Abstract
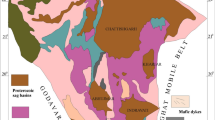
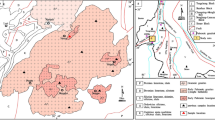
Magmatism in the Huili area (SW margin of the Yangtze block) was active during the early Mesoproterozoic, and has important implications on the early tectonic evolution of the Yangtze block. We report new data in petrology, whole-rock geochemistry, zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopes for the Yaopengzi dolerite in the Huili area. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the dolerite yielded an early Mesoproterozoic age of ca. 1515–1513 Ma, coeval with the Columbia supercontinent breakup. The dolerite belongs to the alkali basalt series, and is enriched in light rare earth elements (LREE) and large ion lithophile elements (LILE), resembling typical oceanic island basalt (OIB) in geochemistry. Zircons from the Yaopengzi dolerite yielded 176Hf/177Hf = 0.28192–0.28203 and εHf(t) =–0.3 to 5.3. Our integrated study suggests that parental magma of the Yaopengzi dolerite may have originated from the enriched mantle, and was slightly contaminated by crustal materials during its evolution. Combining with regional tectonic background, the early Mesoproterozoic mafic magmatism at/ around Yaopengzi may have formed in a mantle plume-related intracontinental rift setting. This reflects that the early Mesoproterozoic extension in the Yangtze block may have resulted from mantle plume activities led by the Columbia supercontinent breakup.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åhäll, K.I., Connelly, J.N., and Brewer, T.S., 2000, Episodic rapakivi magmatism due to distal orogenesis? Correlation of 1.69–1.50 Ga orogenic and inboard, “anorogenic” events in the Baltic Shield. Geology, 28, 823–826.
Agrawal, S., Guevara, M., and Verma, S.P., 2008, Tectonic discrimination of basic and ultrabasic volcanic rocks through log-transformed ratios of immobile trace elements. International Geology Review, 50, 1057–1079.
Andersen, T., 2002, Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192, 59–79.
Barnes, S.J., Naldrett, A.J., and Gorton, M.P., 1985, The origin of the fractionation of platinum-group elements in Terrestrial magmas. Chemical Geology, 53, 303–323.
Beloisova, B.A., Griffin, W.L., and O’Reilly, S.Y., 2006, Zircon crystal morphology, trace element signatures and Hf isotope composition as a tool for petrogenetic modeling: examples from Eastern Australian granitoids. Journal of Petrology, 47, 329–353.
Blichert, J. and Albarene, F., 1997, The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148, 243–258.
Condie, K.C., 2005, High field strength element ratios in Archean basalts: a window to evolving sources of mantle plumes? Lithos, 79, 491–504.
Cox, K.G., Bell, J.D., and Pankhurst, R.J., 1979, The Interpretation of Igneous Rocks. Allen and Unwin, London, 450 p.
Cox, K.G., 1980, A model for flood basalt volcanism. Journal of Petrology, 21, 629–650.
Depaolo, D.J. and Daley, E.E., 2000, Neodymium isotopes in basalts of the southwest basin and range and lithospheric thinning during continental extension. Chemical Geology, 169, 157–185.
Ernst, R.E., Buchan, K.L., Hamilton, M.A., Okrugin, A.V., and Tomshin, M.D., 2000, Integrated paleomagnetism and U-Pb geochronology of mafic dikes of the eastern Anabar shield region, Siberia: implications for Mesoproterozoic paleolatitude of Siberia and comparison with Laurentia. The Journal of Geology, 108, 381–401.
Ernst, R.E., Pereira, E., Hamilton, M.A., Pisarevsky, S.A., Rodriques, J., Tassinari, C.C.G., Teixeira, W., and Van-Dunem, V., 2013, Mesoproterozoic intraplate magmatic ‘barcode’ record of the Angola portion of the Congo craton: newly dated magmatic events at 1505 and 1110 Ma and implications for Nuna (Columbia) supercontinent reconstructions. Precambrian Research, 230, 103–118.
Evans, D.A.D. and Mitchell, R.N., 2011, Assembly and breakup of the core of Paleoproterozoic–Mesoproterozoic supercontinent Nuna. Geology, 39, 443–446.
Fan, H.P., Zhu, W.G., Li, Z.X., Zhong, H., Bai, Z.J., He, D.F., Chen, C.J., and Cao, C.Y., 2013, Ca. 1.5 Ga mafic magmatism in South China during the break-up of the supercontinent Nuna/Columbia: the Zhuqing Fe-Ti-V oxide ore-bearing mafic intrusions in western Yangtze Block. Lithos, 16, 85–98.
Geng, Y.S., Liu, Y.Q., Gao, L.Z., Peng, N., and Jiang, X.J., 2012, Geochronology of the Mesoproterozoic Tong’an Formation in southwestern margin of Yangtze craton: new evidence form zircon LAICP- MS U-Pb ages. Geological Journal of China Universities, 86, 1479–1490. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Goldberg, A.S., 2010, Dyke swarms as indicators of major extensional events in the 1.9–1.2 Ga Columbia supercontinent. Journal of Geodynamics, 50, 176–190.
Guo, Y., Wang, S.W., Sun, X.M., Yang, B., Liao, Z.W., Zhou, B.G., Jiang, X.F., Hou, L., and Yang, B., 2014, The Paleoproterozoic breakup event in the southwest Yangtze Block: evidence from U-Pb zircon age and geochemistry. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88, 1652–1665. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hou, K.J., Li, Y.H., Zou, T.R., Qu, X.M., Shi, Y.R., and Xie, G.Q., 2007, Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23, 2595–2604. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu, Z.C., Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., Liu, W.G., Zhang, W., Tong, X.R., Lin, L., Zong, K.Q., Li, M., Chen, H.H., Zhou, L., and Yang, L., 2012, Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and Jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICPMS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 27, 1391–1399.
Jackson, S.E., Pearson, N.J., and Griffin, W.L., 2004, The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology. Chemical Geology, 211, 47–69.
Kerrich, R., Polat, A., Wyman, D., and Hollings, P., 1999, Trace element systematics of Mg-, to Fe-tholeiitic basalt suites of the Superior Province: implications for Archean mantle reservoirs and greenstone belt genesis. Lithos, 46, 163–187.
Kinny, P.D. and Maas, R., 2003, Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53, 327–341.
Knudsen, T.L., Griffin, W., Hartz, E., Andresen, A., and Jackson, S., 2001, In-situ hafnium and lead isotope analyses of detrital zircons from the Devonian sedimentary basin of NE Greenland: a record of repeated crustal reworking. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 141, 83–94.
Langmuir, C.H., Klein, E.M., and Plank, T., 1992, Petrological systematics ofmid-ocean ridge basalts: constraints on melt generation beneath ocean ridges. Mantle Flow and Melt Generation at Midocean Ridges, 71, 183–280.
Li, H., Xi, X.S., Sun, H.S., Kong, H., Wu, Q.H., Wu, C.M., and Gabo-Ratio, J.A.S., 2016, Geochemistry of the Batang Group in the Zhaokalong area, Yushu, Qinghai: implications for the Late Triassic tectonism in the northern Sanjiang region, China. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 90, 704–721.
Lei, H.C., Xiang, H., Zhang, Z.M., Qi M., Dong, X., and Lin, Y.H., 2014, Paleoproterozoic UHT granulite in the Sulu orogen and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30, 2435–2445. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin, G.C., Li, X.H., and Li, W.X., 2006, SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotope of Neoproterozoic magmatic rocks in western Sichuan: petrogenesis and tectonic significance. Science in China (Series D Earth Sciences), 07, 630–645.
Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Zong, K.Q., Gao, C.G., Gao, S., and Xu, J., 2010, Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55, 83–93.
Ludwig, K.R., 2003, User’s manual for Isoplot/Ex Version 3.0: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, Berkeley, 74 p.
Liu, W., Yang, X.Y., Shu, S.Y., Liu, L., and Yuan, S.H., 2018, Precambrian basement and Late Paleoproterozoic to Mesoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the SW Yangtze Block, South China: constraints from zircon U-Pb dating and Hf Isotopes. Minerals, 8, 333. https:// doi.org/10.3390/min8080333
Mathieu, L., Vries, B.V.W.D., Holohan, E.P., and Troll, V.P., 2008, Dykes, cups, saucers and sills: analogue experiments on magma intrusion into brittle rocks. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 271, 1–13.
McDonough, W.F. and Sun, S.S., 1995, The composition of the Earth. Chemical Geology, 120, 223–253.
Neal, C.R., Mahoney, J.J., and Chazey, W.J., 2002, Mantle sources and the highly variable role of continental lithosphere in basalt petrogenesis of the Kerguelen Plateau and Broken Ridge LIP: results from ODP Leg 183. Journal of Petrology, 43, 1177–1250.
Niu, Y.L., 2008, The origin of alkaline lavas. Science, 320, 883–884.
Niu, Y.L. and O’Hara, M.J., 2003, Origin of ocean island basalts: a new perspective from petrology, geochemistry, and mineral physics considerations. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 108, 283–299.
Patchett, P.J., Kouvo, O., Hedge, C.E., and Tatsumoto, M., 1982, Evolution of continental crust and mantle heterogeneity: evidence from Hf isotopes. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 78, 279–297.
Patranabis, D.S., 2003, Proterozoic felsic volcanism in the Pranhita Godavari valley, India: its implication on the origin of the basin. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 21, 623–631.
Pearce, J.A., 1975, Basalt geochemistry used to investigate past tectonic environments on Cyprus. Tectonophysics, 25, 41–67.
Pearce, J.A., 2008, Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos, 100, 14–48.
Pearce, J.A., 2014, Immobile element fingerprinting of ophiolites. Elements, 10, 101–108.
Peng, M., Wu, Y.B., Wang, J., Jiao, W.F., Liu, X.C., and Yang, S.H., 2009, Paleoproterozoic Mafic Dyke form Kongling Terrain in the Yangtze Craton and Its Implication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54, 1098–1104.
Peng, M., Wu, Y.B., Gao, S., Zhang, H.F., Wang, J., Liu, X.C., Gong, H.J., Zhou, L., Hu, Z.C., Liu, Y.S., and Yuan, H.L., 2012, Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope compositions of Paleoproterozoic aluminous A-type granites form the Kongling terrain, Yangtze Block: constraints on petrogenesis and geologic implications. Gondwana Research, 22, 140–151.
Polat, A. and Hofmann, A.W., 2003, Alteration and geochemical patterns in the 3.7–3.8 Ga Isua greenstone belt, West Greenland. Precambrian Research, 126, 197–218.
Polat, A., Hofmann, A.W., and Rosing, M.T., 2002, Boninite-like volcanic rocks in the 3.7–3.8 Ga Isua greenstone belt, West Greenland: geochemical evidence for intra-oceanic subduction zone processes in the early Earth. Chemical geology, 184, 231–254.
Reichow, M.K., Saunders, A.D., White, R.V., Al’Mukhamedov, A.I., and Medvedev, A.Y., 2005, Geochemistry and petrogenesis of basalts from the west Siberian basin: an extension of the Permo-Triassic Siberian traps, Russia. Lithos, 79, 425–452.
Robinson, J.A.C. and Wood, B.J., 1998, The depth of the spinel to garnet transition at the peridotite solidus. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 164, 277–284.
Rogers, J.J.W. and Santosh, M., 2002, Configuration of Columbia, a Mesoproterozoic Supercontinent. Gondwana Research, 5, 5–22.
Roy, A., Sarkar, A., Jeyakumar, S., Aggrawal, S.K., and Ebihara, M., 2002, Mid-Proterozoic plume related thermal event in eastern Indian craton: evidence from trace elements, REE geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotope systematics of basic-ultrabasic intrusives from Dalma volcanic belt. Gondwana Research, 5, 133–146.
Rudnick, R.L. and David, M.F., 1995, Nature and composition of the continental crust: a lower crustal perspective. Reviews of Geophysics, 33, 267–309.
Rudnick, R.L., McClennan, S.M., and Taylor, S.R., 1985, Large ion lithophile elements in rocks from high-pressure granulite facies terrains. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49, 1645–1655.
Silveira, E.M., Söderlund, U., Oliveira, E.P., Ernst, R.E., and Menezes Leal, A.B., 2012, First precise U-Pb Baddeleyite ages of 1500 Ma mafic dykes form the São Francisco Craton, Brazil, and tectonic implications. Lithos, 174, 144–156.
Sun, S.S. and Macdonough, W.F., 1989, Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders, A.D. and Norry, M.J. (eds.), Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42, p. 313–345.
Sun, S.S., McDonough, W.F., and Ewart, A., 1989, Four component dynamic model for East Australian basalts. In: Johnson R.W. (ed.), Intraplate Volcanism in Eastern Australia and New Zealand. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p. 333–347.
Teixeira, W., DAgrella-Filho, M.S., Ernst, R.E., Hamilton, M.A., Girardi, V.A.V., Mazzucchelli, M., and Bettencourt, J.S., 2012, U-Pb (IDTIMS) baddeleyite ages and paleomagnetism of 1.79 and 1.59 Ga tholeiitic dyke swarms, and position of the Rio de la Plata Craton within the Columbia supercontinent. Lithos, 174, 157–174.
Wager, L.R. and Brown, G.M., 1968, Layered Igneous Rocks. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh, 588 p.
Wang, W. and Zhou, M.F., 2014a, Provenance and tectonic setting of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group in the southwestern Yangtze Block, South China: implication for the breakup of the supercontinent Columbia. Tectonophysics, 610, 110–127.
Wang, Q.H., Yang, H., Yang, D.B., and Xu, W.L., 2014b, Mid-Mesoproterozoic (similar to 1.32 Ga) diabase swarms from the western Liaoning region in the northern margin of the North China Craton: baddeleyite Pb-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and implications for the final breakup of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 254, 114–128.
Wang, L.J., Griffin, W.L., Yu, J.H., and O’Reilly, S.Y., 2013b, U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes in detrital zircon from Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks in the northern Yangtze Block: implications for Precambrian crustal evolution. Gondwana Research, 23, 1261–1272.
Wang, D.B., Yin, F.G., Sun, Z.M., Wang, L.Q., Wang, B.D., Liao, S.Y., Tang, Y., and Ren, G.M., 2013a, Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of Paleoproterozoic mafic intrusion on the western margin of the Yangtze Block and their implications. Geological Bulletin of China, 32, 617–630. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, W., Bolhar, R., Zhou, M.F., and Zhao, X.F., 2018, Enhanced terrestrial input into Paleoproterozoic to Mesoproterozoic carbonates in the southwestern South China Block during the fragmentation of the Columbia Supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 313, 1–17.
Wang, Z., Guo, Y., Yang, B., Wang, S., Sun, X., Hou, L., Zhou, B., and Liao, Z., 2013c, Discovery of the 1.73 Ga Haizi anorogenic type granite in the western margin of Yangtze Craton, and its geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica-English edition, 87, 931–942. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Weaver, B.L., 1991, The origin of ocean island basalt end-member composition: trace element and isotopic constraints. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 104, 381–397.
Williams, H., Turner, S., Kelley S., and Harris, N., 2001, Age and composition of dikes in Southern Tibet: new constraints on the timing of east-west extension and its relationship to postcollisional volcanism. Geology, 29, 339–342.
Wilson, M., 1993, Magmatism and the geodynamics of basin formation. Sedimentary Geology, 86, 5–29.
Winchester, J.A. and Floyd, P.A., 1977, Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile element. Chemical Geology, 20, 325–343.
Wood, D.A., Joron, J.L., and Treuil, M., 1979, A re-appraisal of the use of trace elements to classify and discriminate between magma series erupted in different tectonic settings. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 45, 326–336.
Wu, Y. and Zheng, Y., 2004, Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49, 1554–1569.
Wu, F.Y., Li, X.H., Zheng, R.F., and Gao, S., 2007, Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologic China, 02, 185–220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu, M.D., Duan, J.S., Song, X.L., Chen, L., and Dan, Y., 1990, Geology of Kunyang Group in Yunnan Province. Scientific Press of Yunnan Province, Kunming, 265 p. (in Chinese)
Wu, Y.B., Zheng, Y.F., Gao, S., Jiao, W.F., and Liu, Y.S., 2008, Zircon UPb age and trace element evidence for Paleoproterozoic granulite facies metamorphism and Archean crustal rocks in the Dabie Orogen. Lithos, 101, 308–322.
Wu, Y.B., Gao, S., Gong, H.J., Xiang, H., Jiao, W.F., Yang, S.H., Liu, Y.S., and Yuan, H.L., 2009, Zircon U-Pb age, trace element and Hf isotope composition of Kongling terrane in the Yangtze Craton: refining the timing of Paleoproterozoic high-grade metamorphism. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 27, 461–477.
Wu, J.H., Li, H., Xi, X.S., Kong, H., Wu, Q.H., Peng, N.L., Wu, X.M., Cao, J.Y., and Gabo-Ratio, J.A.S., 2017, Geochemistry and geochronology of the mafic dikes in the Taipusi area, northern margin of North China Craton: implications for Silurian tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogen. Journal of Earth System Science, 126, 64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0841-z
Xiong, Q., Zheng, J.P., Yu, C.M., and Su, Y.P., 2009, Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of Quanyishang A-type granite in Yichang: signification for the Yangtze continental cratonization in Paleoproterozoic. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54, 436–446.
Yang, H., Liu, P.H., Meng, E., Wang, F., Xiao, L.L., and Liu, C.H., 2014, Geochemistry and its tectonic implications of metabasite in the Dahongshan Group in southwestern Yangtze block. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30, 3021–3033. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang, J., Gao, S., Hu, Z., Yuan, H., Gong, H., Li, M., Xiao, G., and Wei, J., 2008, Age and growth of the Archean Kongling terrain, South China, with emphasis on 3.3 Ga granitoid gneisses. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72, 153–182.
Zhang, S.B., Zheng, Y.F., Wu, Y.B., and Wu, F.Y., 2006a, Zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotope evidence for Paleoproterozoic metamorphic event in South China. Precambrian Research, 151, 265–288.
Zhang, D.L., Huang, D.Z., Zhang, H.F., Wang, G.Q., and Du, G.F., 2016, Chronological framework of basement beneath the Xiangmgzhong Basin: evidence by U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from Xikuangshan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32, 3456–3468. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, L.J., Ma, C.Q., Wang, L.X., She, Z.B., and Wang, S.M., 2011, Discovery of Paleoproterozoic rapakivi granite on the northern margin of the Yangtze block and its geological significance. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56, 306–318.
Zhang, S.B., Zheng, Y.F., Wu, Y.B., Zhao, Z.F., Gao, S., and Wu, F.Y., 2006b, Zircon isotope evidence for =3.5 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of China. Precambrian Research, 146, 16–34.
Zhao, G., Cawood, P.A., Wilde, S.A., and Sun, M., 2002, Review of global 2.1–1.8 Ga orogens: implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent. Earth-Science Reviews, 59, 125–162.
Zhao, G.C., Li, S.Z., Sun, M., and Wilde, S.A., 2011, Assembly, accretion, and break-up of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia supercontinent: record in the North China Craton revisited. International Geology Review, 53, 1331–1356.
Zhao, G.C., Sun, M., Wilde, S.A., and Li, S.Z., 2004, A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Supercontinent: assembly, growth and breakup. Earth-Science Reviews, 67, 91–123.
Zhao, X.F., Zhou, M.F., Li, J.W., Sun, M., Gao, J.F., Sun, W.H., and Yang, J.H., 2010, Late Paleoproterozoic to early Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group in Yunnan, SW China: implications for tectonic evolution of the Yangtze Block. Precambrian Research, 182, 57–69.
Zheng, J., Griffin, W.L., O’Reilly, S.Y., Zhang, M., Pearson, N., and Pan, Y.M., 2006, Widespread Archean basement beneath the Yangtze craton. Geology, 34, 417–420.
Zhou, M.F., Arndt, N.T., Malpas, J., Wang, C.Y., and Kennedy, A., 2008, Two magma series and associated ore deposit types in the Permian Emeishan large igneous province, SW China. Lithos, 103, 352–368.
Zhou, M.F., Zhao, X.F., Chen, W.T., Li X.C., Wang, W., Yan, D.P., and Qiu, H.N., 2014, Proterozoic Fe-Cu metallogeny and supercontinental cycles of the southwestern Yangtze Block, southern China and northern Vietnam. Earth-Science Reviews, 139, 59–82.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB440901), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 51608192), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2016JJ4031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Huang, C., Du, G. et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and zircon Hf-isotopes of the early Mesoproterozoic Yaopengzi dolerite in SW Yangtze block (Sichuan, SW China): implications for the Columbia supercontinent breakup. Geosci J 23, 557–573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0082-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0082-4