Abstract
Background
The influence of socioeconomic status and insurance type has not been studied extensively for RCR, particularly not in the high risk massive RCT population. The purpose of this study is to identify relationships between Medicaid payer status and patient outcomes following massive RCR.
Methods
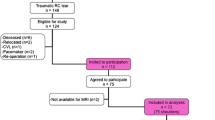
A retrospective review of shoulder surgery database identified 29 patients undergoing massive rotator cuff repair. Patients were stratified based on insurance type into two cohorts, Medicaid (14 patients) and non-Medicaid (15 patients). Missed routine follow-up appointments and comorbidities were recorded and compared between groups. Group comparisons were made for pre- and postoperative patient-reported and functional outcomes. Outcome scores included American Shoulder and Elbow Shoulder Score (ASES), the Penn Shoulder Score, and the Subjective Shoulder Value (SSV). A p value of < 0.05 was considered significant for all statistical analyses.
Results
Medicaid patients were on average 7.1 years younger than non-Medicaid patients (49.8 vs. 56.9 years, respectively), and remaining demographics were comparable between groups. Preoperative patient-reported outcomes were only significantly different for ASES and ASES pain (p = 0.010, 0.037). There was excellent average improvement for Medicaid patients but no significant differences compared to non-Medicaid patients for ASES (p = 0.630), PENN scores (p = 0.395), and SSV (p = 0.198). Medicaid patients also had a higher number of missed and canceled appointments (28%) compared to non-Medicaid patients (18%).
Conclusion
Medicaid coverage will expand to millions of uninsured Americans under current healthcare reform. Medicaid patients with massive RCT appear to significantly improve with surgical treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bey MJ, Peltz CD, Ciarelli K, Kline SK, Divine GW, van Holsbeeck M, Muh S, Kolowich PA, Lock TR, Moutzouros V (2011) In vivo shoulder function after surgical repair of a torn rotator cuff: glenohumeral joint mechanics, shoulder strength, clinical outcomes, and their interaction. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2117–2129. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0363546511412164
Kurdziel MD, Moravek JE, Wiater BP, Davidson A, Seta J, Maerz T, Baker KC, Wiater JM (2015) The impact of rotator cuff deficiency on structure, mechanical properties, and gene expression profiles of the long head of the biceps tendon (LHBT): implications for management of the LHBT during primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Orthop Res 33(8):1158–1164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jor.22895
Vidt ME, Santago AC 2nd, Marsh AP, Hegedus EJ, Tuohy CJ, Poehling GG, Freehill MT, Miller ME, Saul KR (2016) The effects of a rotator cuff tear on activities of daily living in older adults: a kinematic analysis. J Biomech 49(4):611–617. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2016.01.029
Mather RC 3rd, Koenig L, Acevedo D, Dall TM, Gallo P, Romeo A, Tongue J, Williams G Jr (2013) The societal and economic value of rotator cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95(22):1993–2000. http://dx.doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.l.01495
Colvin AC, Egorova N, Harrison AK, Moskowitz A, Flatow EL (2012) National trends in rotator cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(3):227–233. http://dx.doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.j.00739
Makhni EC, Swart E, Steinhaus ME, Mather RC 3rd, Levine WN, Bach BR Jr, Romeo AA, Verma NN (2016) Cost-effectiveness of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty versus arthroscopic rotator cuff repair for symptomatic large and massive rotator cuff tears. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2016.01.063
Habermeyer P, Magosch P, Lichtenberg S (2006) Classifications and scores of the shoulder. Springer, Berlin
Davidson J, Burkhart SS (2010) The geometric classification of rotator cuff tears: a system linking tear pattern to treatment and prognosis. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 26(3):417–424. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2009.07.009
DeOrio JK, Cofield RH (1984) Results of a second attempt at surgical repair of a failed initial rotator-cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Ser A 66(4):563–567
Gerber C, Fuchs B, Hodler J (2000) The results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Ser A 82(4):505–515
Gilot GJ, Alvarez-Pinzon AM, Barcksdale L, Westerdahl D, Krill M, Peck E (2015) Outcome of large to massive rotator cuff tears repaired with and without extracellular matrix augmentation: a prospective comparative study. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 31(8):1459–1465. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2015.02.032
Goutallier D, Postel J-M, Gleyze P, Leguilloux P, Van Driessche S (2003) Influence of cuff muscle fatty degeneration on anatomic and functional outcomes after simple suture of full-thickness tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 12(6):550–554. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1058-2746(03)00211-8
Greenspoon JA, Petri M, Warth RJ, Millett PJ (2015) Massive rotator cuff tears: pathomechanics, current treatment options, and clinical outcomes. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24(9):1493–1505. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.04.005
Chung SW, Kim JY, Kim MH, Kim SH, Oh JH (2013) Arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: outcome and analysis of factors associated with healing failure or poor postoperative function. Am J Sports Med 41(7):1674–1683. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0363546513485719
Kim JR, Cho YS, Ryu KJ, Kim JH (2012) Clinical and radiographic outcomes after arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears using a suture bridge technique: assessment of repair integrity on magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med 40(4):786–793. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0363546511434546
Miller BS, Downie BK, Kohen RB, Kijek T, Lesniak B, Jacobson JA, Hughes RE, Carpenter JE (2011) When do rotator cuff repairs fail? Serial ultrasound examination after arthroscopic repair of large and massive rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2064–2070. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0363546511413372
Park JY, Lhee SH, Oh KS, Moon SG, Hwang JT (2013) Clinical and ultrasonographic outcomes of arthroscopic suture bridge repair for massive rotator cuff tear. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 29(2):280–289. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2012.09.008
Yoo JC, Ahn JH, Koh KH, Lim KS (2009) Rotator cuff integrity after arthroscopic repair for large tears with less-than-optimal footprint coverage. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 25(10):1093–1100. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2009.07.010
Zumstein MA, Jost B, Hempel J, Hodler J, Gerber C (2008) The clinical and structural long-term results of open repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(11):2423–2431. http://dx.doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.g.00677
Bae KH, Kim JW, Kim TK, Kweon SH, Kang HJ, Kim JY, Joo MS, Kim DM (2016) Is the arthroscopic modified tension band suture technique suitable for all full-thickness rotator cuff tears? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(9):1457–1463. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2016.01.004
Barlow JD, Bishop JY, Dunn WR, Kuhn JE (2016) What factors are predictors of emotional health in patients with full-thickness rotator cuff tears? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2016.04.007
Fermont AJ, Wolterbeek N, Wessel RN, Baeyens J-P, de Bie RA (2015) Prognostic factors for recovery after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prognostic study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24(8):1249–1256. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.04.013
Kim JH, Hong IT, Ryu KJ, Bong ST, Lee YS, Kim JH (2014) Retear rate in the late postoperative period after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med 42(11):2606–2613. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0363546514547177
Neyton L, Godeneche A, Nove-Josserand L, Carrillon Y, Clechet J, Hardy MB (2013) Arthroscopic suture-bridge repair for small to medium size supraspinatus tear: healing rate and retear pattern. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 29(1):10–17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2012.06.020
D’Apuzzo MR, Villa JM, Alcerro JC, Rossi MD, Lavernia CJ (2016) Total joint arthroplasty: a granular analysis of outcomes in the economically disadvantaged patient. J Arthroplast. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.066
Patterson BM, Spang JT, Draeger RW, Olsson EC, Creighton RA, Kamath GV (2013) Access to outpatient care for adult rotator cuff patients with private insurance versus Medicaid in North Carolina. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 22(12):1623–1627. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2013.07.051
Manoso MW, Cizik AM, Bransford RJ, Bellabarba C, Chapman J, Lee MJ (2014) Medicaid status is associated with higher surgical site infection rates after spine surgery. Spine 39(20):1707–1713. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000000496
Leggin BG, Michener LA, Shaffer MA, Brenneman SK, Iannotti JP, Williams GR Jr (2006) The Penn shoulder score: reliability and validity. J Orthop Sports Phys Therapy 36(3):138–151. http://dx.doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2006.36.3.138
Michener LA, McClure PW, Sennett BJ (2002) American shoulder and elbow surgeons standardized shoulder assessment form, patient self-report section: reliability, validity, and responsiveness. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 11(6):587–594. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mse.2002.127096
Gilbart MK, Gerber C (2007) Comparison of the subjective shoulder value and the Constant score. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 16(6):717–721. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2007.02.123
Morris SB (2007) Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ Res Methods 11(2):364–386. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1094428106291059
Blumenthal D, Abrams M, Nuzum R (2015) The affordable care act at 5 years. N Engl J Med 372(25):2451–2458. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMhpr1503614
McClure P, Michener L (2003) Measures of adult shoulder function: the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons Standardized Shoulder Form Patient Self-Report Section (ASES), Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH), Shoulder Disability Questionnaire, Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI), and Simple Shoulder Test. Arthritis Care Res 49(S5):S50–S58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/art.11404
Potter MQ, Wylie JD, Greis PE, Burks RT, Tashjian RZ (2014) Psychological distress negatively affects self-assessment of shoulder function in patients with rotator cuff tears. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(12):3926–3932. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3833-1
Hinman A, Bozic KJ (2008) Impact of payer type on resource utilization, outcomes and access to care in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 23(6 Suppl 1):9–14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2008.05.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Vani Sabesan is a paid consultant for Arthrex Inc, receives research support from Exactech Inc and Pacira Pharmaceuticals, and was a recipient of an Orthopaedic Research and Education Foundation grant. One author is a paid consultant for Pacira and receives research support from Exactech, Inc. All other authors, their immediate family, and any research foundation with which they are affiliated did not receive any financial payments or other benefits from any commercial entity related to the subject of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabesan, V., Whaley, J., Petersen-Fitts, G. et al. The effect of Medicaid payer status on patient outcomes following repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Musculoskelet Surg 102, 267–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-017-0528-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-017-0528-2