls WJ, Brakensiek DL, Savabi MR (1989) Infiltration parameters for rangeland soils. J Range Manag 42:139–142
Refsgaard JC, Van der Sluijs JP, Højberg AL, Vanrolleghem PA (2007) Uncertainty in the environmental modelling process–a framework and guidance. Environ Model Softw 22(11):1543–1556
Sanyal J, Densmore AL, Carbonneau P (2014) Analysing the effect of land-use/cover changes at sub-catchment levels on downstream flood peaks: a semi-distributed modelling approach with sparse data. Catena 118:28–40
Senarath SU, Ogden FL, Downer CW, Sharif HO (2000) On the calibration and verification of two-dimensional, distributed, Hortonian, continuous watershed models. Water Resour Res 36(6):1495–1510
Shamsudin S, Dan’azumi S, Ab Rahman A (2011) Uncertainty analysis of HEC-HMS model parameters using Monte Carlo simulation. Int J Model Simul 31(4):279–286
Sheikh V, Van Loon E, Hessel R, Jetten V (2010) Sensitivity of LISEM predicted catchment discharge to initial soil moisture content of soil profile. J Hydrol 393(3):174–185
Stedinger JR, Vogel RM, Lee SU, Batchelder R (2008) Appraisal of the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) method. Water Resour Res 44(12)
Thorndahl S, Beven KJ, Jensen JB, Schaarup-Jensen K (2008) Event based uncertainty assessment in urban drainage modelling, applying the GLUE methodology. J Hydrol 357(3):421–437
Usace (US Army Corps of Engineers) (2000) Hydrologic modeling system (HEC-HMS) technical reference
Usace (US Army Corps of Engineers) (2008) Hydrologic modeling system (HEC-HMS) applications guide
Van Griensven A, Meixner T (2007) A global and efficient multi-objective auto-calibration and uncertainty estimation method for water quality catchment models. J Hydroinf 9(4):277–291
Vázquez RF, Feyen J (2010) Rainfall-runoff modelling of a rocky catchment with limited data availability: defining prediction limits. J Hydrol 387(1):128–140
Viola F, Noto LV, Cannarozzo M, La Loggia G (2009) Daily streamflow prediction with uncertainty in ephemeral catchments using the GLUE methodology. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 34(10):701–706
Vrugt JA, Gupta HV, Bouten W, Sorooshian S (2003) A shuffled complex evolution metropolis algorithm for optimization and uncertainty assessment of hydrologic model parameters. Water Resour Res 39(8). doi:10.1029/2002WR001642
Vrugt JA, Ter Braak CJ, Clark MP, Hyman JM, Robinson BA (2008) Treatment of input uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: doing hydrology backward with Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation. Water Resources Research 44(12)
Vrugt JA, Ter Braak CJ, Gupta HV, Robinson BA (2009) Equifinality of formal (DREAM) and informal (GLUE) Bayesian approaches in hydrologic modeling? Stoch Env Res Risk A 23(7):1011–1026
Yahiaoui A, Touaïbia B, Bouvier C, Dechemi N (2011) Modélisation du régime de crue en Débit–durée–Fréquence du bassin de l’oued Mekerra dans l’Ouest Algérien. Revue des sciences de l’eau/Journal of Water Science 24(2):103–115
Yahiaoui A, Touaibia B, Ferrari E (2014) A methodology for evaluation and mapping of flood risk—a Case study of Oued Mekerra in the West of Algeria. In Vulnerability, Uncertainty, and Risk: Quantification, Mitigation, and Management (pp. 1373–1384). ASCE
Yang SC, Yang TH (2014) Uncertainty assessment: reservoir inflow forecasting with ensemble precipitation forecasts and HEC-HMS. Adv Meteorol 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/581756
Zacharias S, Wessolek G (2007) Excluding organic matter content from pedotransfer predictors of soil water retention. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71(1):43–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehbab-Boukezzi, Z., Boukezzi, L. & Errih, M. Uncertainty analysis of HEC-HMS model using the GLUE method for flash flood forecasting of Mekerra watershed, Algeria. Arab J Geosci 9, 751 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2771-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2771-5