Abstract
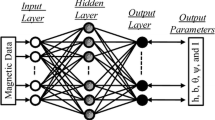
A new approach is proposed to interpret magnetic anomalies caused by 2D fault structures. This approach is based on the artificial neural network inversion, utilizing particularly modular neural network algorithm. The inversion process is implemented to estimate the parameters of 2D fault structures where it has been verified first on synthetic models. The results of the inversion show that the parameters derived from the inversion agree well with the true ones. The analysis of noise has been studied in order to investigate the stability of the approach where it has been tested for contaminated anomalies with 5 and 10 % of white Gaussian noise. The results of the inversion provide satisfactory results even with contaminated signals.
The validity of the approach has been demonstrated through real data taken from New South Wales, Australia. A comparable and satisfactory agreement is shown between the inversion results of the neural network and those from techniques published in literatures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Chalabi M (1970) Interpretation of two-dimensional magnetic profiles by non-linear optimization. Bolletino Di Geofisica Teorica Ed Applicata 12:3–20
Al-Chalabi M (1971) Some studies relating to non-uniqueness in gravity and magnetic inverse problems. Geophysics 36(5):835–855
Al-Chalabi M (1972) Interpretation of gravity anomalies by non-linear optimization. Geophys Prospect 10:1–15
Al-Garni MA (2009) Interpretation of some magnetic bodies using neural networks inversion. Arab J Geosci 2:175–184
Al-Garni MA (2010) Interpretation of spontaneous potential anomalies from some simple geometrically shaped bodies using neural network inversion. Acta Geophysica 58:143–162
Al-Garni MA (2013) Inversion of residual gravity anomalies using neural network. Arab J Geosci 6:1509–1516
Al-Garni MA (2015) Interpretation of magnetic anomalies due to dipping dikes using neural network inversion. Arab J Geosci 8:8721–8729
Al-Garni MA, Srinivas Y, Sundararajan N (2010) Sundararajan transform—an application to geophysical data analysis. Arab J Geosci 3:27–32
Am K (1972) The arbitrary magnetized dike: interpretation by characteristics. Geoexploration 10:63–90
Atchuta Rao D, Ram Babu HV (1983) Standard curves for the interpretation of magnetic anomalies over vertical faults. Geophy Res Bull 21:71–89
Azam F (2000) Biologically inspired modular neural networks, PhD dissertation. Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, p 183, http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-06092000-12150028/unrestricted/etd.pdf
Bean RJ (1966) A rapid graphical solution for the aeromagnetic anomaly of the two-dimensional tabular body. Geophysics 31:963–970
Bescoby DJ, Cawley GC, Chroston PN (2006) Enhanced interpretation of magnetic survey data from archaeological sites using artificial neural networks. Geophysics 71:H45–H53
Bhatt A, Helle H (2002) Committee neural network for porosity and permeability prediction from well logs. Geophys Prospect 50:645–660
Bishop CM (1995a) Training with noise is equivalent to Tikhonov regularization. Neural Comp 7(1):108–116
Bishop CM (1995b) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 482
Bruckshaw JM, Kunaratnam K (1963) The interpretation of magnetic anomalies due to dikes. Geophys Prosp 11:519–522
El-Kaliouby H (2001) Extracting IP parameters from TEM data. In: Poulton MM (ed) Computational neural networks for geophysical data processing. Pergamon Press, Inc, Pergamon
El-Kaliouby HM, Al-Garni MA (2009) Inversion of self-potential anomalies caused by 2D inclined sheets using neural networks. J Geophys Eng 6:29–34
El-Kaliouby H, Poulton M (1999) Inversion of coincident loop TEM data for layered polarizabe ground using neural networks. Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) 69th annual meeting, Houston
El-Qady G, Ushijima K (2001) Inversion of DC resistivity data using neural networks. Geophys Prospect 49:417–430
Fossati M, Zerilli A, Ronchini G, Apollono B (1992) Lineament analysis for potential field data using neural network: 62nd Annual International Meeting, SEG, expanded abstracts., pp 6–9
Gay SP (1963) Standard curves for interpretation of magnetic anomalies over long tabular bodies. Geophysics 28:161–200
Gay SP (1965) Standard curves for the interpretation of magnetic anomalies over long horizontal cylinders. Geophysics 30:818–828
Grant FS, Martin L (1966) Interpretation of aeromagnetic anomalies by the use of characteristic curves. Geophysics 31:135–148
Grant FS, West GF (1965) Interpretation theory in applied geophysics. Mc Graw Hill Book Co., New York
Haykin S (1994) Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. Macmillan Publication Co., New York
Helle HB, Bhatt A, Ursin B (2001) Porosity and permeability prediction from wireline logs using artificial neural networks: a North sea case study. Geophys Prospect 49:431–444
High JE, Smith MJ (1975) Standard curves for interpretation of magnetic anomalies due to thin dikes of finite depth extent. Australian Govt. Public Service, Canberra
Hjelt SE (1973) Experiences with automatic magnetic interpretation using the thick plate model. Geophys Prospect 21:243–265
Hjelt SE (1975) Performance comparison of non-linear optimization methods applied to interpretation in magnetic prospecting. Geophysica 13:144–166
Jain LC, Martin NM (1999) Fusion of neural networks, fuzzy sets and genetic algorithms: industrial applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Jang JSR, Sun CT, Mizutani E (1997) Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing: a computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Prentice-Hall Inc, USA
Koulomzine T, Lamontagn Y, Nadeau A (1970) New methods for the direct interpretation of magnetic anomalies caused by inclined dikes of infinite length. Geophysics 35:812–830
Macias C, Sen M, Stoffa P (2000) Artificial neural networks for parameter estimation in geophysics. Geophys Prospect 48:21–47
Masters T (1993) Practical neural network recipes in C++. Academic Press Inc, San Diego
Moo JKC (1965) Analytic aeromagnetic interpretation the inclined prism. Geophys Prosp 13:203–224
Murthy IVR, Swamy KV, Rao SJ (2001) Automatic inversion of magnetic anomalies of faults. Comput Geosci 27(3):315–325
Parakasa Rao TKS, Krishna Murthy AS (1978) Interpretation of magnetic anomalies caused by dykes using caharacteristic curves, A.E.G. Seminar. Andhra University, Andhra, pp 19–21
Paul MK, Datta S, Banerjee B (1966) Direct interpretation of two-dimensional structural faults from gravity data. Geophysics 31(5):940–948
Poulton MM (2001) Computational neural networks for geophysical data processing. Pergamon Press Inc, Pergamon
Poulton MM (2002) Neural networks as an intelligence amplification tool: a review of applications. Geophysics 67:979–993
Poulton MM, Sternberg BK, Glass CE (1992a) Location of subsurface targets in geophysical data using neural networks. Geophysics 57:1534–1544
Poulton MM, Sternberg BK, Glass CE (1992b) Neural network pattern recognition of subsurface EM images. J Appl Geophys 29:21–36
Powell DW (1965) A rapid method of determining dip or magnetization, inclination from magnetic anomalies due to dike-like bodies. Geophys Prosp 13:197–202
Powell DW (1967) Fitting observed profiles to a magnetized dike or fault-step-model. Geophys Prosp 15:208–220
Quereshi R, Nalaye AM (1978) A method for the direct interpretation of magnetic anomalies caused by two-dimensional vertical faults. Geophysics 43:179–188
Radhakrishna Murthy IV (1985) The mid-point method: magnetic interpretation of dykes and faults. Geophysics 50(5):834–839
Radhakrishna Murthy IV (1990) Magnetic anomalies of two-dimensional bodies and algorithm for magnetic inversion of dykes and basement topographies. Proc Indiana Acad Sci 99(4):549–579
Radhakrishna Murthy IV, Krishnamacharyulu SKG (1990) Automatic inversion of gravity anomalies of faults. Comput Geosci 16(4):539–548
Radhakrishna Murthy IV, Visweswara Rao C, Gopala- krishna G (1980) A gradient method for interpreting magnetic anomalies due to horizontal circular cylinders, infinite dykes and vertical steps. Proc Indiana Acad Sci 89(1):31–42
Raiche A (1991) A pattern recognition approach to geophysical inversion using neural nets. Geophys J Int 105:629–648
Rama Rao C, Veeraswamy K, Sarma MRL, Baskara Rao DS (1987) Interpretation of magnetic anomalies due to infinite dyke and vertical steps using relation figures. Geophys Res Bull 25(4):178–183
Rao BSR, Murthy IVR (1978) Gravity and magnetic methods of prospecting. Arnold Heinmann, New Delhi
Smellie DW (1956) Elementary approximation in aero-magnetic interpretation. Geophysics 21:1021–1040
Spichak V, Popova I (2000) Artificial neural network inversion of magnetotelluric data in terms of three-dimensional earth macroparameters. Geophys J Int 142:15–26
Srinivas Y, Stanley Raj A, Hudson Oliver D, Muthuraj D, Chandrasekar N (2012) A robust behavior of feed forward back propagation algorithm of artificial neural networks in the application of vertical electrical sounding data inversion. Geosci Front 3:729–736
Stanley Raj A, Srinivas Y, Hudson Oliver D, Muthuraj D (2014) A novel and generalized approach in the inversion of geoelectrical resistivity data using artificial neural networks (ANN). J Earth Syst Sci 123:395–411
Stanley JM, Green R (1976) Gravity gradients and the interpretation of the truncated plate. Geophysics 41:1370–1376
Subrahmanyam M (2013) A short note: a computer program in FORTRAN for interpreting the magnetic anomalies over a tabular bodies. Inter. J. Software web Sci (I.J.S.W.S) 4:103–108
Telford WM, Geldart LP, Sheriff RA, Keys DA (1976) Applied geophysics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ucan ON, Bilgili E, Albora AM (2002) Magnetic anomaly separation using genetic cellular neural networks. J Balkan Geophysical Soc 5:65–70
Van der Baan M, Jutten C (2000) Neural networks in geophysical applications. Geophysics 65:1032–1047
Williams PM (1995) Bayesian regularization and pruning using a Laplace prior. Neural Comp 7(1):117–143
Won IJ (1981) Application of Gauss’s method to magnetic anomalies of dipping dykes. Geophysics 46:211–215
Yarger HL, Robertson RR, Wentland RL (1978) Diurnal drift removal from aeromagnetic data using least squares. Geophysics 46:1148–1156
Zhang Q, Gupta K (2000) Neural networks for RF and Microwave design. Artech House Inc., Boston
Zhang L, Poulton MM, Wang T (2002) Borehole electrical resistivity modeling using neural networks. Geophysics 67:1790–1797
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Garni, M.A. Artificial neural network inversion of magnetic anomalies caused by 2D fault structures. Arab J Geosci 9, 156 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2256-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2256-y