Abstract
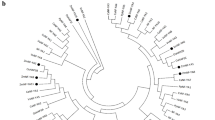
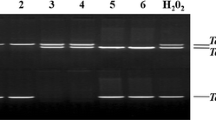
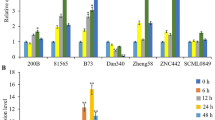
MYBs are a vital family of transcription factors that play critical roles in plant development and stress response. However, knowledge concerning the functions of MYBs in the non-model plants is still limited. In this study, we isolated a R1-type MYB gene from maize (Zea mays L.), designated as ZmMYB48. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that ZmMYB48 expression was induced by drought and ABA treatments. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that ZmMYB48 protein was targeted to the nucleus in tobacco leaf epidermal cells. Transactivation assay in yeast demonstrated that ZmMYB48 had transcriptional activation ability. Heterologous overexpression of ZmMYB48 in Arabidopsis remarkably improved plant tolerance to drought stress, as determined through physiological analyses of survival rate, relative water content, malonaldehyde content, relative electrolyte leakage and proline content. Moreover, overexpression of ZmMYB48 enhanced the expression of stress/ABA-responsive genes such as P5CS1, RD22, RD29B and ABI1. In addition, ZmMYB48-overexpressing plants accumulated higher content of ABA than WT plants under drought stress. These results demonstrate that ZmMYB48 might act as a positive regulator that participates in the drought stress response through ABA signalling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15:63–78
Agarwal M, Hao YJ, Kapoor A, Dong CH, Fujii H, Zheng XW, Zhu JK (2006) A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J Biol Chem 281:37636–37645
Araki S, Ito M, Soyano T, Nishihama R, Machida Y (2004) Mitotic cyclins stimulate the activity of c-Myb-like factors for transactivation of G(2)/M phase-specific genes in tobacco. J Biol Chem 279:32979–32988
Bomal C, Bedon F, Caron S, Mansfield SD, Levasseur C, Cooke JEK, Blais S, Tremblay L, Morency MJ, Pavy N (2008) Involvement of pinus taeda MYB1 and MYB8 in phenylpropanoid metabolism and secondary cell wall biogenesis: a comparative in planta analysis. J Exp Bot 59:3925
Cao YP, Han YH, Li DH, Lin Y, Cai YP (2016) MYB transcription factors in Chinese Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.): genomewide identification, classification, and expression profiling during fruit development. Front Plant Sci 7
Cedroni ML, Cronn RC, Adams KL, Wilkins TA, Wendel JF (2003) Evolution and expression of MYB genes in diploid and polyploid cotton. Plant Mol Biol 51:313–325
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium -mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Dias AP, Braun EL, McMullen MD, Grotewold E (2003) Recently duplicated maize R2R3 Myb genes provide evidence for distinct mechanisms of evolutionary divergence after duplication. Plant Physiol 131:610–620
Du H, Yang SS, Liang Z, Feng BR, Liu L, Huang YB, Tang YX (2012) Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12
Fornalé S, Sonbol FM, Maes T, Capellades M, Puigdomènech P, Rigau J, Caparrós-Ruiz D (2006) Down-regulation of the maize and Arabidopsis thaliana caffeic acid O-methyl-transferase genes by two new maize R2R3-MYB transcription factors. Plant Mol Biol 62:809–823
Ganesan G, Sankararamasubramanian HM, Harikrishnan M, Ashwin G, Parida A (2012) A MYB transcription factor from the grey mangrove is induced by stress and confers NaCl tolerance in tobacco. J Exp Bot 63:4549–4561
Heine GF, Malik V, Dias AP, Grotewold E (2007) Expression and molecular characterization of ZmMYB-IF35 and related R2R3-MYB transcription factors. Mol Biotechnol 37:155–164
Higginson T, Li SF, Parish RW (2003) AtMYB103 regulates tapetum and trichome development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 35:177–192
Jung C, Seo JS, Han SW, Koo YJ, Kim CH, Song SI, Nahm BH, Do Choi Y, Cheong JJ (2008) Overexpression of AtMYB44 enhances stomatal closure to confer abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146:623–635
Jiang Y, Liang G, Yu D (2012) Activated Expression of WRKY57 confers drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant 5:1375–1388.
Karpinska B, Karlsson M, Srivastava M, Stenberg A, Schrader J, Sterky F, Bhalerao R, Wingsle G (2004) MYB transcription factors are differentially expressed and regulated during secondary vascular tissue development in hybrid aspen. Plant Mol Biol 56:255–270
Katiyar A, Smita S, Lenka SK, Rajwanshi R, Chinnusamy V, Bansal KC (2012) Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics 13:544
Lee MW, Qi M, Yang YO (2001) A novel jasmonic acid-inducible rice myb gene associates with fungal infection and host cell death. Mol Plant Microbe In 14:527–535
Li CN, Ng CKY, Fan LM (2015) MYB transcription factors, active players in abiotic stress signaling. Environ Exp Bot 114:80–91
Li MR, Lin XJ, Li HQ, Pan XP, Wu GJ (2011) Overexpression of AtNHX5 improves tolerance to both salt and water stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Tiss Org 107:283–293
Li SJ, Zhou X, Chen LG, Huang WD, Yu DQ (2010) Functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY39 in heat stress. Mol Cells 29:475–483
Lippold F, Sanchez DH, Musialak M, Schlereth A, Scheible WR, Hincha DK, Udvardi MK (2009) AtMyb41 regulates transcriptional and metabolic responses to osmotic stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149:1761–1772
Liu JF, Ding J, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2014) Magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with in situ derivatization for the highly sensitive determination of acidic phytohormones in rice leaves by UPLC-MS/MS. Analyst 139:5605–5613
Mccarthy RL, Zhong R, Fowler S, Lyskowski D, Piyasena H, Carleton K, Spicer C, Ye ZH (2010) The poplar MYB transcription factors, PtrMYB3 and PtrMYB20, are involved in the regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1084–1090
Muller D, Schmitz G, Theres K (2006) Blind homologous R2R3 Myb genes control the pattern of lateral meristem initiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:586–597
Newman LJ, Perazza DE, Lusa J, Campbell MM (2004) Involvement of the R2R3-MYB, AtMYB61, in the ectopic lignification and dark-photomorphogenic components of the det3 mutant phenotype. Plant J 37:239–250
Niu CF, Wei W, Zhou QY, Tian AG, Hao YJ, Zhang WK, Biao MA, Lin Q, Zhang ZB, Zhang JS (2012) Wheat WRKY genes TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 regulate abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Environ 35:1156
Pazares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987) The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J 6:3553–3558
Preston J, Wheeler J, Heazlewood J, Li SF, Parish RW (2004) AtMYB32 is required for normal pollen development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 40:979–995
Steiner-Lange S, Unte US, Eckstein L, Yang C, Wilson ZA, Schmelzer E, Dekker K, Saedler H (2003) Disruption of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB26 results in male sterility due to non-dehiscent anthers. Plant J 34:519–528
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:447–456
Su CF, Wang YC, Hsieh TH, Lu CA, Tseng TH, Yu SM (2010) A novel MYBS3-dependent pathway confers cold tolerance in Rice. Plant Physiol 153:145–158
Szabados LL, Savourcb A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89
Vannini C, Locatelli F, Bracale M, Magnani E, Marsoni M, Osnato M, Mattana M, Baldoni E, Coraggio I (2004) Overexpression of the rice Osmyb4 gene increases chilling and freezing tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant J 37:115–127
Xiong HY, Li JJ, Liu PL, Duan JZ, Zhao Y, Guo X, Li Y, Zhang HL, Ali J, Li ZC (2014) Overexpression of OsMYB48-1, a novel MYB-Related transcription factor, enhances drought and salinity tolerance in rice. Plos One 9
Yang A, Dai X, Zhang WH (2012) A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 63:2541
Yang SC, Sweetman JP, Amirsadeghi S, Barghchi M, Huttly AK, Chung WI, Twell D (2001) Novel anther-specific myb genes from tobacco as putative regulators of phenylalanine ammonialyase expression. Plant Physiol 126:1738–1753
Yuan Y, Qi L, Yang J, Wu C, Liu Y, Huang L (2015) A Scutellaria baicalensis R2R3-MYB gene, SbMYB8, regulates flavonoid biosynthesis and improves drought stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tiss Org 120:961–972
Zhang JJ, Zhang SS, Li H, Du H, Huang HH, Li YP, Hu YF, Liu HM, Liu YH, Yu GW, Huang YB (2016) Identification of transcription factors ZmMYB111 and ZmMYB148 involved in phenylpropanoid metabolism. Front Plant Sci 7
Zhang LC, Zhao GY, Xia C, Jia JZ, Liu X, Kong XY (2012) Overexpression of a wheat MYB transcription factor gene, TaMYB56-B, enhances tolerances to freezing and salt stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis. Gene 505:100–107
Zhang S, Fang ZJ, Zhu J, Gao JF, Yang ZN (2010) OsMYB103 is required for rice anther development by regulating tapetum development and exine formation. Chinese Sci Bull 55:3288–3297
Zhang SJ, Li N, Gao F, Yang AF, Zhang JR (2010) Over-expression of TsCBF1 gene confers improved drought tolerance in transgenic maize. Mol Breeding 26:455–465
Zhao L, Gao LP, Wang HX, Chen XT, Wang YS, Yang H, Wei CL, Wan XC, Xia T (2013) The R2R3-MYB, bHLH, WD40, and related transcription factors in flavonoid biosynthesis. Funct Integr Genomic 13:75–98
Zhao Y, Ma Q, Jin XL, Peng XJ, Liu JY, Deng L, Yan HW, Sheng L, Jiang HY, Cheng BJ (2014) A novel maize Homeodomain- Leucine Zipper (HD-Zip) I gene, Zmhdz10, positively regulates drought and salt tolerance in both rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 55:1142–1156
Zheng J, Fu JJ, Gou MY, Junling H, Liu YJ, Jian M, Huang QS, Guo XY, Dong ZG, Wang HZ (2010) Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of two maize inbred lines under drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 72:407
Zhou QY, Tian AG, Zou HF, Xie ZM, Lei G, Huang J, Wang CM, Wang HW, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008) Soybean WRKY-type transcription factor genes, GmWRKY13, GmWRKY21, and GmWRKY54, confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:486–503
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247
Zhu N, Cheng SF, Liu XY, Du H, Dai MQ, Zhou DX, Yang WJ, Zhao Y (2015) The R2R3-type MYB gene OsMYB91 has a function in coordinating plant growth and salt stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 236:146–156
Zsigmond L, Szepesi A, Tari I, Rigó G, Király A, Szabados L (2012) Overexpression of the mitochondrial PPR40 gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 182:87–93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Liu, M. et al. Overexpression of a maize MYB48 gene confers drought tolerance in transgenic arabidopsis plants. J. Plant Biol. 60, 612–621 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-017-0273-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-017-0273-y