Abstract
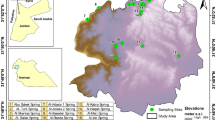
The lithology of the studied aquifers has an important effect on their hydrogeologic setting. Moreover, the structural patterns have their imprint on the geologic setting and consequently the hydrogeologic conditions of the area. Lake Nasser recharges the groundwater in the study area by large amount of water increasing the groundwater level. A comparison of the depth to water in the same wells at two different periods (1998 and 2014 ) shows that the depth to water increases with average rise 11.1 m during 16 years. The constructed water table map shows that the groundwater flow is mainly towards the northwest direction reflecting recharge from Lake Nasser. The hydraulic parameters of the Abu Aggag and Sabaya sandstone aquifers are determined in the present work from pumping tests. The transmissivity of the studied aquifers reflects the moderate to high potentiality. The groundwater salinity of the studied aquifers is fresh water and varies from 353 to 983 ppm (part per million) and suitable for all purposes. It increases due to the west direction coinciding with groundwater flow direction. The main result of the present study shows that the seepage water from Lake Nasser attains 17 mcm/year.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper HH, Jacob CE (1946) A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well history. Geophys Union Trans 27:526–534
Continental Oil Company (CONOCO, 1987). Geologic map of Egypt (scale 1:500,000): (Conoco), NF 36 NW El-Saad El-Ali, Cairo, Egypt
Darcy H (1856) Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dyon. V. Dalmont, Paris, 647 p
Durov SA (1948) Natural waters and graphic representation of their compositions. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 59:87–90
El-Naggar ZR, 1970. On a proposed lithostratigraphic subdivision for the Late Cretaceous-Early Paleogene succession in the Nile Valley, Egypt. In: 7 th Arab Petroleum Congress, Kuwait, pp 1–50 B-53
Geological Survey Authority of Egypt (EGSMA) (1988) Geology of the Nubia–Darb El-Arbeain area. Internal report No. 30, Cario, Egypt, 258p
General Company for Research and groundwater (REGWA) (2002) The hydrogeological data of Tushka area. Internal report, Cario, Egypt
Gheorhge A., 1979. Processing and synthesis of hydrogeological data. Abacus Press, pp 390
Ghoubachi SY 2004 Comparative hydrogeological studies of the Nubia sandstone aquifer system in East El-Oweinat and Bir El-Shabareas, South Western Desert, Egypt: Ph. Thesis, Fac. Sci., Al-Azhar Univ., Cairo, 303 p
Hendricks, FL, Luger H, Kallenbach JH, Schroeder G (1984) Sttratigraphical and sedimentological frameworkof the Kharga-Sinn El-Kaddab strech (Western and Southern part of the Upper Nile Basin) Western Desert, Egypt. Berl Geowiss Abh A 50:117–151
Schrank E 1987 Paleozoic and Mesozoic palynomorphs from NE-Africa (Egypt and Sudan): Berliner geowissenschaftliche Abhandlungen, A, V. 75, pp. 149–310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghoubachi, S.Y., El-Abd, ES.A. Hydrogeological studies for the Nubia sandstone aquifers in Garf Hussein area, Western Desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 9, 596 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2603-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2603-7