Abstract
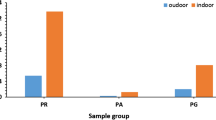
Specific radioactivity of U-238, Ra-226, Th-232, and K-40 was measured for selected samples of Iraqi ore phosphate rocks, fertilizers, and phosphogypsum. Gamma spectroscopy system based on HPGe detector with efficiency of 30 % used for the analysis. The activity (in Bq/kg) of U-238 ranges between 53.1 and 682.7; Ra-226, between 15.1 and 409.7; and Th-232, between below detection level and 2.3 while K-40 activity was below detection level in all the samples. The result shows that about 13 % of initial U-238 transferred to the phosphogypsum while its activity in triple superphosphate samples increased to be about 166 % of initial U-238 in the ore phosphate rock while about 75 % of radium-226 in phosphate rock migrates to the phosphogypsum. The radiological hazards for workers and the public due to the using and manufacturing processes of the phosphate fertilizers were estimated. The radiation doses due to exposure to the direct gamma rays emitted from a stock of ore phosphate are found to be 0.16 μSv/h while doses caused by using three types of fertilizers are in the range of 0.03 to 2.2 mSv per fertilizer application. The use of monoammonium phosphate fertilizer causes a less effective dose because it contains low concentration of radium. The resulting radiation dose by using phosphogypsum as plaster material is 0.27 μSv per year, which could be considered negligible.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aba Husain A (1987) Geochemical, petrographical and mineralogical study of the Paleocene phosphatic units in the Gaara–Akashat area. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Baghdad
Abbady AGE, Uosif MAM, El-Taher A (2005) Natural adioactivity and dose rate assessment of phosphate rocks from Wadi El-Mashash and El-Mahamid mines, Egypt. J Environ Radioact 84:65–78
Ahmed NK (2005) Measurement of natural radioactivity in building materials in Qena city, Upper Egypt. J Environ Radioact 83:91–99
Al-Bassam K (1974) The mineralogy and geochemistry of the marine sedimentary phosphate deposits of Iraq and other areas in the Middle East. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wales (Cardiff), UK
Al-Bassam K (2007) Uranium in the Iraqi phosphorites. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 3(2):13–31
Al-Bassam K, Karim SM, Yakta KS, Saeed L, Salman M (1990) Geological survey of the Upper Cretaceous–Lower Tertiary phosphorite-bearing sequence. Western Desert, Iraq (scale 1: 25 000). GEOSURV, int. rep. no. 2008
Al-Dahan A (1977) Petrology and geochemistry of Upper Cretaceous phosphatic rocks from the Western Desert. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Baghdad
Al-Jaleel HS (1983) Geochemistry and mineralogy of the Lower Eocene phosphorite in the Western Desert area. MSc. Thesis, University of Baghdad
Attar LA, Al-Oudat M, Kanakri S, Budeir Y, Khalily H, Hamwi AA (2011) Radiological impacts of phosphogypsum. J Environ Manag 92:2151–2158
Bolívar JP, García-Tenorio R, García-Leon M (1996) On the fractionation of natural radioactivity in the production of phosphoric acid by the wet acid method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Lett 214(2):77–88
Dahlkamp FJ (1993) Uranium ore deposits. Springer, Berlin, 460 p
EC (1999) Commission of the European Communities. Establishment of reference levels for regulatory control of workplaces where materials are processed which contain enhanced levels of naturally-occurring radionuclides, radiation protection 107, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
EC (2000) Nuclear Safety and the Environment. Natural radionuclide concentrations in materials processed in the chemical industry and the related radiological impact, report EUR 19264, Directorate-General Environment, Luxembourg
Esma’ail Sh, Omer A (2010) Akashat phosphate mining. State Company for Phosphate. Iraq. Interior report (in Arabic)
Guimond RJ, Hardin JM (1989) Radioactivity released from phosphate-containing fertilizers and from gypsum. Radiat Phys Chem 34:309–315
Harben PW, Kizvart M (1996) Industrial minerals, a global geology. Industrial Minerals Information, Ltd., Metal Bulletin PLC, London, 462 p
Haridasan PP, Pillai PMB, Tripathi RM, Puranik VD (2009) An evaluation of radiation exposures in a tropical phosphogypsum disposal environment. Radiat Prot Dosim 135(3):211–215
Hilton J (2006) Phosphogypsum—management and opportunities for use: resolving a conflict between negative externality and public good? Proc. No. 587, International Fertiliser Society, Leek, UK
Hofman J, Leicht R, Wingender, HJ, Worner J (2000) Natural radionuclide concentrations in materials processed in the chemical industry and the related radiological impact. European Commission Report EUR-19264, Directorate General Environment
IAEA (2013) Radiation protection and management of norm residues in the phosphate industry. Safety Reports Series No. 78
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) (1994) Gamma-ray surveys in uranium exploration. Technical Report Series No. 186, International Atomic Energy Agency
Jassim SZ, Goff GC (2006) Geology of Iraq. Dolin, Prague and Moravian Museum, Brno
Jassim SZ. Hagopian DH. and Al-Hashimi HA. (1990) Geological map of Iraq. (Scale 1:1000000). D.G. of Geological Survey and Mineral Investigation. Baghdad, Iraq.
Khater AEM, Al-Sewaidan HA (2008) Radiation exposure due to agricultural uses of phosphate fertilizers. Radiat Meas. doi:10.1016/j.radmeas.2008.04.084
Kratz S, Knappe F, Rogasik J, Funder U (2007) Uranium balances in agroecosystems, International Symposium Protecting Water Bodies from Negative Impact of Agriculture, Loads and Fate of Fertilizer Derived Uranium, Braunschweig, Germany
Lambert R, Grant C, Sauve C (2007) Cadmium and zinc in soil solution extracts following the application of phosphate fertilizers. Sci Total Environ 378:293–305
LeMone DV, Goodell PC, Harris AH, Winston JW (2009) Phosphate rocks: sustainable secondary source for uranium and their agricultural impact. Waste Management for the Nuclear Renaissance WM2009 Conference, March 1–5, 2009. Phoenix, AZ
Mazzilli B, Palmiro V, Saueia C, Nisti MB (2000) Radiochemical characterization of Brazilian phosphogysum. J Environ Radioact 49:113–122
Mohammad IQ (1985) Petrography and geochemistry of phosphate rocks of Upper Cretaceous–Paleocene age in Rutba–H3 area, Western Desert, Iraq. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Baghdad
Roesseler CE (1990) Control of radium in phosphate mining, beneficiation and chemical processing. In: The environmental behaviour of radium. Vol. 2 p. 269. IAEA, Vienna, Austria. Technical report Series No. 310
Roesseler CE, Smith ZA, Bolch WE, Prince RJ (1979) Uranium and Radium-226 in Florida phosphate materials. J Health Phys 37:269–277
Sahu SK, Ajmal PY, Bhangare RC, Tiwari M, Pandit GG (2014) Natural radioactivity assessment of a phosphate fertilizer plant area. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:123–128
Stewart WM, Hammond LL, Van Kauwenbergh SJ (2005) Phosphorous as a natural resource. In: Sims JT, Shapely AN (eds) Phosphorous: agriculture and the environment, Monograph 46, ASA-CSSA-SSSA, 3–22
Tufail M, Akhtar N, Waqas M (2006) Radioactive rock phosphate: the feed stock of phosphate fertilizers used in Pakistan. Health Phys 90(4):361–370
UNSCEAR (1993) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Report to the General Assembly with scientific annexes. United Nations, New York
USEPA (2002) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, National emission standards for hazardous air pollutants, subpart R of 40 CFR part 61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, K.K., Awad, Y.D. Radiological assessment of Iraqi phosphate rock and phosphate fertilizers. Arab J Geosci 8, 9481–9488 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1898-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1898-0