Abstract
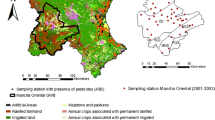
Located at the northeastern part of Morocco, the plain of Triffa is characterized by a semi-arid climate where water resources are rather fragile and influenced by a highly irregular rainfall distribution, both in time (annual and inter-annual distribution) and in space. The mean annual rainfall does not exceed 240 mm. In the Triffa plain, the impact of anthropogenic activities on the groundwater resources is reflected both by (a) the decrease in the piezometric level due to the over exploitation and droughts and (b) the deterioration of the chemical quality of water. Currently, this situation is felt mainly by the farmers. The unconfined aquifer is under stress due to the increase of the pollution rate, especially by nitrates that are above the WHO standards, and salinity. Organochlorine pesticides are ubiquitous and persistent organic pollutants used widely in agriculture. Due to their extensive use in agriculture, organic environment contaminants such as hexachlorocyclohexane, DDT, and DDD along organochlorine pesticides are distributed globally by transport through water. Pesticides such as aldrin, lindane, and heptachlor have also been detected and were considered as indicators showing the need to inform and to train farmers on the pesticides and fertilizers use in order to reduce the threat of groundwater contamination.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarhloule Y, Fekkoul F, Boughriba M, Kabbabi A, Carneiro J, Correia A, Rimi A, Houadi B (2009) Climate change and human activities impact on the groundwater of the Eastern Morocco: case of Triffa plain and shallow coastal Mediterranean aquifer at Saïdia. Innovation in groundwater governance in MENA region. J SIWI 14:13–17
El Mandour A (1998) Contribution hydrogéologique de la plaine des Triffa salinisation et modélisation. Thesis, Université Mohamed Ier, Faculté des Sciences
El Idrysy EH, De Smedt F (2006) Modelling groundwater flow of the Triffa aquifer, Morocco. J Hydrogeol 14:1265–1276
Boughriba M, Melloul A, Zarhloule Y, Ouardi A (2006) Extension spatiale de la salinisation des ressources en eau et modèle conceptuel des sources salées dans la plaine des Triffa (Maroc nord-oriental). C R Geosci 338(11):768–774
Laftouhi N, Vanclooster M, Jalal M, Witam O, Aboufirassi M, Bahir M, Persoons E (2003) Groundwater nitrate pollution in the Essaouira Basin (Morocco). C R Geosci 335(3):307–317
El Bakouri H, Ouassini A, Morillo J, Usero J (2008) Pesticides in ground water beneath Loukkos perimeter, Northwest Morocco. J Hydrol 34:270–278
Saâdi Z, Maslouhi A, Zéraouli M, Gaudet JP (1999) Analysis and modelling of seasonal nitrate concentration variations in the groundwater of the Mnasra aquifer, Morocco. C R A S Earth Planet Sci 329(8):579–585
Fakir Y, Zerouali A, Aboufirassi M, Bouabdelli M (2001) Exploitation et salinité des aquifères de la Chaouia côtière, littoral atlantique, Maroc. English edition: Fakir Y, Zerouali A, Aboufirassi M, Bouabdelli M (2001) Potential exploitation and salinity of aquifers, Chaouia coast, Atlantic shoreline, Morocco. Journal African Earth Sciences 32(4):791–801
Mairess H (2011) Salinité des sols du périmètre irrigué de la plaine des Triffa (Maroc nord oriental). Master’s Thesis, UCL/Earth and Life Institute
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL (2008) Application of multiple isotopic and geochemical tracers for investigation of recharge, salinization, and residence time of water in the Souss-Massa aquifer, southwest of Morocco. J Hydrol 352(3–4):267–287
Morvan X, Mouvet C, Baran N, Gutierrez A (2006) Pesticides in the groundwater of a spring draining a sandy aquifer: temporal variability of concentrations and fluxes. J Contam Hydrol 87(3–4):176–190
Hildenbrandt A, Guillaom M, Lacorte S, Tauler R, Barcelo D (2008) Impact of pesticides used in agriculture and vineyards to surface and groundwater quality (North Spain). Water Res 42:3315–3326
Batista S, Silva E, Galhardo S, Viana P, Cerejeira MJ (2002) Evaluation of pesticide contamination of ground water in two agricultural areas of Portugal. Int J Environ Anal Chem 82:601–609
Cerejeira MJ, Viana P, Batista S, Pereira T, Silva E, Valério MJ, Silva A, Ferreira M, Silva-Fernandes AM (2003) Pesticides in Portuguese surface and ground waters. Water Res 37:1055–1063
Soutter M, Musy A (1998) Coupling 1D Monte-Carlo simulations and geostatistics to assess groundwater vulnerability to pesticide contamination on a regional scale. J Contam Hydrol 32(1–2):25–39
Baran N, Mouvet C, Négrel P (2007) Hydrodynamic and geochemical constraints on pesticide concentrations in the groundwater of an agricultural catchment (Brévilles, France). Environ Pollut 148:729–738
Bijay-Singh Y-S, Sekhon GS (1995) Fertilizer-N use efficiency and nitrate pollution of groundwater in developing countries. J Contam Hydrol 20:167–184
Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E, Karpouzas DG, Patsias J, Kotopoulou A, Milothridou A, Kintzikoglou K, Vlachou P (2004) The potential of pesticides to contaminate the groundwater resources of the Axios river basin in Macedonia. Northern Greece. Part I: monitoring study in the north part of the basin. Sci Total Environ 321(1–3):127–146
Andrade AIASS, Stigter TY (2009) Multi-method assessment of nitrate and pesticide contamination in shallow alluvial groundwater as a function of hydrogeological setting and land use. Agric Water Manag 96:1751–1765
Matin A, Malek MA, Amin MR, Rahman S, Khatoon J, Rahman M, Aminuddin M, Mian JC (1998) Organochlorine insecticide residues in surface and underground water from different regions of Bangladesh. Agric Ecosyst Environ 69(1):11–15
Sankararamakrishnan N, Sharma AK, Sanghi R (2005) Organochlorine and organophosphorous pesticide residues in ground water and surface waters of Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Int 31(1):113–120
Worrall F, Kolpin DW (2004) Aquifer vulnerability to pesticide pollution-combining soil, land-use and aquifer properties with molecular descriptors. J Hydrol 293(1–4):191–204
FAO/PNUE (1991) Programme conjoint FAO/PNUE pour l'application de la procédure d'information et de consentement préalable, Documents d'orientation des décisions Aldrine
Makni J, Bouri S, Ben Dhia H (2012) Hydrochemistry and geothermometry of thermal groundwater of southeastern Tunisia (Gabes region). Arab J Geosci 1–11. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0510-5
Kamel S (2011) Salinisation, origin and hydrogeochemical behaviour of the Djerid oasis water table aquifer (southern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0502-5
Ben Brahim F, Bouri S, Khanfir H (2011) Hydrochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality of a Mio-Plio-Quaternary aquifer system in an arid regions: case of El Hancha, Djebeniana and El Amra regions, Tunisia. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0481-6
Acknowledgments
The authors warmly thank the anonymous reviewers for their detailed and constructive criticisms, which were of great help in improving this manuscript. The authors also wish to express their thanks to OCP for the financial support and the ABHM for the acquisition of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fekkoul, A., Zarhloule, Y., Boughriba, M. et al. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the groundwater resources of the unconfined aquifer of Triffa plain (Eastern Morocco). Arab J Geosci 6, 4917–4924 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0740-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0740-1