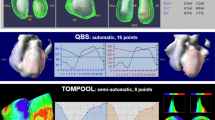
Abstract
Background
The assessment of right ventricular function is crucial for management of heart disease. TOMPOOL is a software that processes data acquired with Tomographic Equilibrium Radionuclide Ventriculography. In this report, TOMPOOL’s diagnostic accuracy and inter-observer reproducibility were assessed in a cohort of patients with various etiologies of ventricular dysfunction.
Methods and Results
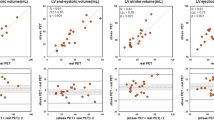
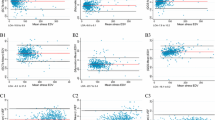
End-diastolic volume (EDV), ejection fraction (EF), and cardiac output (CO) were calculated for the right ventricle (RV) and the left ventricle (LV) using TOMPOOL in 99 consecutive patients. Thirty-five patients underwent cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) considered as the reference-standard to measure EDV and EF; the Spearman’s rho correlation coefficients were r = 0.73/0.80 and 0.67/0.73 for right/left EF and EDV, respectively. Twenty-one patients had thermodilution measurements of right CO (reference-standard), the correlation was r = 0.57. The best cut-off points (sensitivity/specificity) in order to diagnose a ventricular dysfunction or enlargement were 46% for RVEF (67%/89%), 62% for LVEF (100%/90%), 94 mL for RVEDV (77%/73%), and 84 mL for LVEDV (100%/91%). The areas under the ROC curve were, respectively, 0.79, 0.91, 0.83, and 0.99. Inter-observer reproducibility was r = 0.81/0.94, 0.77/0.90, and 0.78/0.75 for Right/Left EF, EDV, and CO, respectively.
Conclusion
TOMPOOL is accurate: measurements of EDV, EF, and CO are reproducible and correlate with CMR and thermodilution. However, thresholds must be adjusted.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hesse B, Lindhardt TB, Acampa W, Anagnostopoulos C, Ballinger J, Bax JJ, et al. EANM/ESC guidelines for radionuclide imaging of cardiac function. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:851-85.
Klocke FJ, Baird MG, Lorell BH, Bateman TM, Messer JV, Berman DS, et al. ACC/AHA/ASNC guidelines for the clinical use of cardiac radionuclide imaging—Executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASNC Committee to Revise the 1995 Guidelines for the Clinical Use of Cardiac Radionuclide Imaging). Circulation 2003;108:1404-18.
Di Salvo TG, Mathier M, Semigran MJ, Dec GW. Preserved right ventricular ejection fraction predicts exercise capacity and survival in advanced heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25:1143-53.
de Groote P, Millaire A, Foucher-Hossein C, Nugue O, Marchandise X, Ducloux G, et al. Right ventricular ejection fraction is an independent predictor of survival in patients with moderate heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;32:948-54.
Cohn JN, Johnson GR, Shabetai R, Loeb H, Tristani F, Rector T, et al. Ejection fraction, peak exercise oxygen consumption, cardiothoracic ratio, ventricular arrhythmias, and plasma norepinephrine as determinants of prognosis in heart failure. The V-HeFT VA Cooperative Studies Group. Circulation 1993;87:VI5-16.
van der Maas N, Braam RL, van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, Meerman J, Cozijnsen L, Scholte AJ. Right ventricular ejection fraction measured by multigated planar equilibrium radionuclide ventriculography is an independent prognostic factor in patients with ischemic heart disease. J Nucl Cardiol 2012;19:1162-9.
Sibille L, Bouallegue FB, Bourdon A, Micheau A, Vernhet-Kovacsik H, Mariano-Goulart D. Comparative values of gated blood-pool SPECT and CMR for ejection fraction and volume estimation. Nucl Med Commun 2011;32:121-8.
Mariano-Goulart D, Piot C, Boudousq V, Raczka F, Comte F, Eberle MC, et al. Routine measurements of left and right ventricular output by gated blood pool emission tomography in comparison with thermodilution measurements: A preliminary study. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:506-13.
Mariano-Goulart D, Dechaux L, Rouzet F, Barbotte E, Caderas de Kerleau C, Rossi M, et al. Diagnosis of diffuse and localized arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia by gated blood-pool SPECT. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1416-23.
Mariano-Goulart D, Collet H, Kotzki PO, Zanca M, Rossi M. Semi-automatic segmentation of gated blood pool emission tomographic images by watersheds: Application to the determination of right and left ejection fractions. Eur J Nucl Med 1998;25:1300-7.
Daou D, Harel F, Helal BO, Fourme T, Colin P, Lebtahi R, et al. Electrocardiographically gated blood-pool SPECT and left ventricular function: Comparative value of 3 methods for ejection fraction and volume estimation. J Nucl Med 2001;42:1043-9.
Caderas de Kerleau C, Crouzet JF, Ahronovitz E, Rossi M, Mariano-Goulart D. Automatic generation of noise-free time-activity curve with gated blood-pool emission tomography using deformation of a reference curve. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2004;23:485-91.
Carr JC, Simonetti O, Bundy J, Li D, Pereles S, Finn JP. Cine MR angiography of the heart with segmented true fast imaging with steady-state precession. Radiology 2001;219:828-34.
Haddad F, Hunt SA, Rosenthal DN, Murphy DJ. Right ventricular function in cardiovascular disease. Part I: Anatomy, physiology, aging, and functional assessment of the right ventricle. Circulation 2008;117:1436-48.
Lorenz CH, Walker ES, Morgan VL, Klein SS, Graham TP Jr. Normal human right and left ventricular mass, systolic function, and gender differences by cine magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 1999;1:7-21.
Kim SJ, Kim IJ, Kim YS, Kim YK. Gated blood pool SPECT for measurement of left ventricular volumes and left ventricular ejection fraction: Comparison of 8 and 16 frame gated blood pool SPECT. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2005;21:261-6.
Kim SJ, Kim IJ, Kim YS, Kim YK, Shin YB, Kim DS. Automatic quantification of right ventricular volumes and right ventricular ejection fraction with gated blood pool SPECT: Comparison of 8- and 16-frame gated blood pool SPECT with first-pass radionuclide angiography. J Nucl Cardiol 2005;12:553-9.
De Bondt P, Claessens T, Rys B, De Winter O, Vandenberghe S, Segers P, et al. Accuracy of 4 different algorithms for the analysis of tomographic radionuclide ventriculography using a physical, dynamic 4-chamber cardiac phantom. J Nucl Med 2005;46:165-71.
Adachi I, Umeda T, Shimomura H, Suwa M, Komori T, Ogura Y, et al. Comparative study of quantitative blood pool SPECT imaging with 180 degrees and 360 degrees acquisition orbits on accuracy of cardiac function. J Nucl Cardiol 2005;12:186-94.
Akinboboye O, Nichols K, Wang Y, Dim UR, Reichek N. Accuracy of radionuclide ventriculography assessed by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with abnormal left ventricles. J Nucl Cardiol 2005;12:418-27.
Nichols K, Humayun N, De Bondt P, Vandenberghe S, Akinboboye OO, Bergmann SR. Model dependence of gated blood pool SPECT ventricular function measurements. J Nucl Cardiol 2004;11:282-92.
Xie BQ, Tian YQ, Zhang J, Zhao SH, Yang MF, Guo F, et al. Evaluation of left and right ventricular ejection fraction and volumes from gated blood-pool SPECT in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: Comparison with cardiac MRI. J Nucl Med 2012;53:584-91.
Nichols K, Saouaf R, Ababneh AA, Barst RJ, Rosenbaum MS, Groch MW, et al. Validation of SPECT equilibrium radionuclide angiographic right ventricular parameters by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. J Nucl Cardiol 2002;9:153-60.
Papavassiliu T, Kuhl HP, Schroder M, Suselbeck T, Bondarenko O, Bohm CK, et al. Effect of endocardial trabeculae on left ventricular measurements and measurement reproducibility at cardiovascular MR imaging. Radiology 2005;236:57-64.
Nichols KJ, Van Tosh A, Wang Y, Palestro CJ, Reichek N. Validation of gated blood-pool SPECT regional left ventricular function measurements. J Nucl Med 2009;50:53-60.
Harel F, Finnerty V, Gregoire J, Thibault B, Marcotte F, Ugolini P, et al. Gated blood-pool SPECT versus cardiac magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:427-34.
Kjaer A, Lebech AM, Hesse B, Petersen CL. Right-sided cardiac function in healthy volunteers measured by first-pass radionuclide ventriculography and gated blood-pool SPECT: Comparison with cine MRI. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2005;25:344-9.
Keng FTR, Chua T, Koh T. Quantitative blood pool single photon emission computed tomography (QBS) program: Comparison to cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR). J Nucl Cardiol 2003;10:S5.
Nichols K, Saouaf R, Ababneh AA, Barst RJ, Rosenbaum MS, Groch MW, et al. Accuracy of gated blood pool SPECT ventricular function parameters: Validation by MRI. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37:394A.
Chin BB, Bloomgarden DC, Xia W, Kim HJ, Fayad ZA, Ferrari VA, et al. Right and left ventricular volume and ejection fraction by tomographic gated blood-pool scintigraphy. J Nucl Med 1997;38:942-8.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the staff of the departments of nuclear medicine and radiology of Rangueil for their technical support.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Disclosure
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dercle, L., Giraudmaillet, T., Pascal, P. et al. Is TOMPOOL (gated blood-pool SPECT processing software) accurate to diagnose right and left ventricular dysfunction in a clinical setting?. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 21, 1011–1022 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-014-9915-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-014-9915-3